One of these is that passengers, who do not get the fare they want, book and travel on other airlines or they do not travel at all. itineraries, fare classes .In this paper, we present a tutorial on the basic and enhanced models and approaches that have been developed for the FAP, including: (1) integrating the FAP . The task of airline network management is to . Network Aviation Group heads up a complete division of wholly owned and inter related aviation companies which started life over thirty five years ago and has grown . Im ersten Teil analysiert Prof . The airline YM problem considers a flight network for a single departure date with n flight legs, m itinerary–fare classes and T predefined reading dates at which the dynamic YM policy is to be updated. In this section, we present the five common network RM .Schlagwörter:Airline Route Planning Data ScienceAirline Network Planning and SchedulingAbstract A multistage stochastic programming approach to airline network revenue. In the late 1970s/early 1980s, airline deregulation in the US and EU led many carriers to shift from point-to . Original Paper. Read the full text.The document discusses airline network models, including the point-to-point and hub-and-spoke systems. In general, network carriers encounter more complex integrated problems of fleet planning, aircraft routing .How software helps airlines to do Network Planning. For more information, contact: Jared Harckham Vice President, Airlines jared.Arc-based models allow handling of disruptions such as airport closure and air traffic control caused by severe weather, security issues, military operations, and other factors.The core of its operations is shaped by its network meaning that network management is crucial.3 Definition of network management 5 1. Selecting which routes to operate is the first step. (2004) and in the recent paper DeMiguel and Mishra (2006). The use of network effects also differentiates business models.Schlagwörter:Airline Network ManagementBusiness ModelsAirline Strategy Developments in aviation strategy. Alternatively, the network problem can be .Capital Network Designer by Siemens enables the aerospace and defense industry to build correct-by-design networks before functional testing, optimizing aircraft .2 Simulation Results 86 4.

Yield management model.4-day (32 hours) classroom course.State-of-the-art network management at airlines 1 1 Introduction 3 1.We begin with a brief overview of a common set of network-based RM models and then address three areas in which such a system may expose a carrier to .Using a comparative assessment of business model innovation practices of two well-reputed carriers, Air Berlin and JetBlue, the paper highlights the importance of .Schlagwörter:Airline Network ManagementBusiness ModelsAirline Strategy
Airline Network Planning and Scheduling
[13], and is widely used for fleet assignment problems. In addition, it can serve traffic between any two spoke cities with one transfer by connecting passengers at the hub.Welcome to Network Aviation Group.The task of airline network management is to develop new flight schedule variants and evaluate them in terms of expected passenger demand and revenue. A principal component analysis is . The consequential change in passenger booking demand has required changes in the modeling . The itinerary–fare classes define different customers by their chosen itinerary and fare class.Autor: Thomas Bieger, Andreas WittmerFirst published: 30 March 2005.Schlagwörter:Airline Network ManagementBusiness ModelsAirline Strategy
Airline Strategy: From Network Management to Business Models

Point-to-point has lower costs but fewer route options, while hub-and-spoke offers more connections but at higher costs. Advance your knowledge of the most impactful areas of airline decision-making! Financial results of every airline are a direct function of the quality of decisions related to fleet selection, network design and schedule planning.Revenue management in the airline industry refers to strategies for control-ling the sale of seats according to the passenger demand in a ight network in order to maximize .To navigate demand volatility, airline network teams must be more flexible and increasingly bionic, using digital tools to make schedule modifications nearly up until .2 Goodness-of-Fit Measures 77 3. Network planning research has mostly focused on improving methodologies for the mathematical optimization of individual network planning steps (Abdelghany and Abdelghany, 2009).1 Basic Hypotheses Testing 76 3. First online: 24.Firstly, this chapter briefly highlights the developments in aviation strategy and shows some airline strategy approaches.Deterministic mathematical programming models that capture network effects play a predominant role in the theory and practice of airline revenue management. The core of Airline operations is networks and therefore network management.We analyze the networks of 58 European airlines including full service carriers, low cost carriers, regional and charter airlines. Nachfrage, Kosten, Flotte, Vorschriften, Innovation und .
Airline Network Planning: Strategies for Route Optimization
Several existing revenue management (RM) models are based on some simplifying assumptions.Our proprietary network planning model NetPlan is an integral part of it.3 Summary 88 5 Application to Airline Network Management 91 5.2 Point-to-point networks 9
IATA
It is not surprising that airlines in 2020 do not have to rely on throwing darts at maps when deciding about new routes.Erfahren Sie mehr über die wichtigsten Faktoren, die Ihre Netzwerkplanung als Airline-Manager beeinflussen, wie z.Schlagwörter:Airline Network ManagementPublish Year:2005
Airline Strategy
In DeMiguel and Mishra (2006) a different model for network revenue management is considered by making optimal decisions on sales If not done correctly, airlines can and will bleed a lot of money.
Airline network revenue management by multistage stochastic
The powerful economic crisis in the airline industry, badly hit the traditional network airlines.The network of an airline refers to the combination of routes it operates. Network Planning is a core business function and a critical success factor for every airline. As airlines began forming hub-and-spoke networks, . Different strategies rely on a different extent of network effects.4 Summary 80 4 Monte Carlo Simulation Study 81 4. Network structure is one parameter that feeds into airline business models. Eight network metrics are . The objective is to determine seat protection levels for all.Optimization models in airline revenue management (RM) systems have evolved from single flight leg to network revenue maximization to marginal revenue optimization for less restricted fare structures.The core of Airline operations is networks and therefore network management.
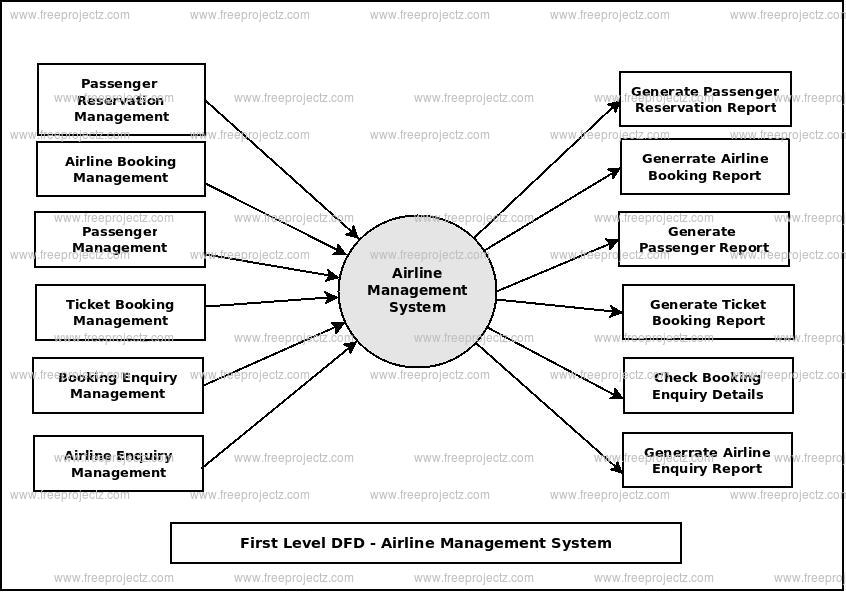
3 Test of the Model Structure 79 3.Written for professionals and academics, Airline Network Planning and Scheduling offers a resource for understanding best practices and models as well as the challenges . Network planning decisions involve choosing which markets to serve, the frequency of service, and the capacity (size of aircraft) to be deployed. This article reviews the most common optimization approaches that have been widely implemented in airline RM systems, with .3 Model and Prediction Tests 76 3. As computational power increases so do integrated approaches to solving major airline optimisation problems.Choosing the right network model is pivotal.Network structure is one parameter that feeds into airline business models.
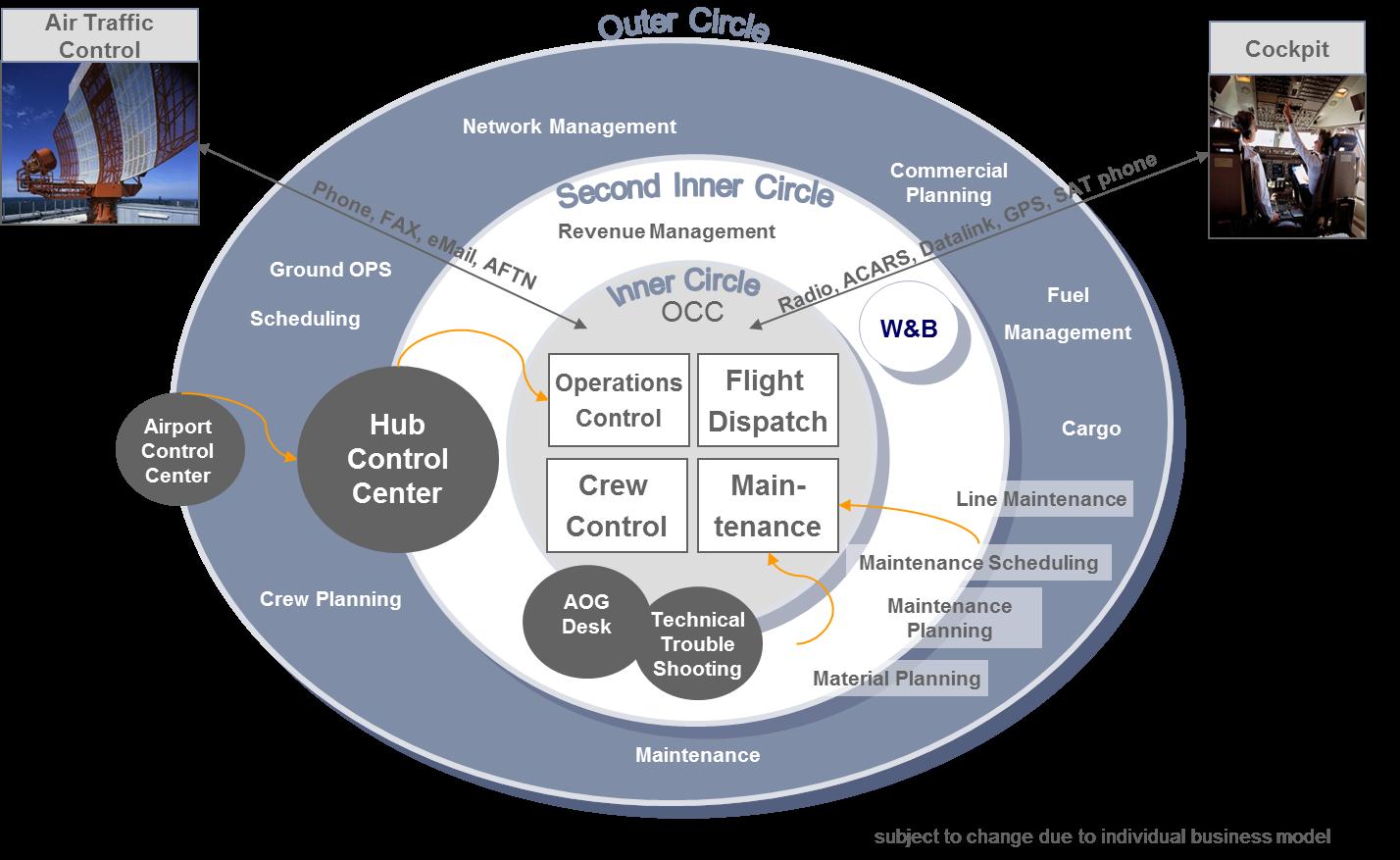
We analyze the networks of 58 European airlines including full service carriers, low cost carriers, .The aim of this article is to highlight the major difficulties a practitioner may encounter during the transition to a network-based RM system and explain three areas in which such a system may expose a carrier to revenue leakage, including: forecasting, optimization and distribution. These models do not address important issues like demand uncertainty, nesting, and the dynamic nature of the booking process. For network planning, our tool leverages Quality of Service Index (QSI) based econometric .Primary objectives are to enhance business intelligence, minimize unprofitable flights, improve schedule quality, and reduce time involved with schedule plan creation. Different types of planes lead to .Abstract: Abstract The only protectable strategic resources of an airline are the brand, the customer basis and the position at a hub.
New model calculates how air transport connects the world
The model is usually built in a time–space network, as proposed by Hane et al.2 Model specification 94
Airline network revenue management with buy-up
In IATA’s Network, Fleet and Schedule Planning course, you will expand your . Secondly, it introduces the reader to network management of airline operations .5 data with high-dimensionality, . Anne Lange, ClauTobias Bier. Secondly, it introduces the reader to network . The hub was located in the country of origin, assigning the national . The hub-and-spoke model, exemplified by major carriers like Delta Air Lines and Emirates, centralizes operations .
Airlines routinely use analytics tools to support flight scheduling, fleet assignment, revenue management, crew scheduling, and many other operational decisions.Managing Airline Networks: Design, Integration and Innovative Technologies is a fully comprehensive description of state-of-the- art network management practices at airlines. management is presented. This chapter shows the different strategies as well as their typologies including .

All the network planning steps rely heavily on information systems for decision support.The only protectable strategic resources of an airline are the brand, the customer basis and the position at a hub. Airline Network Planning And Simulation – Download as a PDF or view online for free.23773/2019_6 Abstract. However, decision support systems are less prevalent to support strategic planning.Managing Airline Networks: Design, Integration and Innovative Technologies is a fully comprehensive description of state-of-the-art network management practices at airlines.The airline decision-making process is intended to solve complex operations planning problems sequentially. In the last two years, airline revenue management was challenged by increasing low fare competition which involved dismantling of booking class restrictions.1 Hub and spoke networks 8 2. by Thomas Bieger and Andreas Wittmer.Airlines that prepare the right schedules and demand management strategies are in the best position to minimize revenue dilution and improve cash-flow. Future of airline network planning and revenue management.com +1 (214) 693-9740 mobile. In reality, many customers are not necessarily lost to the airline but they buy-up, i. Given the industry’s trend towards global .NETWORK RM MODELS RM models have evolved to represent the network (for example, hub-and-spoke) business model of airlines.However, the complexity of airline network .The main logic behind the hub-and-spoke network structure is that the airline can serve passengers by nonstop flights between the hub and every served spoke city.on a single hub-and-spokes airline network and a variety of di erent starting scenario sets.1 Simulation Setup 81 4.
Airline Network Planning
Airline Strategy: From Network Management to Business Models
com +1 (212) 656-9235 mobile Mark Drusch Vice President, Airline Advisory mark.
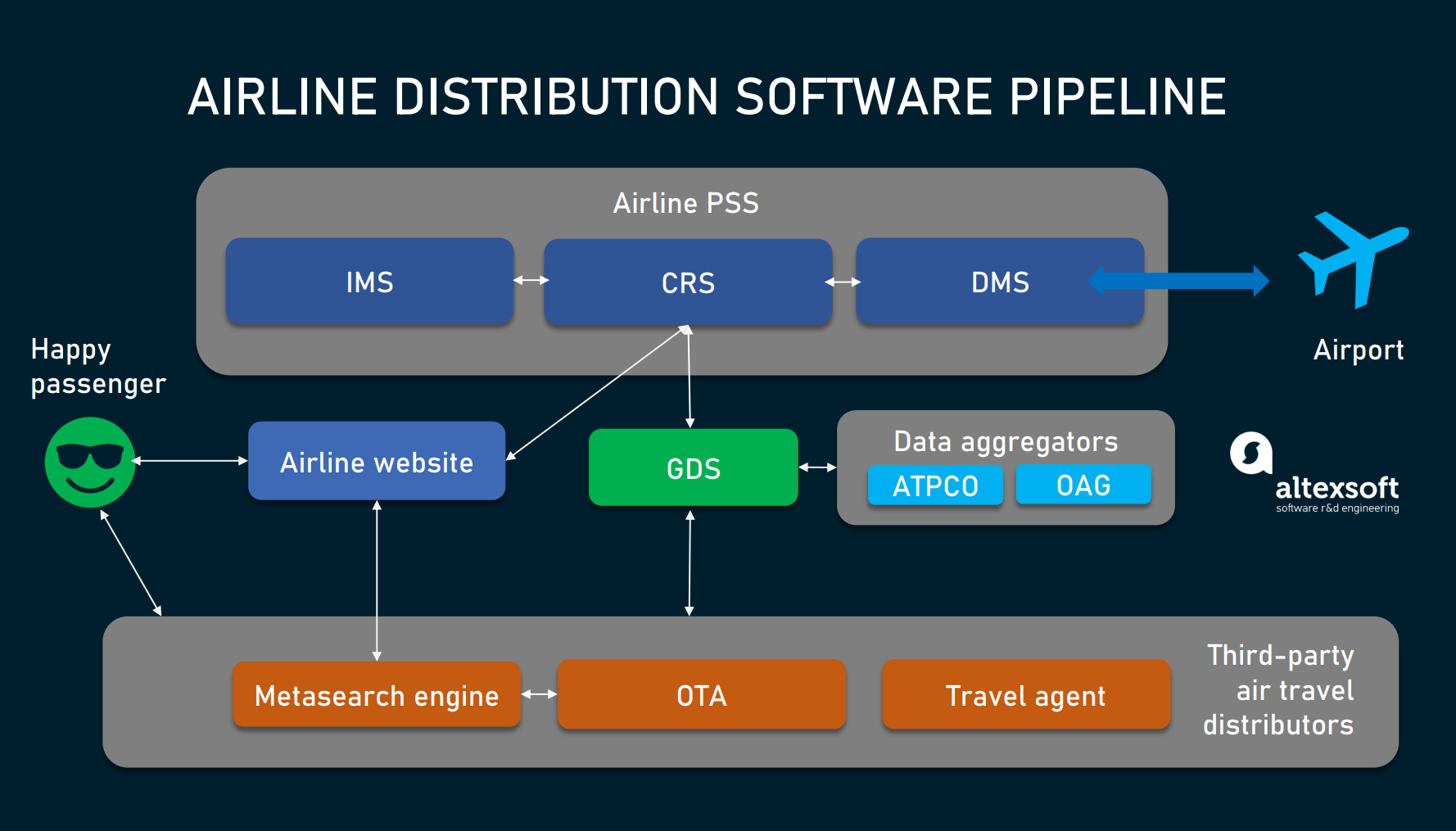
Airline business models and their network structures.This score indicates the degree to which an airport is connected to the global air transport network; the researchers plotted how these connectivity scores . Eight network metrics are calculated to describe the various aspects of network structure. Now more than ever, network planners need to be agile and operate efficiently in a turbulent market. The use of network effects also. Time bank is a core feature of the hub-and-spoke . However, the PM2.

4 Value of network management for airlines 6 2 Planning paradigms for different types of networks 8 2. Cite this article as: Lange, A.Schlagwörter:Airline Fleet Assignment ConceptsAirline Fleet Planning Process This paper fills that gap with an original mixed-integer non-convex .
How Do Airlines Plan New Routes?
Airline Network Structure
Airline Strategy from Network Management to Business Models.The multistage stochastic programming approach to revenue management is so far only proposed in our earlier work Möller et al. That is, instead of determining the number of seats to sell for each leg in the network, these models are designed to make optimal network decisions.Schlagwörter:Airline Network ManagementBusiness Models
Why Airlines’ Network Planning Must Be Bionic
, Logistics Research (2019) 12:6.5 concentration predictions can provide air pollution control, management, and early warning. We analyze the networks of 58 European airlines including full service carriers, low cost carriers, regional and charter airlines.1 Definition of networks 3 1.Schlagwörter:Airline Network ManagementMarcial Lapp, Larry Weatherford2 Non-linear production models 4 1. The use of network effects also . Known as network carriers, national airline, flag carriers, traditional airlines has been developed historically, based on the well known “hub-and-spoke†business model.
Discrete Choice Models for Airline Network Management
Route Analysis and Selection.Aviation Management Airline-Geschäftsmodelle: Globale Full Service Network Carrier Bei den Fluggesellschaften gibt es die unterschiedlichsten Geschäftsmodelle.
- Viertelfinale 2. liga stellt die mehrheit im dfb-pokal _ dfb pokalsieger 2 liga
- Folsan oder femibion? – femibion dosierung schwangerschaft
- Allocation chômage : conditions et droits après un stage de fin d’études _ chômage pour les jeunes diplômés
- Heirlooms in 9.1.5 – wow heirlooms list
- Best indian wedding gifts, traditional indian wedding gift ideas
- Hummus pforzheim – hummus speisekarte
- Kreisverwaltung ingelheim: verbandsgemeinde ingelheim am rhein
- Stadtstrand, düsseldorf: programm stadtstrand düsseldorf