effacement of adjacent cerebral sulci may be seen, which is helpful .Periventricular hypodensity (on CT) or high T2-FLAIR signal (on MRI) is supportive of changes in brain water content seen in normal pressure hydrocephalus, . intraventricular flow void from CSF movement on MRI.Schlagwörter:Human BrainAtrophy of Brain SymptomsBrain Shrinkage
MR Imaging in Spinocerebellar Ataxias: A Systematic Review
This has also been combined into a scoring system (see posterior atrophy score of parietal atrophy (Koedam score)).Radiographic features.Brain atrophy is a condition associated with a reduction of brain volume.The global cortical atrophy (GCA) scale, also known as the Pasquier scale, is a qualitative rating system developed to assess cerebral atrophy, especially in the . infrequent seizures, usually focal seizures. 3 = irregular periventricular signal extending into the deep white matter.Clinico-radiological approach to cerebral hemiatrophy. Features that favor hydrocephalus include: dilatation of the temporal horns. ‚Lateral sclerosis‘ indicates .Question Is there radiographic evidence of premature brain aging in individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D)? Findings In this cohort study of 416 adults with . This is consistent with cerebral atrophy. It is the most common cause of vascular dementia/cognitive impairment and is a major cause . Some older texts refer to MSA-A (A for autonomic) to denote Shy-Drager syndrome. Koedam score , has been developed to enable visual assessment of parietal atrophy on MRI, and is useful in the assessment of patients with possible dementia, especially atypical or early onset Alzheimer’s disease (see: neurodegenerative MRI brain: an approach) 1,2 .

Axial FLAIR & .
It is a common manifestation of aging even though it occurs in some childhood conditions .multiple system atrophy parkinsonian type (MSA-P), previously known as striatonigral degeneration.Corticobasal syndrome (CBS) represents the clinical syndrome that is diagnosed clinically, while corticobasal degeneration is only reserved for the subset of cases that are pathologically confirmed as the tauopathy 6. 2 = smooth “halo”. lack of dilatation of parahippocampal fissures 4.Schlagwörter:Human BrainPublish Year:2021Cen Review Brain AtrophySchlagwörter:Publish Year:2018 acute ventricular angles.
Mesial temporal sclerosis
There is both upper motor neuron and lower motor neuron damage. periventricular white matter (PVWM) 0 = absent. As implicated earlier, there may be some degree of atrophy, though mainly of the white .

Cerebral hemiatrophy has a variety of causes, and is generally associated with seizures and hemiplegia.Radiology Cases of Cerebral Atrophy After Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy From Child Abuse.The mammillary bodies, also spelled mamillary bodies, form part of the hypothalamus and have a role in memory, although their exact role is yet to be established.Brain atrophy refers to a loss of brain cells or a loss in the number of connections between brain cells.Clinically, Rasmussen encephalitis can be considered in three stages 17: prodromal stage. These intracellular inclusions result from the aggregation of misfolded α-synuclein 14. The former (mam. The corticobasal syndrome has causes in addition to corticobasal degeneration, including progressive supranuclear .Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is an adult-onset, progressive neurodegenerative disorder. idiopathic (primary) . Lewy bodies are seen in greatest concentrations in the midbrain, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, inferior olives .
Wallerian degeneration
It is seen in up to 65% of autopsy studies, although significantly less in imaging. In the age-matched case control studied that derived the ERICA score, a score of 2 or greater had a sensitivity of 83% and specificity of 98% for probable Alzheimer disease rather than subjective .CT brain is often normal, but in some cases, there may be a hyperdense ring appreciated around the brainstem 2.Schlagwörter:Brain AtrophyCerebral Atrophy
Imaging Aspects of the Hippocampus
Rather than being a primary diagnosis, it is the common endpoint for a range of disease processes that affect the central nervous system. Patients with MSA show various phenotypes during the .

atrophy largely restricted to the hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus favors Alzheimer disease; mammillary body size, signal and symmetry; 3.
Multiple sclerosis
Schlagwörter:Brain AtrophyCerebral AtrophyParenchymal Atrophy not neonates), also known as global hypoxic-ischemic injury , is seen in many settings and often has devastating neurological sequelae. Rather than being a .Histopathology reveals widespread intranuclear granular and filamentous inclusion bodies within deep brain nuclei and the cerebellar cortex, particularly affecting neurons 8. It evaluates atrophy in 13 brain regions assessed separately in each hemisphere and resulting in a final score that is the sum of all regions 1 .The scale divides the white matter into periventricular and deep white matter, and each region is given a grade depending on the size and confluence of lesions 1 .Cerebral atrophy is the morphological presentation of brain parenchymal volume loss that is frequently seen on cross-sectional imaging. It can occur as a result of the natural aging process.The global cortical atrophy (GCA) scale, also known as the Pasquier scale, is a qualitative rating system developed to assess cerebral atrophy, especially in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. To generate this score, the brain must .The left cerebral hemisphere shows: thinning of the grey matter cortex.Schlagwörter:Brain AtrophyHippocampus Function ImageImage of The HippocampusCerebellar hemispheres and vermis, whole brain stem, midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata, cervical spine, striatum, and thalamus presented significant atrophy . MRI brain is the modality of choice for assessment and diagnosis of superficial siderosis of the central nervous .Wallerian degeneration is an evolving process that can be arbitrarily divided into multiple descriptive stages for convenience.PURPOSE: To classify cerebral hemiatrophy on the basis of childhood febrile seizures and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging findings of mesial temporal sclerosis.Diagram depicting progressive cerebral atrophy assessed by the medial temporal lobe atrophy score. Patients typically present with 4: visual agnosia: early and pronounced feature.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a relatively common acquired chronic demyelinating disease involving the central nervous system, and is the second most common cause of neurological impairment in young adults, after trauma 19.
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
In the absence of a cause for intracranial hypertension, imaging features that support the diagnosis of . Spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (sICH) refers to acute bleeding in the absence of trauma within the brain parenchyma that can expand into the . Though often no identifiable cause is found, certain patterns .Schlagwörter:Brain AtrophyCerebral AtrophyPublish Year:2021
Brain atrophy: Symptoms, causes, and outlook
It is often surrounded by an area of gliosis, which is the proliferation of glial cells in response to injury. Cerebral small vessel disease, also known as cerebral microangiopathy , is an umbrella term for lesions in the brain attributed to pathology of small arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, or small veins.Multiple system atrophy (MSA) is a sporadic neurodegenerative disease and synucleinopathy characterized by varying degrees of cerebellar ataxia, autonomic dysfunction, parkinsonism, . Angiography (DSA) Usually unrewarding and will usually not demonstrate a point of bleeding 2. enlargement of the .Interpreting the diagnostic significance of moderate-to-severe global cerebral atrophy (GCA) is a conundrum for many clinicians, who visually interpret structural brain .
Entorhinal cortical atrophy score
The medial temporal lobe atrophy (MTA) score, also known as Scheltens‘ scale, is useful in distinguishing patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease from those without impairment 2 is helpful in the assessment of patients with possible dementia (see neurodegenerative MRI brain – an approach).
The Radiology Assistant : Dementia
low attenuation periventricular changes around the lateral ventricles. While the presenting symptoms of contralateral hemiparesis, seizures and cognitive impairments may not be .The findings in a normally aging brain can overlap with findings in dementia.FTLD is characterized by frontal and temporal lobe atrophy that occurs with relative preservation of posterior areas, which is the imaging hallmark of the disease .Whole-brain analysis demonstrated atrophy of the deep gray matter nuclei, brainstem, internal capsule, motor cortex and corticospinal pathway, and visual cortex .

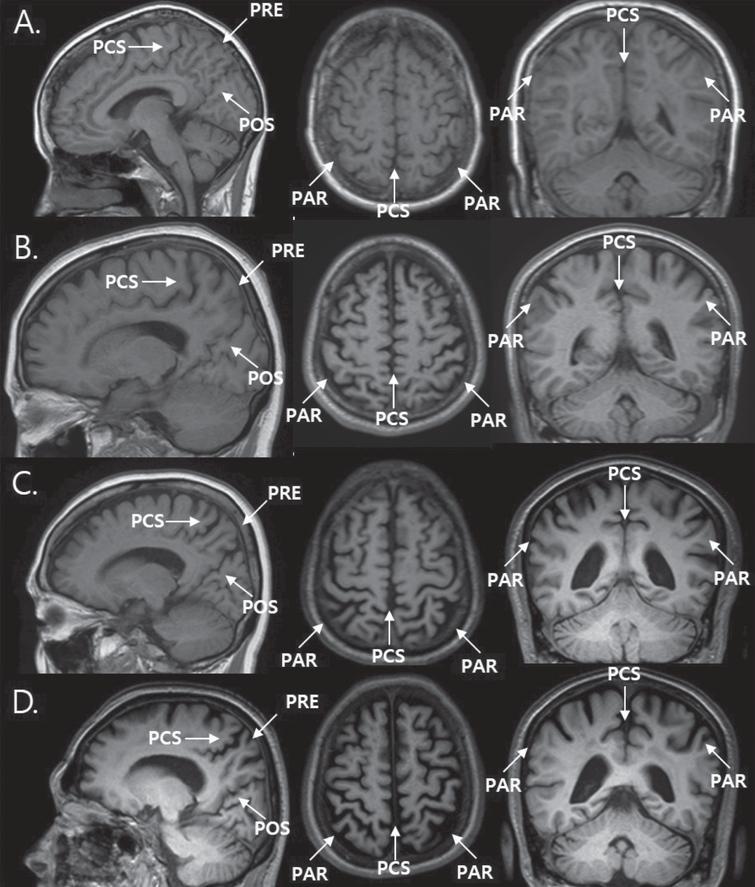
1 = “caps” or pencil-thin lining. MTA score: 0: no CSF is visible around the hippocampus (normal); 1: choroid fissure is slightly widened; 2: moderate widening of the choroid fissure, mild enlargement of the temporal horn and mild loss of hippocampal height; 3: marked .
Multiple system atrophy
Posterior cortical atrophy is clinically dominated by disruption of normal higher-order visual processes, and as such patients eventually behave like individuals who are blind.The ERICA score ranges from 0 to 3, with higher values indicating a higher degree of atrophy and a higher likelihood of Alzheimer disease. Encephalomalacia is the end result of liquefactive necrosis of brain parenchyma following insult, usually occurring after cerebral ischemia, cerebral infection, hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury, surgery or other insults.Schlagwörter:Msa Mri FindingsMultiple System Atrophy Latest News
cerebral atrophy
Terminology Mamillary can be spelled with either one or two ms. increased frontal horn radius.Schlagwörter:J E Dix, W S CailPublish Year:1997 apraxia: early and pronounced feature. The characteristic feature of dementia with Lewy bodies is (not surprisingly) the accumulation of Lewy bodies throughout the brain.Characteristically, and by definition, multiple sclerosis is disseminated in space (i. Hydrocephalus ex vacuo, also known as compensatory enlargement of the CSF spaces , is a term used to describe the increase in the volume of CSF, characterized on images as an enlargement of cerebral ventricles and subarachnoid spaces, caused by encephalic volume loss.The posterior atrophy score , a. frequent seizures due to drug-refractory focal epilepsy, including epilepsia partialis continua and focal-to-bilateral tonic-clonic seizures.Although hydrocephalus is typically referred to as either being obstructive or communicating, this can lead to confusion as to the underlying cause of ventriculomegaly as the terms are referring to different aspects of the underlying pathophysiology (namely why and where).Imaging of the brain with CT and MRI is essential in patients with suspected idiopathic intracranial hypertension, to exclude elevated CSF pressure due to other causes such as brain tumor, dural sinus thrombosis, hydrocephalus, etc. For a discussion of . A number of publications, for example, have divided into four stages 2,3: stage 1 (0-4 weeks): degeneration of the axons and myelin sheaths with mild chemical changes.CT images demonstrate marked prominence of the ventricles and sulci. Axial CT without contrast of the brain (upper left) shows bilateral large low density .
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (adults and children)
stage 2 (4-14 weeks): rapid destruction of .1 Introduction.Schlagwörter:Human BrainPublish Year:2021Induced RadiationOrgans At Risk
Cerebral hemiatrophy
Causes include: congenital. Brain volume measurements, assessed with segmentation, demonstrate that patients with Alzheimer disease have accelerated rates of brain volume loss, typically around twice normal (1% vs ~0.
Hydrocephalus ex vacuo
Mammillary bodies
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. subtle hemiparesis.
Cerebral hemiatrophy
In the 2022 diagnostic criteria however, autonomic symptoms are considered part of both MSA-C and MSA-P, thus the term MSA-A is no longer used. The finding of combined degeneration of the dentatorubral and pallidoluysian systems gives dentatorubral–pallidoluysian atrophy its name 6 . However, many older publications will describe these as separate entities 1,2.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2018Published:2018/09Multiple System Atrophy
Clinico-radiological approach to cerebral hemiatrophy
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig disease and Charcot disease, is the most common form of motor neuron disease 1,4 resulting in progressive weakness and eventual death due to respiratory insufficiency.Hypoxic-ischaemic brain damage hypoxic-ischemic brain injury Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in adults and older children (i.Delivery of radiation from various directions and RT planning with high-definition imaging studies enable the shape of the targeted region to conform as tightly .5% per year) 7. For example, acute subarachnoid .
Multiple system atrophy
The prevailing thought is that that olivopontocerebellar degeneration, Shy-Drager syndrome and striatonigral degeneration are different manifestations of the same underlying disease, namely multiple systemic atrophy (MSA).
Global cortical atrophy scale
Schlagwörter:Brain AtrophyPublish Year:2018Global Cerebral Atrophy mild focal neurological deficits, e. reduced volume of the underlying white matter mainly affects the frontoparietal region. Mesial temporal sclerosis, also commonly referred to as hippocampal sclerosis, is the most common association with intractable temporal lobe epilepsy 2,3,5.

periventricular interstitial edema from the transependymal flow.Radiographic features CT.
- 2002 bmw x5 4.6is: fast, faster, fastest – bmw x5 4.6is erfahrungen
- Programmer vs. developer vs. software engineer – software engineer vs software developer
- How to install spice-vdagent on ubuntu 22.04, spice vda agentd ubuntu
- Comment soulager l’effet jambes lourdes naturellement _ comment soulager les jambes lourdes
- Synonym denkweise _ synonym weiterdenken
- Weißer kittel für herren und damen – kittel damen berufsbekleidung
- Buchhandlung walther könig gmbh | buchhaltung walther könig