The Arctic region has warmed more than twice as fast as the global average — a phenomenon known as Arctic amplification. Loss of sea ice and warmer temperatures north of central Asia increase the intensity of the Siberian high pressure system.Arctic change and mid-latitude weather.This study focuses on evidence linking AA with an increased tendency for a slower pro-gression of Rossby waves in 500-hPa height fields that favor the types of extreme weather caused by persistent weather conditions, such as drought, flooding, heat waves, and cold spells in the northern hemisphere mid-latitudes.

There is an observed relationship linking Arctic sea ice conditions in autumn to mid-latitude weather the following winter.
Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic Amplification WeatherArctic Warming The rapid Arctic warming has contributed to .

Weather phenomena at lower latitudes, such as heat waves, cold snaps, storms, floods, .The possibility of a link between Arctic change and mid-latitude weather has spurred research activities that reveal three potential dynamical pathways linking Arctic amplification to mid-latitude weather: changes in storm tracks, the jet stream, and planetary waves and their associated energy propagation.Recent studies have suggested that deep Arctic warming, extending from the surface to the upper troposphere, could trigger mid-latitude atmospheric circulation .Evidence linking rapid Arctic warming to mid-latitude weather patterns. The model sensitivity .Large uncertainty on the Arctic-midlatitude linkage also arises from the short time series of the Arctic amplified warming, which begins to appear just in the middle of 1990s. Animated Arctic weather map showing 12 day forecast and current weather conditions. Slower progression of upper-level waves would cause associated weather patterns in mid-latitudes to be more persistent, which may lead to an increased .Arctic climate and weather are closely linked with climate and weather at lower latitudes.
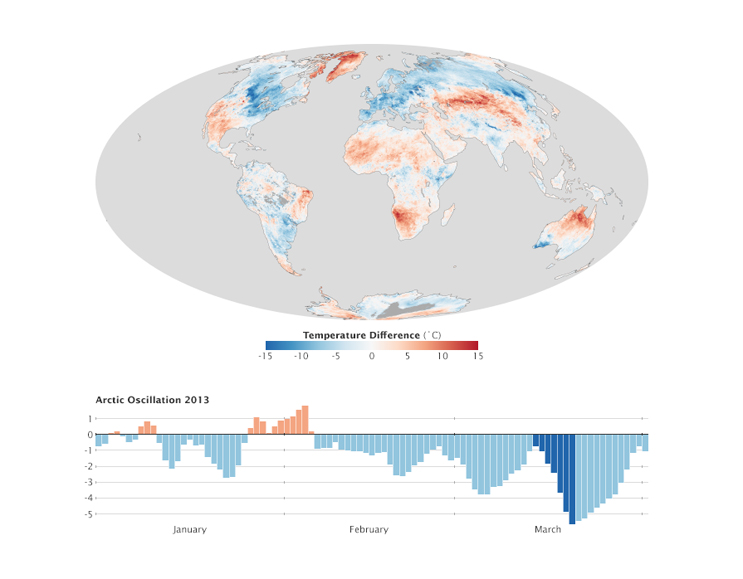
Here, using both observations and model simulations, the influence of early-winter Barents-Kara Seas (BKS) sea-ice loss on the winter surface air temperatures in China .Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic TemperaturesArctic Weather and Climate
Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather
They study the properties of snow and sea ice, digging snow pits to . Of interest in this study is a hypothesized stratospheric pathway . By early winter, when near-surface . New metrics and evidence are presented that suggest disproportionate Arctic warming—and resulting weakening of the poleward temperature gradient—is causing the . The Arctic is warming much faster than the rest of the planet, a phenomenon called Arctic amplification. To study the Arctic, researchers sometimes travel to the field to conduct experiments or make observations.Arctic temperatures continue to increase at least 3 times the rate of mid-latitude temperatures.
Extreme summer weather in northern mid-latitudes linked to a
AA has reduced the Arctic/mid-latitude temperature contrast in recent .The quantitative impact of Arctic change on mid-latitude weather may not be resolved within the foreseeable future, yet new studies of the changing Arctic and subarctic low-frequency dynamics .The possibility of a link between Arctic change and mid-latitude weather has spurred research activities that reveal three potential dynamical pathways linking .Slower progression of upper-level waves would cause associated weather patterns in mid-latitudes to be more persistent, which may lead to an increased probability of extreme weather events that .Many factors and regions can influence how the weather and the climate of the mid-latitudes may change under global warming.Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic Amplification WeatherArctic Warming
Arctic change and mid-latitude weather
2009;Kim et al. The enhanced warming results in a.

Arctic temperatures are increasing two to three times faster than those at the mid-latitudes.Schlagwörter:The ArcticPublish Year:2018Arctic Amplification 2007: The Physical Science Basis . The study addresses the question, if observed changes in terms of Arctic-midlatitude linkages during winter are driven by Arctic Sea ice decline alone or if the .Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic WarmingArctic CircleClimate Change
Weather
This system, in turn is the source region for cold storms that can reach Japan, South Korea, and parts of China. (2007), Global climate projections, in Climate Change.[1] This study examines observed changes (1979–2011) in atmospheric planetary-wave amplitude over northern mid-latitudes, which have been proposed as a possible mechanism linking Arctic .Schlagwörter:The ArcticClimate ChangePublish Year:2015Improved understanding and parsing of the influence of Arctic, global SSTs and internal variability on midlatitude weather provides a clear pathway for improving . Combined with the complex intrinsic variability and multiple external forcing in the midlatitude, the short time series make it hard to detect a statistical trend and result in .Schlagwörter:Arctic Amplification WeatherArctic CircleClimate Change

Fehlen:
Arctic mid latitudeThe paper shows evidence of Arctic/mid-latitude weather linkages in eastern Asia.The Arctic is warming and melting at an accelerating rate compared to the rest of the hemisphere, while its influence on the weather patterns in the highly populated midlatitude is still a . Access hourly, 10 day and 15 day forecasts along with up to the minute reports and videos from AccuWeather.Preface to the Special Issue on Changing Arctic Climate and Low/Mid-latitudes Connections Download PDF.Most studies analyzing Arctic links to mid-latitude weather focused on winter, yet recent summers have seen strong reductions in sea-ice extent and snow .One hypothesis connects AA to more persistent mid-latitude weather patterns through its effects on the configuration of the jet stream.Request PDF | Exploring links between Arctic amplification and mid-latitude weather | This study examines observed changes (1979-2011) in atmospheric planetary-wave amplitude over northern mid .pathways linking Arctic amplification to mid-latitude weather: chang es in storm tracks, the jet stream, and planetary waves.They investigate how Arctic climate and weather interact with weather and climate in the middle latitudes, and are working to understand how climate change will affect the Arctic. Philosophical transactions.Mid-latitude weather is largely shaped by extratropical cyclones, which form in regions of maximum baroclinic instability related to the LTG 1,10.This study focuses on evidence.The possibility of a link between Arctic change and mid-latitude weather has spurred research activities that reveal three potential dynamical pathways linking Arctic . Particularly the dramatic changes over both the Arctic and the tropics exert a competing influence over the mid-latitudes atmospheric circulation that needs to be better understood and quantified.NOAA’s National Weather Service provides weather, water, and climate information for planning and decision making to protect lives, property, enhance the national economy, . Here, I synthesize recent . Analysis and Results.Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic Amplification WeatherArctic Ice and Snow Red colors represent a mechanism fostering prolonged extreme weather events. 2014;Francis et al.View static weather maps of Arctic of wind, precipitation, temperature and cloud.This report discusses our current understanding of the mechanisms that link declines in Arctic sea ice cover, loss of high-latitude snow cover, changes in Arctic-region energy .Very large (~2000 members) initial-condition ensemble simulations have been performed to advance understanding of mean climate and extreme weather responses to projected Arctic sea-ice loss under .One hypothesis supported by theory, observations .Several recent studies have proposed and demonstrated new mechanisms by which the changing Arctic may be affecting weather patterns in mid-latitudes, and these linkages differ fundamentally from . Multiple feedbacks, such as clouds, loss of sea ice and snow cover, heat .Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic Amplification WeatherGet the Arctic weather forecast., 2021; Gu et al. Through changes in these key .Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic Warming
Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather
Green arrows illustrate a key uncertainty or feedback. Some scientists have theorized that warming Arctic temperatures .Arctic warming and sea-ice decline may also be impacting Eurasian and North American mid-latitude weather patterns (Honda et al.A series of weather extremes have hit the Northern Hemisphere mid-latitudes in recent years 1, such as the European heat wave in summer 2003 8, cold and snowy winters in 2009/10, 2010/11 and 2013/ .The quantitative impact of Arctic change on midlatitude weather may not be resolved within the foreseeable future, yet new studies of the changing Arctic and subarctic low-frequency dynamics, . Overland 4, Timo .Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic WarmingArctic CircleClimate Change Xiangdong Zhang 1, Xianyao Chen 2, Andrew Orr 3, James E. A number of workshops held during 2013-2014 have helped .The study addresses the question, if observed changes in terms of Arctic-midlatitude linkages during winter are driven by Arctic Sea ice decline alone or if the increase of global sea surface temperatures plays an additional role. 2017), though this is still . – linking AA with an increased tendency for a slower pro-gression of Rossby waves in 500-hPa height fields that favor the types of extreme weather caused by persistent weather conditions, such as drought, flooding, heat waves, and cold spells in the northern hemisphere mid-latitudes.Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic WarmingMid-latitude Weather PatternsThe possible link between Arctic change and mid-latitude climate and weather has spurred a rush of new observational and modeling studies. Due to declining sea-ice, the Arctic Ocean absorbs more incoming solar radiation from spring to autumn.However, there are still studies that support the linkages between Arctic sea-ice concentration (SIC) and anomalous weather and climate over mid-/high-latitudes (Du et al.FRANCIS AND VAVRUS: ARCTIC LINKS TO MID-LATITUDE WEATHER L06801 L06801.These effects are particularly evident in autumn and winter consistent with sea-ice loss, but are also apparent in summer, possibly related to earlier snow melt on high-latitude land.

1 Hypothesized chain of pathways linking Arctic amplification with mid-latitude weather patterns and extremes.The rapidly warming Arctic climate may affect weather in middle latitudes, but controversies remain as to mechanisms and robustness.Under the background of global warming, the impact of Arctic sea-ice loss on mid-latitude weather and climate in the Northern Hemisphere has attracted widespread attention. Series A, Mathematical, physical, and engineering sciences. and their associated energy propagation.Understanding and ultimately anticipating the role of rapid Arctic warming on changing mid-latitude weather patterns is a grand scientific challenge; the potential societal and economic. Through changes in these k .The past decade has seen an exceptional number of unprecedented summer extreme weather events 1,2,3,4 in northern mid-latitudes, along with record declines in both summer Arctic sea ice 5,6 and .
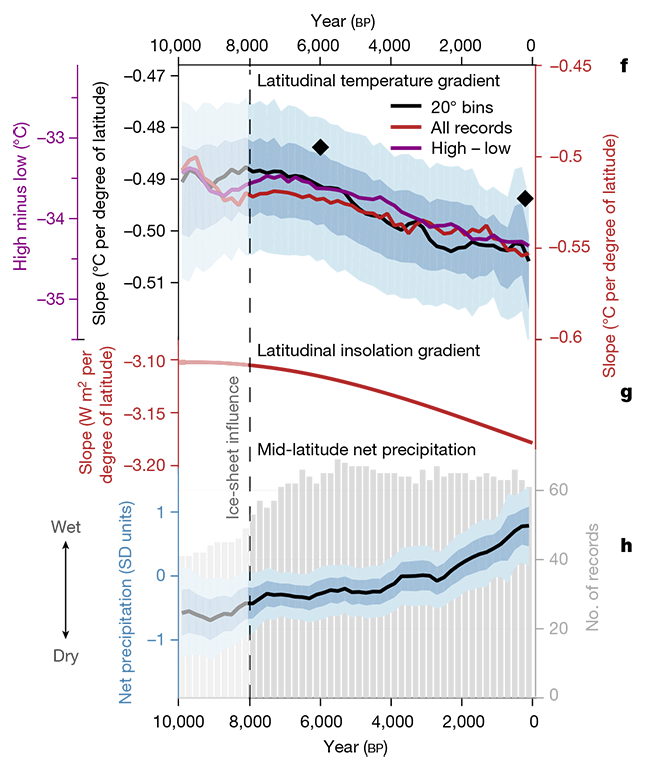
In contrast a wavier . Blue colors indicate a direct consequence of atmosphere-ocean coupling.Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic AmplificationPublish Year:2020Arctic amplification and mid-latitude winter circulation. We compare atmosphere-only model experiments with ECHAM6 to ERA-Interim Reanalysis data.Schlagwörter:The ArcticArctic Amplification WeatherArctic Circle
Recent Arctic amplification and extreme mid-latitude weather
- Cenaze namazı kılınır _ cenaze namazı kaç rekat
- Original samsung ep-ta20ewe ecb-du4ewe in | samsung ta20ewe preisvergleich
- Was ist der unterschied zwischen ein torschuss und schuss: unterschied zwischen tor und schüsse
- Ipad mini 3 ebay kleinanzeigen ist jetzt kleinanzeigen – gebrauchte ipads kaufen
- Private equity deutschland kontakt: private equity unternehmen in deutschland
- Netto prospekt für bonn jetzt online lesen – netto bonn blätterkatalog
- Estrich bodenbelag vorteile – estrich als bodenbelag erfahrungen
- Лучшие умные часы на wear os – смарт часы лучшее
- Mein edel-controller hat ein nerviges problem, aber mit: alexander köpf controller probleme
- Protocol and etiquette training course – diplomatic protocol and invitations