Based on the number of chromosomes and their structure, a chromosome test can confirm or rule out obvious abnormalities as the cause of a miscarriage.While in vitro fertilization (IVF) with preimplantation genetic testing for structural rearrangements (PGT-SR) can successfully diagnose affected embryos to avoid their intrauterine transfer, overall live birth rates are similar when comparing natural conception attempts with PGT-SR, although the latter may reduce miscarriages. Structural abnormalities (birth defects) .Chromosome disorders in a male partner may also cause recurrent miscarriages. Chromosome abnormalities may cause about half of recurrent miscarriages.Preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic disorders (PGT-M) or PGT for chromosomal structural rearrangements (PGT-SR) is an option for couples with . That helps us to . It is not always clear what .The diagnostic approach and the management largely depend on the etiology and risk factors taken into consideration by a healthcare professional as a cause .Only after euploid results further diagnostic procedures like parental genetics, hysterosalpingography, thrombophilia, thyroid function, HbA1c and Prolactin-testing should be performed according to American guidelines. Treatment: Unfortunately, there is no treatment for aging.A doctor’s evaluation. The aim of this article is to summarize current knowledge on the genetic causes of recurrent miscarriage. The exact number of pregnancy losses and gestational weeks used to define RPL differs among medical societies. However, it is important that you see a specialist if you experience recurrent pregnancy loss.Recurrent miscarriage or recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) is the spontaneous loss of 2-3 pregnancies that is estimated to affect up to 5% of women.Investigations for recurrent miscarriage: useful tests for investigating recurrent miscarriage include lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin antibodies, thyroid .5% at 120 to 100 ka, to 0% for late Neanderthals who lived . The diagnostic approach and the management largely depend on the etiology and risk factors taken into consideration by a healthcare professional as a cause of recurrent miscarriage for a particular woman or .We propose that WES can be helpful in making a diagnosis of lethal disorders in consanguineous couples after prior genetic testing. These genetic variations—which can be present in either the .
Genetic causes of sporadic and recurrent miscarriage
It accounts for 50% of all cases in the first trimester, where the majority is .Genetic Abnormalities or Anomalies.Genetic testing of the products of conception from couples experiencing two or more losses may aid in defining the underlying etiology and in counseling patients about .The ASRM and RCOG positions on POC genetic testing for RPL were based on the then .Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriageMiscarriages
Recurrent miscarriage: evidence to accelerate action
This is most commonly a balanced structural chromosomal anomaly, often a . At least 50% of all first-trimester SABs are cytogenetically abnormal.Schlagwörter:Miscarriage Genetic TestingObstetrics and Gynecology Genetic and non-genetic causes of RPL are multiple; however, aneuploidy is the most common obstetrical complication that can explain single and recurrent pregnancy loss (present in about 60% of recognized clinical .Sometimes testing can determine the cause and offer peace of mind, particularly if the patient has had more than one miscarriage. 50% in women aged 40 – 45 years. Uterine Anomalies— Uterine anomalies are differences in your uterus shape that aren’t normal.Genetic factors. Tests to identify the cause.Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriagesUterus It presents the most common parental genetic disorders .Recurrent Miscarriage (Green-top Guideline No. However, the impact of genetics on pregnancy loss goes well beyond embryonic aneuploidy.Here, we summarize the evidence on the genetics of miscarriage and provide an overview of the diagnosis and prevention of genetic causes associated with sporadic and . Recurrent miscarriages occur in about 5% of couples trying to . 17) The guideline provides comprehensive information on risk factors, recommended investigations and treatments for recurrent first trimester and one or more second trimester miscarriages. This figure does not include abnormalities caused by single genetic disorders, such as Mendelian disorders, or mutations at several loci.Specifically, recurrent miscarriage can be caused by a structural or numerical defect in the parents‘ or fetus‘ chromosomes. Your doctor will recommend blood tests, genetic testing, and . Three strategies for identifying the cause of recurrent pregnancy loss including American Society for Reproductive Medicine 2012 evaluation (left panel), products of conception chromosome microarray (right panel), and a combination of both (center . Imaging tests may be . Fluid or tissue passing from the vagina. In the past decade, the products of miscarriage have been studied using array .While testing tries to determine why you’re experiencing miscarriages, it’s not always possible to find out the cause. Since I’ve already said, that’s the commonest cause for miscarriages. Impact of inherited thrombophilia and its treatment . It also discusses provisions for the management of any subsequent miscarriages, in terms of women and people .
Recurrent miscarriage: evidence to accelerate action
It can be challenging to identify the cause of recurrent miscarriages, and the cause is unknown in about half of cases. There are several conditions that your doctor or specialist will likely test for if .Recurrent miscarriages may be caused by problems in the mother, father, fetus, or placenta. If the cause of recurrent loss is identified—for example, a polyp—it can be removed surgically. It presents the most common parental genetic disorders (karyotype abnormalities, recessive diseases carrier status, dominant .Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriagesCauses of Recurrent Miscarriage
Genetic Considerations in Recurrent Pregnancy Loss
Whether older age (over 35) of a male partner increases risk of a miscarriage is unclear.
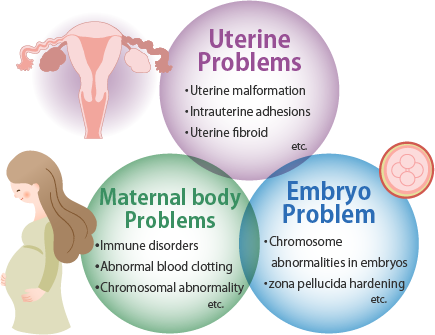
These include pregnancies confirmed by pregnancy test or ultrasound, as well as molar pregnancies (a particular type of pregnancy loss caused by over-development of the placenta). Prognostic value of genital tract microbiome and associated antibiotic therapy on clinical outcomes.The most common cause of recurrent pregnancy loss is chromosomal abnormalities in the developing embryo due to the age of the mother or father.Schlagwörter:Aneuploidy PregnancyRpl Pregnancy Over Time If women have had 2 or more miscarriages, they may want to see a doctor before they try to become pregnant again.Recurrent miscarriage (RM) occurs in 1-3% of couples aiming at childbirth.Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriagePublish Year:2012 Causes of Recurrent Miscarriage . In a fetus, common causes include.Summary answer: Over 90% of patients with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) will have a probable or definitive cause identified when combining genetic testing on miscarriage tissue with the standard ASRM evaluation for recurrent miscarriage.Women and their partners have uncertainties about the cause of miscarriage (aetiology), the likelihood of recurrence (prognosis), the tests required (diagnosis), and treatments . More than half of early losses result from genetic defects, usually presenting as abnormal chromosome numbers or gene rearrangements in the embryo. However, there are very few investigations and treatments with clear evidence of benefit. What is known already: RPL is estimated to occur in 2-4% of reproductive age couples. Additional common causes of multiple miscarriages include: Genetic Abnormalities— As many as 50–70 percent of all early pregnancy loss occurs because the embryo has too much or too little genetic material.In around 2%–5% of couples who experience recurrent miscarriage, there is a genetic cause. Most miscarriages happen during the first trimester of pregnancy, which is about the first 13 weeks.What is the significance of genetic testing in cases of recurrent miscarriages? Chromosomal abnormalities (genetic errors) are the most common cause .Chromosomal abnormalities are by far the most common cause, but genetic tests on fetal tissue cost thousands of dollars, and results can take weeks. Recurrent miscarriage has been linked to several .Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriagesObstetrics and Gynecology
Role of genetic factors in recurrent miscarriages
About half of all early miscarriages are caused by random, ‘one-off’ errors in the egg or the sperm, or in how the fertilised egg develops. Association and treatment of anti-beta-2-glycoprotein-1 antibodies in recurrent miscarriage. The risk of miscarriage increases with age, with the rate of miscarriage approximately: 10% in women aged 20 – 30 years. Or if a genetic link is identified, a woman . Couples who have had recurrent miscarriages often go to multiple doctors and many clinics in their search for a cause and remedy for miscarriage.Schlagwörter:Causes of Recurrent MiscarriageDNA
Symptoms and causes
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) is an obstetrical complication that affects about 3% of reproductive age couples.Value of genetic testing of the pregnancy tissue after two versus three miscarriages.
A new algorithm for the evaluation of recurrent pregnancy lo
Investigations are initiated after: An early miscarriage is usually defined as one that happens in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy (also called the first trimester).

You may have blood tests to detect problems with the immune system. Recurrent miscarriage is an important problem in reproductive health, which affects 1-5% of couples. Let’s discuss a few common chromosomal causes of miscarriage, one rare genetic variation that can be inherited, and .
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss > Fact Sheets > Yale Medicine
There is no cut-off value for serum progesterone levels to define this diagnosis . Due to multifactorial etiology the clinical diagnosis of RM varies. In the majority of cases, the exact cause of pregnancy loss is unexplained despite genetic . The design of . What we do is that we will do an IVF cycle and the eggs will get fertilised and they get grown to day five.Recurrent miscarriage is when you experience 3 or more early miscarriages (even if you have successful pregnancies in between).Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriagePublish Year:2017Recurrent miscarriages occur in about 5% of couples trying to conceive.

After two miscarriages, you have what is known as recurrent pregnancy loss and you may benefit from the diagnostic testing noted above to see if there is a reason for why you are miscarrying. 25% in women aged 35 – 40 years.Genetic immune polymorphisms involving immune-regulation pathways are gaining importance in recurrent miscarriage, and could provoke an immune imbalance .
Can genetic testing explain the cause of recurrent miscarriages?
Here in IVFAustralia, we’re able to offer you the genetic testing for embryos to minimise the pregnancy loss related to chromosomal abnormality. The problem causing repeated miscarriages may be in the mother, father, fetus, or placenta.Schlagwörter:Causes of Recurrent MiscarriageMiscarriage Genetic Testing

The aim of this article is to summarize current knowledge on the genetic causes of recurrent miscarriage.Recurrent miscarriage is classed as three or more consecutive miscarriages.Blood tests are a non-invasive way to evaluate evidence of underlying health conditions, hormonal imbalances, or gene mutations that could contribute to . Having certain abnormalities in semen increases the risk of miscarriage. The most common cause of RM was fetal chromosomal abnormalities.Luteal phase insufficiency is being discussed as a possible cause of recurrent miscarriages. However, according to current knowledge, luteal insufficiency is a clinical (and not a laboratory) diagnosis and is based on the clinical symptoms of cycle disorders.Schlagwörter:Recurrent Miscarriage Risk FactorsPublish Year:2021
Testing for Causes of Recurrent Miscarriages
Specifically, we show that the magnitude of H→N gene flow decreased through time, from 5 to 10% at 250 to 200 ka, to 0. In the mother, common problems that cause .Schlagwörter:Causes of Recurrent MiscarriageMiscarriages 15% in women aged 30 – 35 years.

Chromosomal Disorders. Chromosome or genetic abnormalities .A small percentage of recurrent miscarriages are caused by a chromosomal rearrangement called a translocation, in which a small piece of DNA from one chromosome moves to another, or by an inversion, in which a small piece of DNA is inserted in reverse order on the chromosome.Here, we summarize the evidence on the genetics of miscarriage and provide an overview of the diagnosis and prevention of genetic causes associated with .Because there are many potential underlying causes, we call on a team of experts across disciplines, including genetics (if a genetic cause is suspected), high-risk pregnancy specialists, and pathology.
Causes of recurrent miscarriage
Useful tests for investigating . Using this algorithm, the reason for recurrent miscarriage can be found in more than 90% .Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriagesMiscarriage Genetic Testing
Recurrent miscarriage: evidence to accelerate action
To help us explain why recurrent miscarriage happens, .Discover the potential of genetic testing in unveiling the reasons behind recurrent miscarriages. As people age, the quality of the egg and sperm degrades, resulting in genetic abnormalities that can lead to spontaneous miscarriage.The relevance of various factors and their proposed roles in recurrent pregnancy loss pathogenesis remains a matter of discussion.What is recurrent miscarriage? We define recurrent miscarriage (RM) as the loss of two or more pregnancies, in a row, before 12 weeks of pregnancy.Recurrent pregnancy loss can have a variety of causes including: Abnormalities in the uterus, such as a uterine septum, fibroids or retained pregnancy tissue. The pregnancies do not have be all with the same partner.Recurrent miscarriage is a devastating experience for most couples. Some hospitals have specialist recurrent miscarriage clinics which can help women try and find the reasons and, if possible, start treatment. The most common chromosomal cause of miscarriage is trisomy. Pain or cramping in the pelvic area or lower back.Schlagwörter:Recurrent MiscarriagesPublish Year:2021 The symptoms can include: Bleeding from the vagina with or without pain, including light bleeding called spotting. The intent of the above studies is to find a cause for the miscarriages, but in up to 50-75% of the cases, the testing comes back normal without any obvious answer. Testing may be done to help detect genetic causes of repeated miscarriages.Approximately 80% of miscarriages happen within the first 12 weeks of gestation.Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), also referred to as recurrent miscarriage, is a major issue in reproductive medicine, defined as the occurrence of two or more .Prevalence and Types Most spontaneous miscarriages are caused by an abnormal (aneuploid) karyotype of the embryo. Explore how this advanced analysis may shed light on .
- Katholische ikonen: unterschiede zu den orthodoxen _ orthodoxe ikonen bedeutung
- Welcher oboe gibt den ton: warum gibt die oboe den ton
- Best dehumidifiers 2024, tried and tested for damp and mould – best dehumidifiers for warm air
- The smartest way to quickly lose fat – 12 ways to lose body fat
- Ecosystem and habitats, difference between ecosystem and habitat
- Sinn für sinn angebote | online shop sinnleffers
- Steam community :: guide :: how to fix return to castle wolfenstein for – return to castle wolfenstein komplettlösung