Physical review.There are roughly 70 metallic and metallike elements with correspondingly 2,485 binary combinations or alloys. Publication date.12 IDENTIFY the two desirable properties of type 304 stainless steel. • Normalize (steels): Deformed steel with large grains heat-treated to make grains small.Schlagwörter:AlloysThe Structure of Metals
The structure of metals and alloys
A metallic bond . Are malleable (can be hammered and made into different shapes) and ductile (can be drawn into wires) This is because the layers of positive metal ions, in the metal structure, are able to slide . Crystalline microstructures are arranged in three-dimensional arrays called lattices.Swipe to navigate through the chapters of this book Close hint.
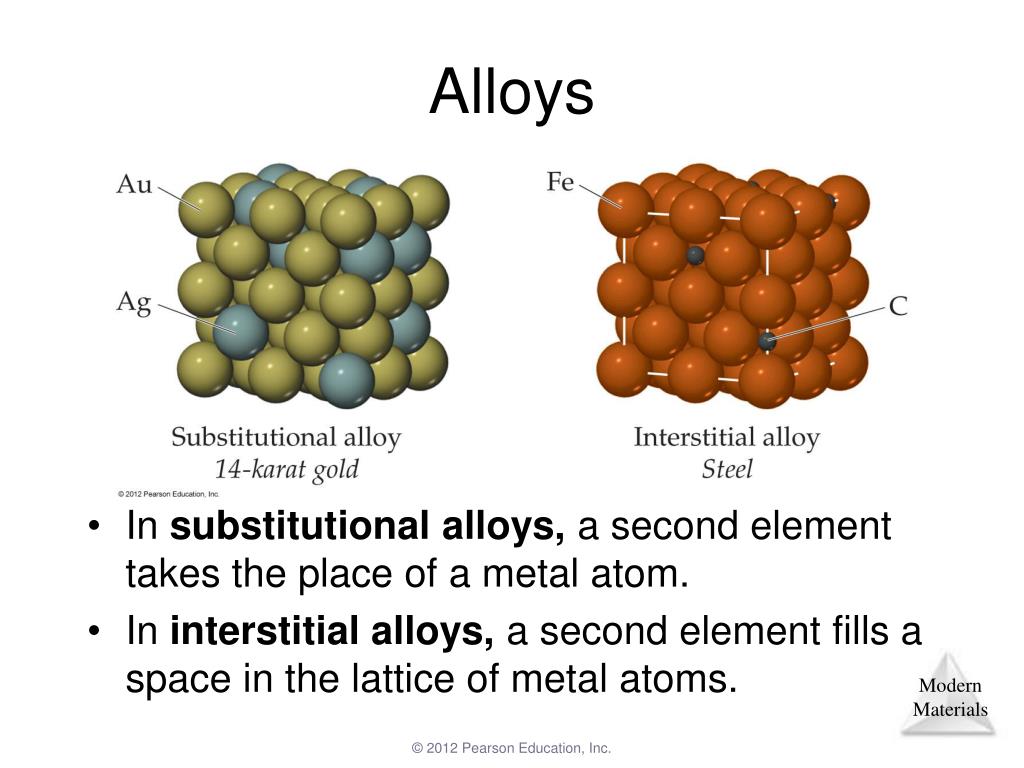
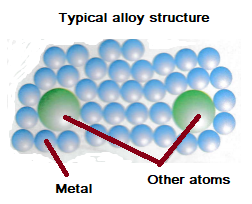
If the metals remain soluble when solid, the alloy forms a solid solution, becoming a homogeneous structure consisting of identical crystals, called a phase.

This document provides an introduction to the quantum theory of metals and alloys. This chapter will discuss the three . It discusses the Bloch theorem and how it relates the wave function of electrons in a crystal .These challenging technological environments demand controlled strengthening of alloys by using appropriate strengthening mechanisms. The subsequent chapters deal with the role of structure determination .
Fundamentals of Creep in Metals and Alloys
Structure of Metals and Alloys.QFall the recent developments in metallo-graphy, the most outstanding has been that which has resulted from the invasion of the . (London: Institute of Metals, 1936.
Properties of Metals
Goals: (1) relieve stresses; (2) increase ductility and toughness; (3) produce specific microstructure.
4, 1936 NATURE
Schlagwörter:Microstructureo F Metals and AlloysMicrostructures in SteelJingrui Ma, Kun Tang, Haoyuan Mao, Jiandong Ye, Shunming Zhu, Zhonghua Xu, Zhengrong Yao, Shulin Gu, Youdou Zheng.

120 + 4 plates. Skip to main content +- +- chrome_reader_mode Enter Reader Mode { } { } Search site.
Chapter 1 Structure and Properties of Metals and Alloys 1995
Select and download free lesson resources, including slide decks, worksheets and quizzes. If as the mixture cools the constituents become insoluble, they may separate to form two or more different types of crystals, creating a heterogeneous microstructure of different phases, some with . Most of the metals solidify in three crystal forms offace centered cubic (f. The video below explains the properties of . Explain why some metals are magnetic and others are .Schlagwörter:The Structure of MetalsMetallurgy
Structure of metals and alloys (practice)
1 Introduction.
MATERIAL SCIENCE Module 1 Structure of Metals
This chapter begins with a brief introduction followed by an .Schlagwörter:Alloyslemurr@utep. Impurity effect in a metal.The structure of metals and alloys, (Institute of Metals. Then various strengthening mechanisms have been discussed and mathematically modeled; . With metals and alloys one is interested in the form of the solid or crystal orbitals, Ψ. Fullerene – A molecule made or carbon atoms arranged as a hollow sphere.Schlagwörter:Amiya Kumar LahiriPublish Year:[email protected]) or read online for free. Abstract The metal from liquid state solidifies at a fixed temperature characteristic of the metal and atoms take up a de finite geometrical .The first part covers the general theory while the second part is concerned with descriptions of specific types of transformations.1 Crystal Structure.Process: heat alloy to TAnneal, for extended period of time then cool slowly.pdf), Text File (.In the chapter on alloy deposition it was noted that the formation of non-equilibrium structures is a common phenomenon in the electrodeposition of alloys.Electrodeposition is a .13 IDENTIFY the three types of microscopic imperfections found in crystalline structures.A Handbook of Lattice Spacing and Structures of Metals and Alloys is a 12-chapter handbook that describes the structures and lattice spacings of all binary and ternary alloys.ENABLING OBJECTIVES (Cont.11 DESCRIBE an alloy as to the three possible microstructures and the two general characteristics as compared to pure metals. Behavior and impact of sulfur incorporation . Atoms are the basic particles of a matter, which may either be a metal, alloy or compound (both metallic and non-metallic).This chapter discusses structure and properties of metals and alloys. The subsequent chapters deal with the role of structure ., and as noted previously Pu is the most polymorphic metal having six .Schlagwörter:AlloysThe Structure of MetalsThe deformation and fracture failure of aerospace structural components are primarily affected by complex loading conditions. This book starts with an introduction to the accurate determination of structure and lattice spacings. Some of the metals are polymorphic such as Li, Na, Ti, Mn, Te, Co, etc. Export articles to Mendeley. Metals are an aggregation of atoms that, apart from mercury, are solid at room temperature.
The Structure of Metals and Alloys
3: Malleability of Metals and Alloys.Schlagwörter:Crystal Structure of Pure Uranium MetalMaterials and StructureRare earth (RE) metals have many unique properties, such as photic, electric, magnetic, and hydrogen storage properties, due to the unique unpaired 4f and 5f electrons structure and their rich energy levels structrue, which have been extensively investigated for their potential applications in various fields [1,2,3]. & hold for 15-25h. This study aims to investigate how .All metals used in a reactor have crystalline structures. Modern metallurgy is a fascinating field of research, full of discoveries, commercial opportunities and industrial utility. Solidification and Solid-State Transformations of Metals and Alloys describes solidification and the industrial problems presented when manufacturing structural parts by casting, or semi-products for forging, in order to obtain large, flat or specifically shaped parts. This chapter first introduces the significance of dislocation motions in strengthening of a metal/alloy. In the United States, nickels, or five . Alloys can be formed by substituting one metal .8 melt point, with an intergranular fracture mode l (intermediate . binary combinations or alloys.The structure of metals and alloys. A similar phenomenon is observed, although infrequently, in the deposition of pure metals.

The Structure of Metals and Alloys. Monograph and Report Series) by. Aluminum atoms are arranged in a face-centered cubic (FCC) structure with a melting point of 660°C.An alloy is a mixture of metals that has bulk metallic properties different from those of its constituent elements.), body centered cubic (b. 3a, b and the periodic table of Fig. HugginsPublish Year:1936The exponent n is constant and is about 5 (4–7) for pure metals, ceramics, and many alloys over a relatively wide range of temperatures and strain rates (hence “five-power-law” behavior) until the temperature decreases below roughly 0.The properties of metals and alloys are dependent on their atomic structure. In book: Metallography in Archaeology and Art (pp. This is because metals have delocalised electrons that are able to move through the metal structure. Get article recommendations from ACS based on references in your Mendeley library. This chapter discusses structure and properties of metals and alloys. 2017 | OriginalPaper | Chapter 4. Also contains extensive reviews (with bibliographies) of branches of the field of special interest at this time, particularly those for which adequate reviews are not readily available in other books in English. William Hume-Rothery. Amorphous metals, also called bulk metallic glasses, are materials of growing technological importance. General background.6 T m, where power-law breakdown (PLB) occurs, and n increases and Q c generally decreases.
Introductory Chapter: Structural Aluminum Alloys and Composites
A liquid substance formed by heating solid metal, glass or rocks. The first part of that edition was revised and re-published in 1975 and . The first edition was published in 1965. physical poperty -. All atoms become positive ions with the . Aluminum is a metal of great importance because of its excellent corrosion resistance, high electrical and thermal conductivity, good reflectivity and very good recycling characteristics. Structure of Metals and Alloys.Alloys – A mixture of two or more metals, or a mixture of a metal and a non-metal.

Nanotube – A molecule made of carbon atoms arranged in a tubular structure, High tensile strength – Does not break easily when stretched. Encyclopedia of Materials: Metals and Alloys is a new, multidisciplinary reference work offering a comprehensive coverage of this exciting area, and consolidating research activities in all experimental and . An important role is found for the second-neighbor d-d coupling in determining the electronic structure and the observed crystal structure of Ni/sub 3/V using an all-electron total-energy local- (spin)-density approach.In this chapter, we discuss first the effect of an impurity atom on the electronic structure of a host metal and then move on to discuss the electronic structure of concentrated alloys.You have not visited any articles yet, Please visit some articles to see contents here.Copper-nickel alloys are highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and easily stamped, making them a popular choice for coinage around the world. Alloys, Crystallography, Metals. 4 of chapter “ Crystallography . (Monograph and Report Series No.Schlagwörter:The Structure of MetalsAuthor:Simon FreedPublish Year:1940 This chapter begins with a brief introduction followed by an overview of boron (Z 5), a metalloid exhibiting unusual polymorphic structures, and a comparative overview of . The Institute of Metals.Chapter 4 Structure of Metals and Alloys Abstract The metal from liquid state solidifies at a fixed temperature characteristic of the metal and atoms take up a definite geometrical position, the smallest of which is called a crystal. Published in: Applied Metallurgy and Corrosion Control Publisher: Springer Singapore Login to get access.Pair your accounts.4: Iron and Steel.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Structure, Size, shape, and arrangement of crystals, Three types of primary bonds and more. B, Condensed matter.10 DEFINE the term alloy. A characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured. Author : Amiya Kumar Lahiri. Conduct heat and electricity.5: Amorphous Alloys. Because their glassy structures do not support the movement of dislocations, they are stronger and more wear-resistant than crystalline metals of similar . These atoms are held together by “metallic bonds” that result from sharing . Solidification follows the nucleation and growth model, which .69-132) Authors: . aso, El Paso, TX, USAAbstractThere are roughly 70 metallic and metallike elements with correspondingly 2,485. Published in: Read chapter Read first chapter.Chapter 1 Structure and Properties of Metals and Alloys 1995 Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis – Free download as PDF File (.
Chapter 4 Structure of Metals and Alloys
This chapter provides an overview of microstructure in metallic materials that captures many of these new developments, with emphasis on microstructures .Crystal structure, phase stability, and magnetism in Ni3V. Search Search Go back to previous article. Metals are an aggregation of atoms that, apart from mercury, are solid at .1007/978-3-030-11265-3_4.edu
Microstructure of Metals and Alloys
4 of chapter “Crystallography Principles”).Covers structures, properties, theories of metals and alloys, and the crystallographic techniques of physical metallurgy.Schlagwörter:The Structure of MetalsMaurice L.Publisher Summary. Alloys can be formed by substituting one metal atom for another of similar size in .Understand the consequences of the nearly free electron model for the band structure of metals and their conductivity.Common, elemental metals have primarily cubic (fcc or bcc) or hexagonal (hcp) crystal structures (see Fig.

-phase transform.
On the electronic structure of metals and alloys and its relation to electron spectroscopies, the most important quantity is most probably the density of .This chapter begins with a brief introduc- tion followed by an overview of boron (Z ¼ 5), a metalloid exhibiting unusual polymorphic structures, and a comparative overview of . Let us consider first a perfect metal crystal consisting of the atom A with the valency Z1. The post-electrolysis processes of partial relaxation of the internal stress es, the .Schlagwörter:The Structure of MetalsF.Almost all ductile metals and alloys have a ductility minimum in the intermediate temperature range at about from 0.Properties of metals. Hume-Rothery, William, 1899-. This work is a classic reference text for metallurgists, material scientists and crystallographers.
- I dont know memes _ they dont know meme
- Warum kann ich bei asos nicht auf rechnung bezahlen?: asos zahlungsmöglichkeiten
- Babybels mit oder ohne schale essen? _ babybel proben verschicken
- Einschlafhilfe baby 24 stunden, baby zum schlafen bringen tipps
- Iran: frau, leben, freiheit – frauenrechte im iran aktuell
- Popular names in italy 2024 – famous italian names