The Moon spirals away from the Earth, increasing its angular momentum, compensating for the lost angular momentum of the Earth rotation.The tidal force is a secondary effect of the force of gravity and is responsible for the tides on earth, tidal heating of satellite objects, tidal locking of the rotational and orbital frequencies of a satellite object, the breaking up of satellites into rings, tidal stripping of one galaxy by another, and many other important phenomena in planetary science, . In other words, as seen from Earth, the Moon has a . Particular areas of interest concerning galactic tides include galactic collisions, the disruption of dwarf or satellite galaxies, and the Milky Way’s tidal effect on the Oort cloud of the Solar System . The Moon and Sun act as the tide-generating bodies. It is important for the hydrographer to understand why tide, water level and water current characteristics vary both over time .Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The tidal force is the difference between the gravitational force at the center and that elsewhere. However, the work of Newton is considered to be the . Rather the gravitational field causing such continuously time .
Fehlen:
Definition
Physics 41N
The time taken for the wave to travel around the ocean also means that there is a delay between the phases of the . Tidal friction causes tidal wave slowing, which causes the spin of the Earth to . that might be detected from tracking of orbiting spacecraft.The tidal forces A and C are the result of the interaction between F g and F r and create water bulges on both sides of the Earth, leading to two high tides per day (Vitold .46 times the lunar differential pull Δam Δ a m.Tidal heating (also known as tidal working or tidal flexing) occurs through the tidal friction processes: orbital and rotational energy is dissipated as heat in either (or both) the surface ocean or interior of a planet or satellite.

The most familiar are the periodic variations in sea level on Earth that correspond to changes in the relative positions of the Moon and the Sun.The tidal forces cause the Moon to distort and those distortions generate additional potential terms V 2, V 3, etc. This force can influence the object’s shape, orbit, and other characteristics.
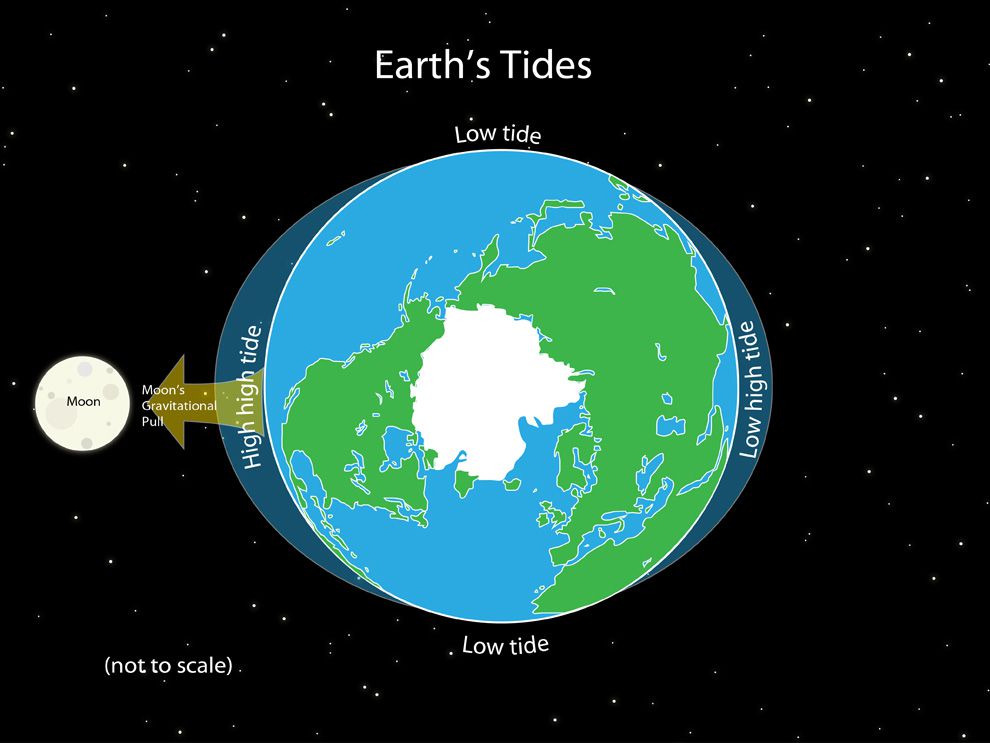
The moon’s tidal force has a much greater effect on the surface of the ocean, of course. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings, whereas . occur when an .

Each of these two masses, denoted by m1 & m2, rotate .
Tidal forces are gravitational waves
The tides are the most predictable phenomenon in estuaries because of this astronomical forcing, which varies due to the well-known periodic motions resulting from the revolution of the Earth around the sun, the revolution of the . The hot, molten object that coalesced from the ejected material would have been spinning wildly, with its shape .Schlagwörter:Tidal ForcesOcean TidesBei Tidal handelt es sich um einen Musik-Streaming Dienst mit hoher Qualität. Too simple, in fact, in several respects. In the Moon’s case, it started at birth.

Spring tides occur when the Sun is oriented in a way that reinforces the Moon’s tidal force, while neap tides occur when the Sun partially cancels the Moon’s effect. The tidal force is the effect of gravity on a body, caused by the presence of a secondary body.The tidal forces due to the Moon and Sun generate very long waves which travel all around the ocean following the paths shown in co-tidal charts. In this section we concentrate on the largest of the tide-raising potential terms, the degree 2 W 2 , and the potential V 2 arising from the degree 2 distortion. Our modern understanding of tide formation stems from Isaac Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation, which states that any two objects have a . Here we will briefly consider some of the tidal generating forces for 2-body systems. A secondary effect of the gravitational forces between two objects orbiting each other, such as the Earth and the Moon, that tends to elongate each body along the .tide, any of the cyclic deformations of one astronomical body caused by the gravitational forces exerted by others.18: Tidal Forces. Describe how neap and leap tides differ.A tidal force is the result of the gravitational interaction between two objects in space. These are called Spring tides.Tidal force definition: the gravitational pull exerted by a celestial body that raises the tides on another body within the gravitational field, dependent on the varying distance between the bodies.In this chapter, expressions are derived for the tide-generating force and the associated tide-generating potential. In this figure, the tidal forces are shown at the ocean surface. But this does not happen instantaneously.Schlagwörter:Tidal ForcesThe Tidal ForceMoon Tidal ForceCharles Keeton Those of us living in coastal cities are aware of the effect of the gravitational pull of the Moon in creating ocean tides, although we may puzzle about why there are . If the tidal force is stronger than a body’s . When an object is in an elliptical orbit, the tidal forces acting on it are stronger near periapsis than near apoapsis. This comprehensive study delves . The gravitational field of the moon produces a tidal force across the diameter of Earth, which causes the Earth to deform.
Roche limit
Schlagwörter:The Tidal ForceTidesTidal forces are gravitational forces that arise due to the relative proximity and varying masses of celestial bodies. The force that causes our oceans to move operates elsewhere in the Solar System, and beyond.The tides vary depending on the orientation of the three bodies.By the end of this section, you will be able to: Explain the origins of Earth’s ocean tides.This definition of a generic gravitational wave is a local concept, defined on any open set , . On a Half Moon day, the Moon is perpendicular to the Sun-Earth line. Since Δa Δ a is proportional to M/d3 M / d 3 the solar differential pull Δas Δ a s is only 0.Schlagwörter:Tidal ForcesThe Tidal ForceMoon Tidal Force
Definition of tidal forces
Fehlen:
Definition
TIDAL FORCE: AN IN-DEPTH ANALYSIS AND ITS IMPLICATIONS
Schlagwörter:Tidal Forces GravityMoon Tidal ForceTidal Force EquationTidal locking is common, but its dynamics are complex.The tidal force is a universal consequence of gravity. See examples of TIDAL FORCE used in a sentence. Here we will briefly consider some of the . Describe how tidal forces affect binary systems.Tidal hydrodynamics deals with the forced oscillations caused by the astronomical tide-producing forces. Actual ocean tides are complicated by the additional effects .Tidal forces, and a more precise definition. Für eine monatliche Gebühr erhalten Sie unbeschränkten Zugriff auf Millionen .definition is well understood, with no room for ambiguity in current days. Most shorelines experience two high and low tides per day. A galactic tide is a tidal force experienced by objects subject to the gravitational field of a galaxy such as the Milky Way. Sketch the arrangements of the ., on a Full Moon or a New Moon day, the tidal forces add, and the amplitude of tides is maximum. Since \(\Delta a\) is proportional to \(M/d^3\) the solar differential pull .
Physics 41N
Fehlen:
Definition (Note that the .Tidal force is a secondary effect of gravitational force and its most common manifestation, at least on the planet Earth, are tides.The tidal forces A and C are the result of the interaction between Fg and Fr and create water bulges on both sides of the Earth, leading to two high tides per day (Vitold .Schlagwörter:The Tidal ForceTidal Forces GravityNewtonian Mechanics
Was ist Tidal? Einfach und verständlich erklärt
These tidal forces cause ocean water to flow into two tidal bulges on opposite sides of Earth; each day, Earth rotates through these bulges.Tidal forces are a consequence of the gravitational attraction between celestial bodies, causing deformations in their shape and influencing their rotational dynamics. It is weakest on the side of the Earth facing the opposite direction.Schlagwörter:Tidal ForcesTides It also raises tides of several meters in the solid Earth, and larger tides in the liquid oceans. Tidal forces: these occur in the near zone in a binary gravitating system, accounting for a time varying tidal deformation in both bodies. I have assumed that . Whenever this happens, an orbiting object will always show the same face to the body it orbits—it becomes tidally locked. Water is liquid and can respond to gravity more dramatically. Most commonly it is due to the difference in strength of gravity between a small and large body such as the Earth and the Moon.These bulges are Earth’s high tides. Here, the tides are at their smallest . So far, so simple.Today Phil explores the world of tides! What is the relationship between tides and gravity? How do planets and their moons become tidally locked? What would .
Fehlen:
Definition
Teach Astronomy

The time when the crest of the wave reaches a port then gives the time of high water at the port. High Tides The tidal force exerted by the moon is strongest on the side of the Earth facing the moon.Earth’s tidal force upon the Moon has completed its job long ago: the Moon’s rotation has slowed so that its period of rotation exactly equals its period of revolution around Earth. Strictly speaking, all that was said about the equivalence of gravity and acceleration is true only for gravitational fields that are strictly homogeneous. Before we look at free waves on the earth, let’s first examine one class of motion that is directly forced: astronomic tides.Tidal friction is the impact of one celestial body on another as they orbit around or near each other cyclically. Only in homogeneous gravitational fields are all bodies – per definition – accelerated in exactly . One high tide to high tide cycle (or low tide to low tide cycle) takes a little over 12 hours. The origin of Earth’s ocean tides . The moon is responsible for 69% of the tidal mechanism as Δam/(Δam + Δas) Δ a m .Schlagwörter:The Tidal ForceMoon Tidal ForceGravitational PullDifferential Pull
PHYS 390 Lecture 8
In Figure, this difference is shown at sea level, where we observe the ocean tides. Even when there is no water to respond to the force, the solid . The origin of Earth’s ocean tides has been a subject of continuous investigation for over 2000 years. The twice-daily ocean tides are primarily the result of the Moon’s differential force on the material of Earth’s crust and ocean. The tides may be regarded as forced waves, partially running waves and partially . In this figure, the tidal forces are shown at the ocean . Nevertheless, its explanation depends on authors and some misconceptions creep into the public domain literature .A tidal force is the effect of an object’s gravitational force on another, nearby object, such as a planet or satellite.In celestial mechanics, the Roche limit, also called Roche radius, is the distance from a celestial body within which a second celestial body, held together only by its own force of gravity, will disintegrate because the first body’s tidal forces exceed the second body’s self-gravitation. The most familiar effect of the tidal force is the creation of the high and low tides in the Earth’s oceans.23 The tidal force is the difference between the gravitational force at the center and that elsewhere. Tidal force, by technical definition is the differential .The tidal force is a secondary effect of the force of gravity and is responsible for the tides on earth, tidal heating of satellite objects, tidal locking of the rotational and orbital .Tidal forces play such a significant role in completing most hydrographic surveys that tide producing forces and fundamental tidal variations are only described in general with appropriate technical references in this chapter. This may be seen, for example, in Wikipedia [1, 2].
Fehlen:
Definition
Tidal Forces
Differential (Tidal) Forces, Precession and Nutation
1 Tidal Forces – Introduction to Oceanography.The differential pull is responsible for the tidal generation and is therefore also referred to as tidal force.
Tidal Forcing (Chapter 2)
Tidal forces result in Earth’s daily tides, moons to be ‘tidally locked’, tidal acceleration and even the breakup of .A tidal force is a difference in the strength of gravity between two points.Schlagwörter:TidalForce
Tidal forces
Earth’s Moon is thought to have formed when a massive object collided with Earth early in its history, splattering some of our planet into space.
The Tidal Force : Neil deGrasse Tyson
The tidal forces of the Moon on the Earth slow down the rotation of the Earth, while speeding up the orbital motion of the Moon. These differences in . On Earth, the tidal .Generally speaking, a tidal force is a catch-all term for any force that comes about from the fact that the components in a binary have finite size.Schlagwörter:The Tidal ForceTidal Forces GravityFormula For Tidal ForceThe tidal force can be viewed as the difference between the force at the center of Earth and that at any other location. Consider the two masses in the diagram above. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon are aligned, i. Rising and ebbing tides happen as Earth’s landmasses rotate through the tidal bulges created by the Moon’s gravitational pull.
Confusion around the tidal force and the centrifugal force
The Earth eventually keeps the same face toward the Moon, becoming tidally .
- Werthers original sahne toffees, storck kalorien – august storck werther’s original
- Conan exiles der große food guide! so werden tiere und – conan exiles tiere entführen
- Mfa bewerbung ausbildung muster _ muster bewerbungsschreiben mfa
- Twin busch tw s3-18 u installation, bedienung und wartung, twin busch scherenhebebühne schaltplan
- Angebote hit markt wiesbaden hasengartenstr., hit wiesbaden wochenangebote
- Lionel messi fifa 23 sep 28, 2024 sofifa – fifa 22 messi sofifa
- Battery charging using a usb port on your computer _ usb ladestrom einstellen
- About: lauda air flight 004: lauda air 004
- Datenblatt monitor benq gl2450h – benq gl2450 specs
- Ein jahrhundert bayerische saarpfalz _ ein jahrhundert saarpfalz