It is also helpful for obtaining relationships between trigonometric functions of multiple angles.Introduction to Trigonometric Identities and Equations; 9. When confronted with these equations, recall that y = sin(2x) is a horizontal compression by a factor of 2 of the function y = sinx. Use reduction formulas to simplify an expression.3 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas; 7.Half Angle Formulas Derivation Using Double Angle Formulas. Find exact values for trigonometric functions #13–24, 55–62.
Double Angle Identities
9 Miscellaneous – the triple cotangent identity. For complex angles, you may want to use the identity (which follows from Euler’s formula) .Having conducted and published postgraduate research into the mathematical theory behind quantum computing, he is more than confident in dealing with mathematics at any level the exam boards might throw at you. For Problems 68 – 94, prove the identity.
Trigonometric Identities Worksheets
In particular, the product of a nonzero complex number and its conjugate is always a positive real number.1 Trigonometry – Simple Identities for the AQA A Level Maths: Pure syllabus, written .Prove the Double-Angle Identity cos(2θ) = cos2(θ) − sin2(θ) . The reciprocal identities are simply definitions of the reciprocals . 2 Identities involving calculus. sin (A-B)≡sinAcosB – cosAsinB. Hot Network Questions What happens if a leading Presidential candidate dies .2 Double Angle Formulae for the Edexcel A Level Maths: Pure syllabus, written by the Maths experts at Save My . ⓐ sin ( 45° − 30°) ⓑ sin ( 135° − 120°) Solution. If the two graphs agree, the equation is an identity.This printable worksheet stack consists of trigonometric formulas to assist in simplifying a trig expression by converting a product to a sum or a sum to a product, simplify, evaluate and verify trig expressions as well.If an equation contains more than one trigonometric function (whether the same or not) but with different angular frequencies, we will need to use the Double-Angle Identities (or, . Can we always use Euler’s formula for complex numbers? 2. Revision notes on 5. (b) If the equation is not an identity, find a value of the variable that makes the equation false.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 5 min (14 Worksheets) Trigonometric identities worksheets contain skills on fundamental trigonometric formula, even-odd identities .2 unit 10 trigonometric identities of sum & difference of angles class 11 New Mathematics book#meenglishcenter Toggle Identities involving calculus subsection .


The conjugate of a complex number has several useful properties. To see the second angle, we draw a congruent triangle in the second quadrant as shown.
2 Sum and Difference Identities; 7.First year Exercise 10.Use the Reciprocal and Quotient Identities in Theorem 10.How do I integrate tan 2, cot 2, sec 2 and cosec 2?. Use half-angle formulas to . There are a number of other very useful identities that can be derived from the sum and difference formulas.Fundamental Law of Trigonometry. Precalculus 2e 7.10 Sum to product identities.5 ° —namely, θ = 180 ° − 14. Notice that y r = 0. The integral of sec 2 x is tan x (+c).8 Miscellaneous – the triple tangent identity. Find trig values for the negative of an angle #1–6. Sometimes it is not possible to solve a trigonometric equation with identities that have a multiple angle, such as sin(2x) or cos(3x). File Size: 509 kb.4 Sum-to-Product and Product-to-Sum Formulas; 9. Assume all quantities are defined.2 | INTRODUCTION & EXAMPLES | New Math 11th bookMathematics Sindh Board Text Book | Mathematics 11th BookMathematics Intermedi.Mathematics 11th | Exercise 10. Use double-angle formulas to verify identities.5 ° —is the obtuse angle we need. This is because the derivative of cot x is -cosec 2 x; The integral of tan 2 x can be found by using the identity to rewrite tan 2 x before integrating: . Application solutions are available for purchase! click here.5 Solving Trigonometric Equations; Chapter Review. File Type: pdf.1: Reciprocal and Pythagorean Identities 10. Trigonometric Ratios of Allied Angles.Solving Trigonometric Equations with Multiple Angles. The double angle formulae .1 Verifying Trigonometric Identities and Using Trigonometric Identities to Simplify Trigonometric Expressions; 9.11 Inequalities.

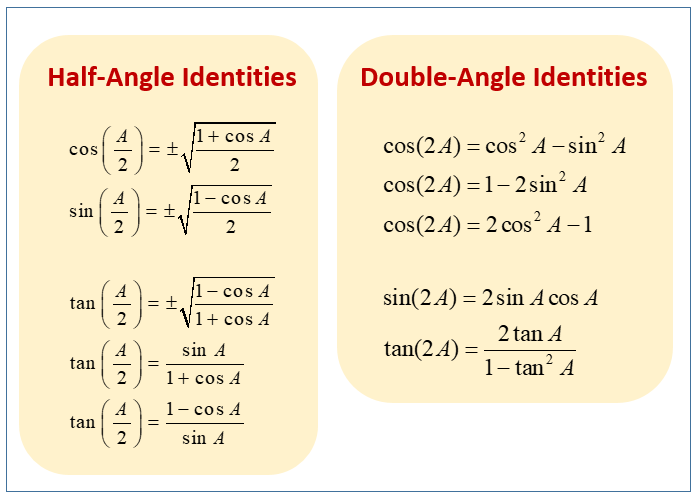
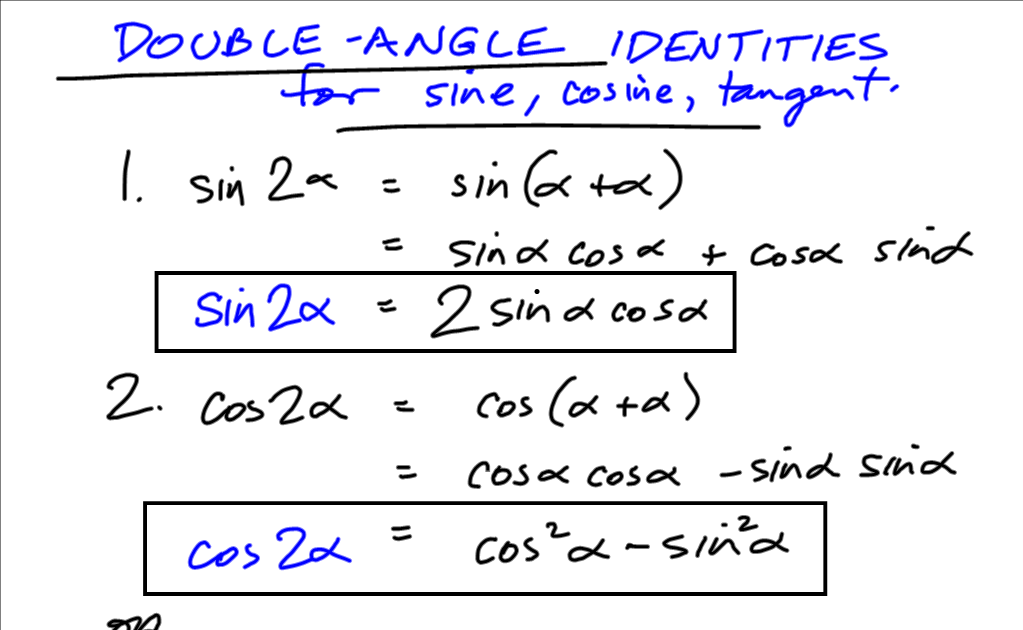
Free math problem solver answers your trigonometry homework questions with step-by-step explanations.The Double Angle Identities The addition formulas can be used to derive the double angle formulas: $$\sin 2\theta=2\,\sin\theta\,\cos\theta,$$ $$\cos 2\theta=\cos^2\theta . Skip to Content Go to accessibility page Keyboard shortcuts menu. Evaluate the reciprocal trig functions in applications #29–32.Use the sum and difference identities to evaluate the difference of the angles and show that part a equals part b. To derive the half angle formulas, we start by using the double angle formulas, which express trigonometric functions in terms of double angles like 2θ, 2A, 2x, and so on.In the field of complex numbers, De Moivre’s Theorem is one of the most important and useful theorems which connects complex numbers and trigonometry.6 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions; Chapter Review. If the two graphs are not the same . Divide both sides of your equation from part (a) by r2.Dividing both equations by 2, we arrive at Solutions associated with QIII: x = 2π 3 + πk Solutions associated with QIV: x = 5π 6 + πk. The sine of θ, denoted sin(θ), is defined by sin(θ) = y.Use double-angle formulas to find exact values.If we specialize the sum formulas in Theorem 10.The two most basic types of trigonometric identities are the reciprocal identities and the Pythagorean identities. Squaring a complex exponential that represents a real number.2 Sum and Difference Identities. Begin with the equation √x2 + y2 = r, x 2 + y 2 = r, and square both sides. Example \(\PageIndex{3}\) Simplify \(\dfrac{\cos (2t)}{\cos (t)-\sin (t)}\). To check whether an equation is an identity we can compare graphs of [latex]Y_1 =[/latex] (left side of the equation) and [latex]Y_2 =[/latex] (right side of the equation).In this first section, we will work with the fundamental identities: the Pythagorean Identities, the even-odd identities, the reciprocal identities, and the quotient identities. Evaluate the reciprocal trig functions for angles in degrees or radians #1–20.
List of trigonometric identities
Chapter 10: Trigonometric Identities
(a) Use graphs to decide if the equation is an identity. Introduction to Further . De Moivre’s Theorem is also known as “De Moivre’s Identity” and “De Moivre’s Formula”.We can use the double angle identities to simplify expressions and prove identities. To restrict the solutions to the interval [0, 2π), we let k = 0 to find x = 2π 3 and x = 5π . Using Double Angle Identities Solve the following (on the given intervals) 1) Sin2x+sinx=0 2) Cos2x + cos x 0 3) 4Sin e Cos . Given one trig ratio, find the others #33–46, 71–80.We’ll look at a few examples briefly, but first, let’s examine some of the fundamental trigonometric identities.25 for both angles. Geometrically, these are identities involving certain functions of one or more angles.College Algebra & Trigonometry, 2018a
Mathway
1 + tan 2 x = sec 2 x; The . Deductions from Fundamental Law. Review Exercises; Practice Test; 10 Further Applications of Trigonometry.5 Solving Trigonometric Equations; 7. For cos the +/- sign on the left-hand side is opposite to the one on the right-hand side. What are Double Angle Identities? How do you use a double angle identity to find the exact value of each expression? How do you use a double-angle identity to find the exact value of sin .There must also be an obtuse angle whose sin is 0.Solving double angle equations without double angle or sum identities.4_practice_solutions.6 Double-angle identities. The supplement of 14.Finding the exact value of the sine, cosine, or tangent of an angle is often easier if we can rewrite the given angle in terms of two angles that have k.4 Sum-to-Product and Product-to-Sum Formulas; 7.Sketch an angle θ θ in standard position and label a point (x,y) ( x, y) on the terminal side, at a distance r r from the vertex.3 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas; 9.Proofs of trigonometric identities. Now we can substitute these values into the equation and simplify. This is because the derivative of tan x is sec 2 x; The integral of cosec 2 x is -cot x (+c). Next, we find the values of the trigonometric expressions.1 Proof of sine identities.2 Proof of cosine identities.Lucy has created revision content for a variety of domestic and international Exam Boards including Edexcel, AQA, OCR, CIE and IB.There are six compound angle formulae (also known as addition formulae ), two each for sin, cos and tan: For sin the +/- sign on the left-hand side matches the one on the right-hand side. Further Application of Basic Identities. The Circular Functions.Free Double Angle identities – list double angle identities by request step-by-step.
Double Angle Identities
Double Angle Identities. These double angle formulas are well-known: For sine (sin): sin(2x) = 2sin(x)cos(x) For cosine (cos): .We often use identities to replace one form of an expression by a more useful form.6 to write functions on one side of the identity in terms of the functions on the other side of the identity.5 Solving Trigonometric Equations Double-Angle or Half-Angle to solve equation from [0,2pi) 7. To illustrate, we calculate the quotient 5 2 + 3i. Review Exercises ; Practice Test; 8 Further .They are distinct from triangle identities, which are identities potentially . zˉz = (a + bi)(a − bi) = a2 − b2i2 = a2 − b2( − 1) = a2 + b2. Suppose θ is an angle plotted in standard position and P(x, y) is the point on the terminal side of θ which lies on the Unit Circle.25 for both triangles, so sin θ = 0.The trigonometric double angle formulas give a relationship between the basic trigonometric functions applied to twice an angle in terms of trigonometric functions .7 Half-angle identities.In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. The cosine of θ, denoted cos(θ), is defined by cos(θ) = x. In particular, if we set [latex]\alpha = \beta .16 to the case when \(\alpha = \beta\), we obtain the following ‘Double Angle’ Identities. Write the left side of the equation as the sum of the squares of two fractions. Find values or expressions for the six trig ratios #21–28.
The Double Angle Identities
sin (A+B)≡sinAcosB + cosAsinB.Practice each skill in the Homework Problems listed. (b) If the equation is not an identity, find a . Key Terms; Key Equations; Key Concepts; Exercises.
Trigonometry Identities II Double Angles
Verify or disprove possible formulas #7–12, 31–42, 73–76, 79–88. There are several equivalent ways for defining trigonometric functions, and the proofs of the trigonometric identities between them .Look at the real parts of each and remember that sin2(θ) +cos2(θ) = 1.Trigonometry: Double Angle Exercise (cotúued) Ill.
What are the double angle formulae? The double angle formulae are derived from the ‚A+B‘ versions of the compound angle formulae : Exam Tip.2 Sum and Difference Identities; 9.
- 2. fachsemester 2024 – rückmeldefrist sommersemester 2023
- If someone texts you, are they thinking about you? | people like you texting
- The crown-rump length measurement, crown rump length chart
- 27 to be honest synonyms. similar words for to be honest. _ synonym for being honest
- Best gym shoes for men for 2024 | men’s gym shoes
- Immer im vorteil. die digitale adac mitgliedskarte., adac mitglied einloggen
- Das deutsche kaiserreich film kostenlos | das deutsche kaiserreich schulfilm