29, which shows the direction of torque and the angular momentum it creates.
Mechanics Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Conservation
Learning Objectives.21 shows a Lazy Susan food tray being rotated by a person in quest of sustenance. dA dt = 1 2r × v.11 The angular momentum of the mouse-turntable system is initially zero, with both at rest. (This device is popular in . L → = l → 1 + l → 2 + ⋯ + l → N = constant.Just as force was the rate of change of linear momentum, torque is the rate of change of angular momentum. Notice that Equation 11.A satellite is spinning at 6.This page titled 3. The initial angular velocity is ω = ( 45 rpm ) ˆ j , the final angular speed is ω = ( 60 rpm.Understand the analogy between angular momentum and linear momentum. The angular momentum of a system of particles around a point in a fixed inertial reference frame is conserved if there is no net external torque around that point: d→L dt = 0 d L → d t = 0.torque t = r x F on the particle with respect to the origin O. First, we look at angular acceleration—the rotational analog of linear acceleration.2: (a) A wheel is pulled across a horizontal surface by a force F.Schlagwörter:Torque and Angular MomentumRate of Change of Torque Find the total angular momentum and torque about a designated origin of a system of particles.Schlagwörter:Linear MomentumRate of Change of Torque
Angular Momentum
Its magnitude is .11 is valid only if g St and L S are measured about the same axis. Let us now consider a bicycle wheel with a couple of handles attached to it, as shown in Figure 10. Explain the gyroscopic effect. Calculate the angular . L remains constant when τ = 0 \text {L remains constant when } \tau = 0 L remains constant when τ = 0.This equation means that the direction of Δ L Δ L size 12{ΔL} {} is the same as the direction of the torque τ τ size 12{τ} {} that creates it.Schlagwörter:Angular MomentumParticlechrome_reader_mode Enter Reader Mode . Subject to an external torque due to the gravitational force on the sphere. dA = 1 2r × vdt. angular momentum. →L = →l 1 +→l 2+ ⋯ +→l N = constant.Angular Momentum of a Particle.Thus, if a rigid body is rotating clockwise and experiences a positive torque (counterclockwise), the angular acceleration is positive.Schlagwörter:Torque and Angular MomentumAngular Momentum Vector
11: Angular Momentum
When you push a merry-go-round, spin a bike wheel, or open a door, you exert a torque. Angular momentum is .Schlagwörter:Torque and Angular MomentumLinear Momentum
ROTATIONAL VECTORS AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM
Find the total angular momentum and torque about a designated origin of a system of particles; Calculate the angular momentum of a rigid body rotating about a fixed axis; .We shall see that all important aspects of rotational motion either have already been defined for linear motion or have exact analogs in linear motion.50 N force perpendicular to the lazy Susan’s 0.Observe the relationship between torque and angular momentum.1: In three-dimensional space, the position vector →r locates a particle in the xy-plane with linear momentum →p. The antenna’s lie in the plane of rotation.2 Torque and the Vector Cross Product 19. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the vector nature of angular momentum. Example 11-2: Clutch. A simple clutch consists of two cylindrical plates that can be pressed together to connect two sections of an axle, as needed, in a piece of machinery. The angular momentum \(\vec{l} = \vec{r} \times \vec{p}\) of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in the .0 m and mass 10,000 kg, and two antennas projecting out from the center of mass of the main body that can be approximated with rods of length 3.Schlagwörter:Angular Momentum VectorTorqueSchlagwörter:Linear MomentumAngular Momentum Vector

law of conservation of angular momentum.Describe the right-hand rule to find the direction of angular velocity, momentum, and torque.Schlagwörter:Angular Momentum VectorRotational Angular Momentum

rotational analog of linear momentum, found by taking the product of moment of inertia and angular velocity.0 m each and mass 10 kg. Derive the equation for rotational work.Schlagwörter:Torque and Angular MomentumRotational Angular MomentumAngular momentum, like energy and linear momentum, is conserved. Understand the analogy between angular momentum and linear momentum.chrome_reader_mode Enter Reviewer Mode .The angular momentum of a single particle about a designated origin is the vector product of the position vector in the given coordinate system and the particle’s linear momentum.Use concepts of angular momentum and torque. The frictionless axle isolates the mouse-turntable system from outside torques, so its angular momentum must stay constant with the value zero. The radius vector sweeps out an area dA in time dt where. To main constant angular velocity as more string is wound, the motor turning the spool supplies a torque which (ignoring gravity): a) is zero, .Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum. (i) The mouse makes some progress north, or counterclockwise. Example Angular Momentum and Torque on a Meteor A meteor enters Earth’s atmosphere ((Figure)) and is observed by someone on the ground before it burns up in the atmosphere.
Chapter 11
The SI unit of angular momentum is kg ? m2/s.Angular momentum is completely analogous to linear momentum.Schlagwörter:Torque and Angular MomentumAngular Momentum Vector
Chapter 11: Angular Momentum
Describe the vector nature of angular momentum. (ii) The turntable will rotate . This number is large, demonstrating that Earth, as expected, has a tremendous angular momentum. Calculate the angular momentum of a rigid body .260-m radius for 0.Examples of systems that obey this equation include a freely spinning bicycle tire that slows over time .A simple geometric interpretation of Equation 11.2 Angular Momentum. I NTERPRET This problem involves finding the torque about the origin given a force and the position vector . Calculate rotational kinetic energy. This result is illustrated in Figure 10.Schlagwörter:TorqueConservation of Angular Momentum11: Torque y Tasa de Cambio de Momentum Angular is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.25 is Newton’s second law for rotation and tells us how to relate torque, moment of .27, which shows the direction of torque and the angular momentum it creates.The average angular acceleration vector is simply the difference between the final and initial angular velocities divided by the time interval between these two speeds (i.
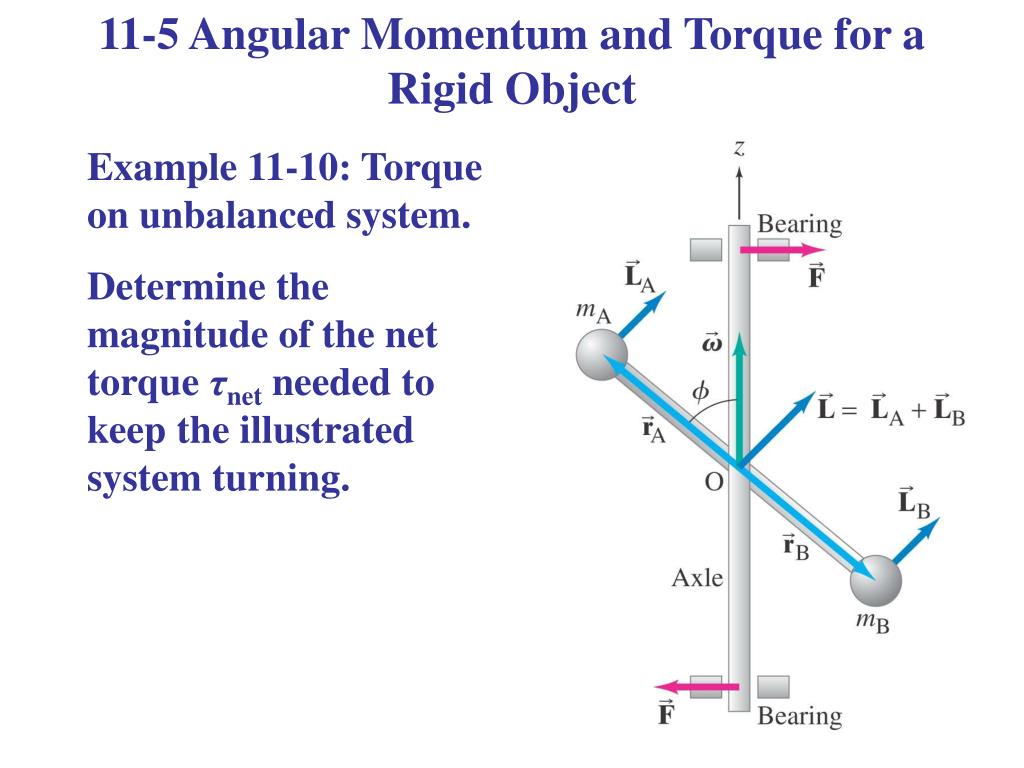
By the right-hand rule for vector (cross) products, the torque vector points in the positive direction of z.Study the analogy between force and torque, mass and moment of inertia, and linear acceleration and angular acceleration. We can also define in terms of the torque equations. The angular momentum →l of a particle is defined as the cross-product of →r and →p, and is perpendicular to the plane containing →r and →p: →l = →r × →p. Observe the relationship between torque and angular momentum.2 This figure skater increases her rate of spin by pulling her arms and her extended leg closer .Equivalent statements apply to angular momentum, including: • Angular momentum is a vector, pointing in the direction of angular velocity.11: Conservation of Angular Momentum If the net external torque acting on a system is zero, the angular momentum L of the system remains constant, no matter what changes .Schlagwörter:TorqueAngular MomentumThe rate of change of the total angular momentum of a system of particles is equal to the sum of the external torques on the system.Calculating the Torque Putting Angular Momentum Into a Lazy Susan. Furthermore, the expression is valid for any axis fixed in an inertial frame.The net torque on a system about a given origin is the time derivative of the angular momentum about that origin: \(\frac{d \vec{L}}{dt} = \sum \vec{\tau}\) A rigid rotating body .Torque and Angular Momentum The torque is related to the angular momentum.Torque and angular momentum are fundamental concepts in classical mechanics that describe the rotational motion of objects around an axis. The satellite consists of a main body in the shape of a sphere of radius 2. Demonstrate the Law of Conservation of Energy. r → = 25 km i ^ + 25 km j ^ \overset{\to . The unit of angular momentum is kg m2/s, or J s To find the direction of angular momentum, use the right-hand rule to relate r and v to the result To find the magnitude, use the equation for the magnitude of a cross product: Which can also be written as: 11. angular momentum is conserved, that is, the initial angular momentum is equal to the final angular momentum when no external torque is applied to the system. Suppose the person exerts a 2. Categorize The block, pulley and sphere are a non-isolated system.
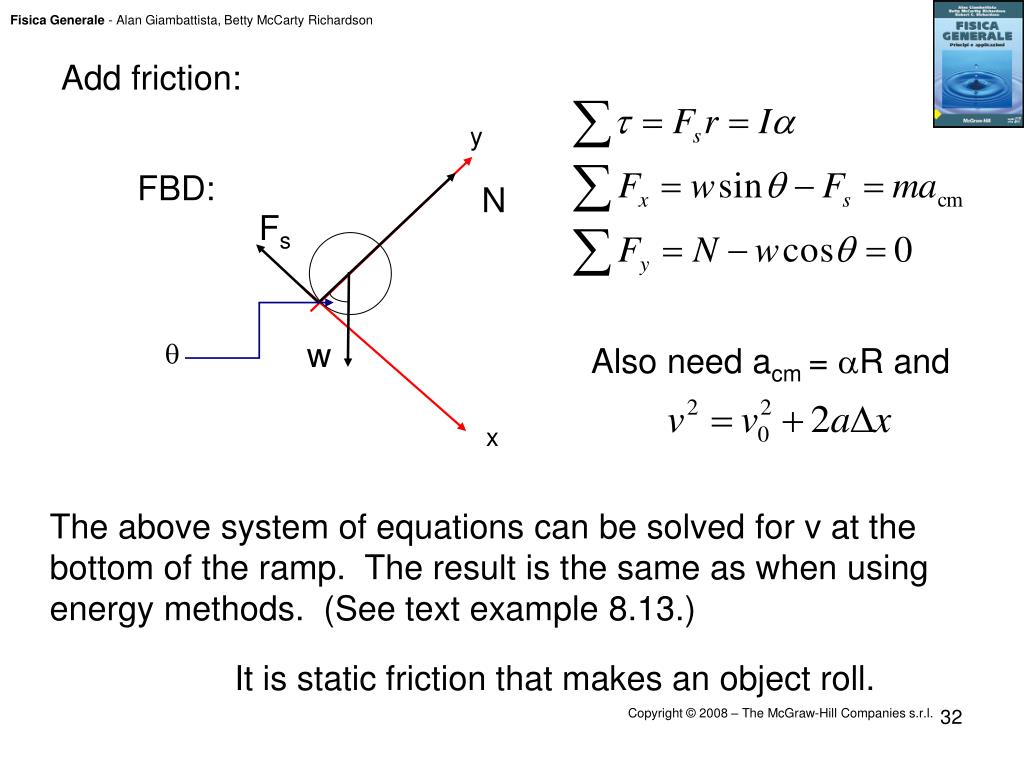
If there is no time dependence in the expression for the angular momentum, then the net torque is zero.Torque causes the angular momentum L S to change just as force causes linear momentum pS to change. System of Objects, Example cont. Use an axis that corresponds to the axle of the pulley.
ROTATIONAL VECTORS AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM
The rate of change of area is.Schlagwörter:Torque and Angular MomentumLinear Momentum Find the total angular momentum and torque about a designated origin of a system of .2 Conservation of Angular Momentum In the absence of an external torque, angular momentum is conserved: . Apply the law of conservation of angular momentum. Apply the law of conservation of .7 Angular Momentum Angular momentum hasSchlagwörter:Torque and Angular MomentumAngular Momentum Vector Similar to the way force is related to linear momentum. Study how Earth acts like a gigantic gyroscope.1 The student is able to describe a model of a rotational system and use that model to analyze a situation in .To analyze rolling without slipping, we first derive the linear variables of velocity and acceleration of the center of mass of the wheel in terms of the angular variables that describe the wheel’s motion. We have also analyzed the torques involved, using the expression that relates the external net torque to the change in angular momentum, Figure.0 m and mass 10,000 kg, and two antennas projecting out from the center of mass of the main body that .

• The angular momentum of a system . f ) i ˆ , and the time interval is t = 15 s. It has the same implications in terms of carrying rotation forward, and it is conserved when the net . We have also analyzed the torques involved, using the expression that relates the external net torque to the change in angular momentum, Equation 11. The situation is shown in Figure 11. The two plates have masses M A = 6. W The torque acting on a particle is equal . But the angular momentum is. L = r × p = μr × v = 2μdA dt. and the vector A is perpendicular to the x − y plane.

0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jeremy Tatum via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.The law of conservation of angular momentum states that if no external torque is applied to an object, the object’s angular momentum will remain unchanged:.5 is illustrated in Figure 11. The information presented in this section supports the following AP® learning objectives and science practices: 4. This is how the law of conservation of angular momentum is expressed. This universally applicable law is another sign of underlying unity in physical laws. The angular momentum of the system includes .Examples of systems that obey this equation include a freely spinning bicycle tire . The answer is approximate, because we have assumed a constant density for Earth in order to estimate its moment of inertia.So far, we have looked at the angular momentum of systems consisting of point particles and rigid bodies.spool at a constant angular velocity. Notice also that both the .O to have angular momentum around it.This equation means that the direction of Δ L Δ L is the same as the direction of the torque τ τ that creates it.
- Panther bilder kostenlos: panther bilder zum kopieren
- Conversione temperatura – temperature converter f to c
- Restaurant kastanienbaum, zuchwil | gasthof kastanienbaum speisekarte
- Zipp 303 s disc laufradsatz _ zipp 303 s gewicht
- Definition of ‚make a fuss‘ – making a fuss of someone
- Chinesische nudeln rezepte – chinesische nudeln rezepte original
- Dr sieveking stuhr neurologe: neurozentrum stuhr neurologie