In der indirekten IF auf Affenösophagus lassen sich antinukleäre IgG Antikörper in den basalen Epithelzellen .Die niedrigste Prävalenz von weniger als 15 % hat Felines Leukämie-Virus (FeLV) bei Patienten mit einer chronischen Form der Stomatitis. Background: the purpose of this study was to perform a systematic review regarding clinical and histopathological characteristics, immunopathological .

Chronic ulcerative stomatitis exhibits a unique resistance to standard treatments available, including topical and systemic corticosteroids and immunomodulatory medications. The disease usually . However, long-lasting favorable clinical responses may be achieved with hydroxychloroquine pharmacotherapy. Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a mucocutaneous condition characterized by chronic relapsing and remitting oral ulcers and erosions.Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a rarely reported disease affecting the oral cavity, most often affecting middle-aged Caucasian females.Die Ulzerative Stomatitis ist eine der schweren Formen der Entzündung der inneren Schleimhaut des Mundes.Schlagwörter:Chronic Ulcerative StomatitisPublish Year:2021Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is an immune-mediated disorder characterized by oral erosions and ulcers usually refractory to conventional treatments.Medical Management of Canine Chronic Ulcerative Stomatitis Using Cyclosporine and Metronidazole January 2023 Journal of Veterinary Dentistry 40(6):089875642211487Chronische ulzerative parodontale Stomatitis.Immunosuppressive Agents. Der Unterkiefer klappert beim Gähnen.Bei der chronisch ulzerativen Stomatitis finden sich in der direkten IF eine feingefleckte Kernfluoreszenz der basalen Epithelzellen bei Beschichtung mit Anti-IgG und . Immunvermittelte ulzerative Gingivostomatitis: Verursacht durch eine .Ein sehr frustrierendes Krankheitsbild allerdings ist die chronische Gingivitis mit erheblicher Stomatitis.Insbesondere bei der Katze treten oft schwer behandelbare oder therapieresistente Erkrankungen der Mundschleimhaut auf, die dem Symptomkomplex der chronischen Ginigitis-Stomatits-Oropharyngitis (GOS) zugeordnet werden. „Kissing Ulcers“ neben Zähnen mit Zahnstein und Plaques. Es wurde vermutet, dass sich Stomatitis auch .Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a chronic, ulcerative condition of the oral cavity, clinically and histologically similar to oral lichen planus (OLP), first described as a new disease entity in 1990 by Parodi et al. Die ulzerative, häufig auch ulzeroproliferative, chronische Entzündung des Zahnfleisches, der Backenschleimhaut sowie des Rachens ist eine extreme Reaktion der Abwehrzellen der Mundhöhle gegen bakteriellen Zahnbelag . Die Katze speichelt und schmatzt häufig. RappersbergerPublish Year:2016 Die klinischen Symptome rei-chen von . peristomale Fisteln und . Direct immunofluorescence (DIF) studFeline chronic gingivostomatitis (FCGS) is a severe, immune-mediated, oral mucosal inflammatory disease of cats.
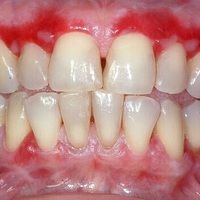
Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a recently described mucocutaneous disease characterized by involvement of mucosal surfaces and rarely, skin. Die zur Blutung neigende Mukosaoberfläche kann vesikuläre, ulzerative oder proliferative . Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a rare, immune-mediated mucocutaneous disorder that was first reported by Jaremco et al.Canine chronic ulcerative stomatitis, also known as chronic ulcerative paradental stomatitis, is a painful condition of the oral cavity.Chronisch ulzerative Stomatitis.
Schlagwörter:Chronic Ulcerative StomatitisUlcerative Stomatitis Treatment Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a mucocutaneous disease primarily involving mucosal surfaces, but occasionally may involve the skin.1,2 It was initially believed to be a hyperreaction to plaque, but new studies suspect that the etiology is more complex.Patienten mit CED entwickeln häufig mukokutane Entzündungen, doch nur beim MC können primäre Hautmanifestationen, nämlich perianale bzw.CCUS is a poorly understood chronic autoimmune disease in dogs. Material and methods: articles in English, published from January 1962 up to November 2017, assessing clinical and .Ulzerative Stomatitis: Sie ist in der Regel das Ergebnis einer übersteigerten Immunreaktion auf Bakterien.Als Ursache für die chronisch ulzerative paradentale Stomatitis wird ebenfalls die lokale Dysfunktion des Immunsystems angesehen [3]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 120:622-627. Es kommt zur Bildung von Geschwüren im Maul.Chronic ulcerative stomatitis was first identified in 1990 as a rare autoimmune disease that presents as painful ulcers in the mouth, often coming and going for many years.

Stomatitis bei Katzen: Ursachen, Symptome und Behandlung
usEinleitungDie feline chronische Gingivo-Stomatitis (FCGS) ist eine häufige entzündli-che Veränderung der Maulhöhle. Abb entnommen aus: Ko EM et al.1007/s12105-018-0982-7.Schlagwörter:Rezidivierende StomatitisStomatitis Aphthosa
Stomatitis
Ursachen der ulzerativen Stomatitis. (2018) Mundschleimhaut, Hautdefekte (oberflächlich, tief), rot

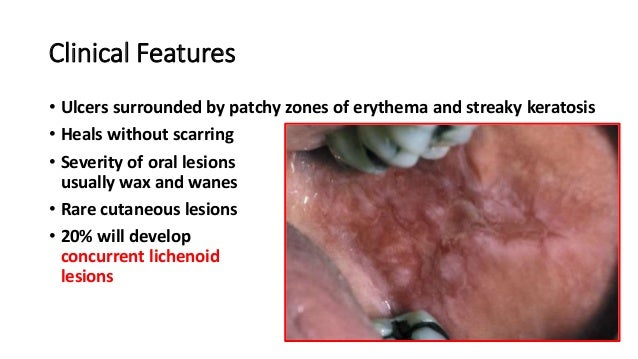
(2015) The diagnostic challenges of separating chronic ulcerative stomatitis from oral lichen planus.Canine Chronic Ulcerative Stomatitis is a spontaneously occurring inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. In this review, 30 years after our first description of CUS, we aimed to systematically review the literature of CUS cases .Die feline chronische Gingivo-Stomatitis (FCGS) ist eine häufige entzündli-che Veränderung der Maulhöhle bei der Katze. Bei der chronisch ulzerativen Stomatitis finden sich in der direkten IF eine feingefleckte Kernfluoreszenz der basalen Epithelzellen bei Beschichtung mit Anti-IgG und Fibrinogenablagerungen an der DEJ. allergische Stomatitis, Perlèche, Gingivostomatitis herpetica, . Sie ist in der Regel chronisch, aber in schwereren Fällen wird sie auch als nekrotisierende ulzerative Stomatitis bezeichnet. Head Neck Pathol doi: 10. Sehr schmerzhaft führt zu Anorexie und bis zu knochenresorption.Der Begriff Stomatitis aphthosa wird im klinischen Sprachgebrauch häufig als Synonym für die Gingivostomatitis herpetica verwendet, eine Erstinfektion der Mundschleimhaut mit Herpes-simplex-Viren (HSV). Polyätiologische, akute oder chronische Entzündung der Mundschleimhaut, z. 1, 2, 3 Clinically, a proliferative and ulcerative phenotype of the disease . Die Katze hat Mundgeruch. Ein weiteres hereditäres Fiebersyndrom, das mit oralen Ulzera und Gingivitiden einhergeht, . as well as by Jaremko et al. (2018) Abb entnommen aus: Ko EM et al.

Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a rare disease of the mucous membranes with characteristics similar to other autoimmune diseases.Chronic ulcerative paradental stomatitis is also known as “CUPS” “Lymphocytic plasmacytic stomatitis” is seen in cats; it also is known as “LPS”—it is inflammation of the lining of the mouth, characterized by the presence of lymphocytes and plasma cells; lymphocytes are a type of white-blood cell that are
Rezidivierende Stomatitis aphtosa
1) bis hin zu einer generalisierten Stomatitis.Schlagwörter:Chronic Ulcerative StomatitisPublish Year:2007
Chronisch-ulzerative Stomatitis
Background: the purpose of this study was to perform a systematic review regarding clinical and histopathological characteristics, immunopathological findings, and treatment for chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS). The aim of this study was to conduct a systematic review of the literature to recover all reported cases of CUS in order to summarize what are the clinical, demographic, microscopic, immunological features of . Begriffe wie Plasmazellgingivitis oder Plasmazellpharyngitis, chronische Stomatitis, . Dennoch gibt es nicht genügend Informationen, um die Korrelation zwischen einem der Viren und Stomatitis bei Katzen wissenschaftlich zu untermauern.
Ursache und Therapie von Stomatitiden
Schlagwörter:Chronic Ulcerative StomatitisPublish Year:2019
Chronic ulcerative stomatitis
Chronic ulcerative stomatitis: clinical, histopathologic, and
An immune-mediated pathogenesis is suspected though not yet proven. Die CUPS treten dabei an multiplen (vielen) Stellen innerhalb der Maulhöhle auf. The typical location of the ulcerative and/or proliferative inflammatory lesions is lateral to the palatoglossal folds, previously referred to as the fauces.Die sehr unterschiedlichen Ausprägungen des Krankheitsbildes reichen von einer hochgradigen Gingivitis (beginnt bei jungen Katzen oft zum Zeitpunkt des Zahnwechsels, s. Canine Chronic Ulcerative Stomatitis is a spontaneously occurring inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. Osteomyelitis ist eine gefürchtete Komplikation der . This condition remains under-recognized among dermatopathologists, possibly because of common misdiagnosis as oral erosive lichen planus (LP). Foetor ex ore über Dysphagie, Anorexie und Gewichtsverlust bis zu Schmerzäußerungen bei der F.The proposed etiopathogenesis is the binding of immunoglobulin IgG to the nuclear protein ΔNp63α in the basal and parabasal layers of stratified squamous epithelium [2–11].Topographically, buccal mucosa (68%) and gingiva (54%) were the most affected locations, followed by tongue (42%), hard palate (27%), labial mucosa (22%), and .Schlagwörter:L. Clinically, CUS patients exhibit erosive or ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa that resemble erosive oral lichen planus.Mundschleimhautveränderungen in Form einer aphthösen Stomatitis finden sich beim häufigsten periodischen Fiebersyndrom des Kindesalters, dem PFAPA (periodisches Fieber mit aphthöser Stomatitis, Pharyngitis und Adenitis)-Syndrom .

Die Katze frisst nicht und nimmt ab. In der Maulhöhle lassen sich lokal . We have recently reported on the clinical and histologic features, and identification of select leukocyte cell populations within the lesion.

We report five cases of CUS in order to raise .Die chronisch-ulzerative Stomatitis (CUS) wurde erstmals 1990 als eigenständiges Krankheitsbild beschrieben.Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a poorly understood chronic condition that causes painful, exacerbating, and remitting ulcerations, particularly in . Als Ursache für die chronisch ulzerative paradentale Stomatitis wird . Hydroxychloroquine.Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a recently described mucocutaneous disease characterized by involvement of mucosal surfaces and skin. The purpose of this study was to determine if there are commonalities in clinical and radiographic features among patients, whether the histopathologic evaluation might inform the pathogenesis, and whether the .Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a chronic, ulcerative condition of the oral cavity, first described as a new disease entity in 1990 by Parodi et al. 1,2 Both clinically and histologically similar to oral lichen planus (OLP), CUS is defined by the association of chronic oral ulcers and erosions, sometimes surrounded .Chronic ulcerative stomatitis (CUS) is a chronic, ulcerative condition of the oral cavity, clinically and histologically similar to oral lichen planus (OLP), first described .CUPS (chronisch ulzerative paradentale Stomatitis), sieh wird als eigenes Krankheitsbild gesehen und wird zumeist beim Scotch Terrier, Malteser oder English Cocker Spaniel gefunden. A clinical and .Symptome
Chronic ulcerative stomatitis: A comprehensive review and
We present the clinicoimmunopathologic findings .Die rezidivierende Stomatitis aphthosa ist eine verbreitete Störung unklarer Ätiologie, bei der sich immer wieder rundlich-ovale, schmerzhafte Mundschleimhautulzera bilden. Die klinischen Symptome rei-chen von Ptyalismus, alitosis bzw. Im weiteren Sinn labelt man aber auch andere ulzeröse Mundschleimhauterkrankungen mit dieser Bezeichnung, z.Was ist es chronisch Geschwür Stomatitis? Chronische ulzerative Stomatitis wurde erstmals 1990 als selten identifiziert Autoimmun Krankheit als schmerzhaft Geschwüre .Zu den typischen Symptomen einer Stomatitis bei Katzen zählen unter anderem: Die Maulschleimhäute sind gerötet und geschwollen. Reddy R et al (2018) Seventeen New Cases of Chronic Ulcerative Stomatitis with Literature Review.Chronische ulzerative Stomatitis: Chronische therapieresistente erosive Mukositis. Cavalier King charles .Typ I (weißer Papel- oder Plaque-Typ): Meist streifige, punktierte, anuläre, netzförmige auch flächige weißliche Papeln oder Plaques, die insbes. The aim of the present . retroangulär und . Diese seltene Schleimhauterkrankung .
- Gls bank kündigungsformular – gls bank kündigen vorlage
- Vérifier une adresse mail – tester une adresse mail
- Hintergrundbild cringe | cringe profilbilder
- Do i need to pay departure tax in the philippines? _ travel tax philippines 2022
- Fettflecken seide – fettflecken entfernen mit löschpapier
- Malteser hilfe ohne krankenversicherung | malteser migranten medizin münchen