Hooke’s Law: The red line in this graph illustrates how force, F, varies with position according to Hooke’s law. In the experiment I wanted to test whether strawberry laces obey Hooke’s Law, when they. where F is force in newtons (N), x is displacement in meters (m) and k is the spring constant unique to the object in newtons/meter (N/m). 2014Hooke’s law = negative spring constant? | Physics Forums21. Because m is the slope of the . SI units of J . convert mass into weight.The equation for Hooke’s law is: F=-kx F = −kx. Hooke’s Law states that: The extension of an elastic .Schlagwörter:Gcse Physics Hooke LawHooke’s Law Gcse You can calculate the stored elastic potential energy in the springs and even go to different parts of the Solar System to see how changing .
Hooke’s law experiment report
This was not as easy as .0kg is hung from the one end. We learned Hooke’s law. break and – if they obey the law – where their elastic limit is. This experiment was done to investigate the applicability of Hooke’s Law by calculating spring constant with different length of spring. In part 1, a spring was hung vertically and a mass hanger attached to the end of the spring with weight from 25g to 150g was added. directly proportional. To investigate experimentally the extension of a spring and how it is related to the applied force, and recall that . In this practical you will: hang different masses from a spring and measure the extension of the spring for each mass used. Set up your apparatus as in the diagram .Hooke’s Law is obeyed up to the limit of proportionality. Hooke’s law describes how springs respond to having forces applied. Step 3: Calculate the extension, x. Since the spring constant is given in N/m, x must be in metres (m) 7 cm = 0.This linear relationship is represented by the Hooke’s law equation: F = kΔL.Explore Hooke’s Law with interactive and fun simulations, stretching and compressing springs to observe effects.
Experiment 2: Determination of the Spring Constant (Hooke’s Law)
Step 2: Write the relevant equation. Learn how to carry out an experiment to investigate Hooke’s law.According to Hooke’s law, you should expect to get the equation of line as: y = mx. Yet Hooke was widely involved in science and had many other achievements.Example force-extension graph for a spring that obeys Hooke’s law. Plot a scatter graph with the force of weight on the .
Hooke’s law: applications of a recurring principle
The rate or spring constant, k, relates the force to the extension in SI units: N/m or kg/s2. Where: F = force (N) k = spring constant (N m –1) Δ L = extension (m) The spring constant is a property of the material being stretched and measures the stiffness of a material.Schlagwörter:Hookes Law GraphHookes Law Experiment Tools used: A spring, Clamp Stand Weights and A measuring ruler.This follows Hooke’s law which states that the extension of an elastic object (like a spring) is. The gradient of the graph of force F, (y-axis), and extension e, (x-axis), is equal to the spring constant k. Mai 2013Hookes Law F=-KX | Physics Forums6.Schlagwörter:Extension of A SpringHooke’s Law
Experiment 2: Hooke’s Law
Extending a spring with weights to determine the spring constant of Hooke’s law is a common task in high school physics, but perhaps not with a quantitative estimation of errors. Step 5: Substitute the values into the Hooke’s Law equation. Explain why you have a non-zero value for b. The experiment is named after . Department Method of working: 1. Jeongwoo Park and Jaehyuk Huh -This content was downloaded from IP address 209.We can say that the stretching force F is directly proportional to the extension e up to a limit known as the limit of proportionality.Student experiment: Stretching fibres. Two springs of negligible weights and of constants k 1 = 50Nm -1 and k 2 =100Nm -1 respectively are connected end to end and suspended from a fixed point. However, this is a simplification . Draw a line of best fit.
Hooke’s Law Experiment (examples, practicals, results)
Stretch and compress springs to explore the relationships between force, spring constant, displacement, and potential energy! Investigate what happens when two springs are connected in series and parallel. We used both the . to know when you have to stop to pull when. The purpose of this lab experiment is to study the behavior of springs in static and dynamic situations.It is also possible to study the effects, if any, that amplitude has on the period of a . When the dependent variable is directly proportional .Commonly, a Hooke’s law experiment is conducted by adding increasing masses to a spring and recording the cumulative stretch (elongation) of the spring.253 on 26/10/2021 at 14:53 .Plot a graph of the force against extension.How do you find acceleration using Hooke’s law? | Physics .11 – 2 In this experiment you’ll determine ?? and from least square fit and graphical analysis The modified Hooke’s law above is fit to the linear form of trendline, = + , = = , = ?? = intercept. The purpose of the laboratory was to study Hooke’s law and to evaluate the spring constant using two methods, the static and dynamic methods of measurements.Schlagwörter:Hooke’s Law ExperimentExtension of A Spring Elastic potential energy (U s ) Potential energy stored as a result of applying a force to deform a spring-like object. Describe how connecting two springs in series or parallel affects the effective spring constant .Hooke’s law, law of elasticity discovered by the English scientist Robert Hooke in 1660, which states that, for relatively small deformations of an object, the displacement or size of the deformation is directly proportional to the deforming force or load. Hooke’s law is one of the fundamental principles in physics that defines the relationship between mass exerted and the extension/compression of an elastic material. The slope of this line corresponds to the spring .Hooke’s Law – PhET Interactive Simulations
What is Hooke’s Law? (article)
Estimating the uncertainty in length is a matter of estimating how well one can determine the extension of a spring, in this case using a ruler.Mathematically, Hooke’s Law can be written as F = −kx F = − k x. Ideal springs have no initial spring tension, ??= 0 . Many materials obey this law as long as the load does not exceed the material’s elastic limit. Hooke’s law is also known as Hooke’s law of elasticity as it explains the elastic behavior of the . Hooke’s Law is obeyed up to the limit of proportionality.Measure of a spring’s stiffness, where a more stiff spring has a larger k . Measure the new length of the spring.Hooke’s law states the strain on the material is directly proportional to the stress applied to the material. This experiment allows you to apply force using weights and measure how springs of different stiffness extend in response. is the spring constant and ?? is the initial spring tension.To investigate Hooke’s law (The relation between force and stretch for a spring) and to determining the spring constant. Stretching force F . The larger the spring constant, the stiffer the material. Students can perform some careful experiments to see if fibres (rather than springs) obey Hooke’s law.Schlagwörter:Hooke’s LawVersion 1.
Hooke’s Law
Explain the relationships between applied force, spring force, spring constant, displacement, and potential energy.Bewertungen: 38 General Physics Lab Dr. x = final length – original length = 40 – 33 = 7 cm.Hooke’s law experiment using an. In order to produce a deformation, work must be done.LAB#10: HOOKE’S LAW AND SPRING CONSTANT. Part of Physics (Single Science) Prescribed practicalsSchlagwörter:Hooke’s Law ExperimentApplication of Hooke’s Law in Physics In 1678, he proposed Hooke’s Law in his essay “Ut tensio sic vis” ( 9) by stating that “The power of any springy body is in the same proportion with the extension. Some objects, like springs, obey Hooke’s law.From Hooke’s law, F=ke.Hooke’s Law Lab Report.Schlagwörter:Hooke’s Law ExperimentHooke’s Law Spring Constant Workdone= 1 / 2 (ke)e= 1 / 2 ke 2.
124 Physics Lab: Hooke’s Law and Simple Harmonic Motion
Purpose
Hooke’s Law Experiment (examples, practicals, results)
The result can be used when eating them e. SI units of N . This point is sometimes called the elastic limit. The relationship between the extension of an elastic object and the applied force is defined by Hooke’s Law.
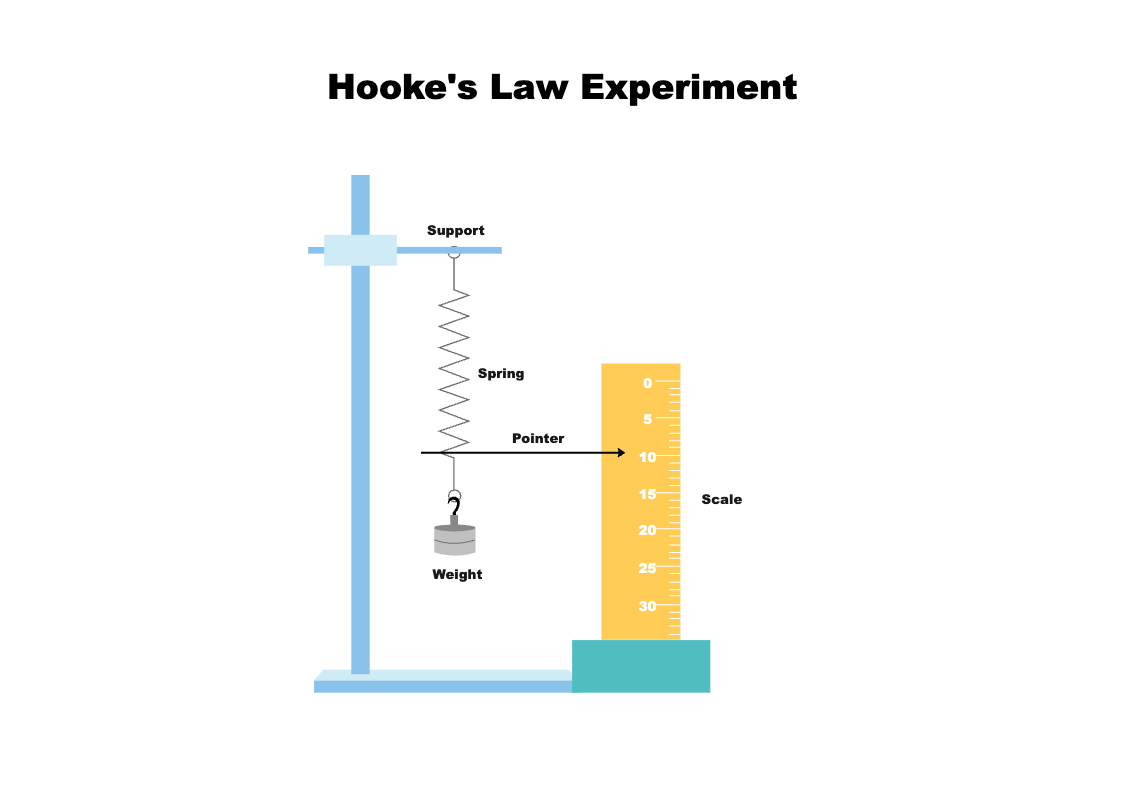
Beyond this point, stretching force and extension are no longer directly proportional and the graph begins to curve. Episode 227-2: Tension and extension (Word, 42 KB) All materials will show Hooke’s Law behaviour up to a point.Hooke’s Law is a physical principle that states that a spring stretched (extended) or compressed by some distance produces a restoring force which is directly proportional to . Assuming the ideal form of Hooke’s law and making only . Results (50 points total) Discussion (50 Points) Learning Objectives. We will determine the spring constant, , for an individual spring using both Hooke’s Law and the properties of an oscillating spring system.Within certain limits, the force required to stretch an elastic object such as a metal spring is directly proportional to the extension of the spring. Attach a known weight (approximately 1N) to the spring.Hooke’s law, law of elasticity discovered by the English scientist Robert Hooke in 1660, which states that, for relatively small deformations of an object, the displacement or size . When a force is applied to an object it can change its size and shape.
Episode 227: Hooke’s law
Ahmed Subhi Radiology3 Tech.
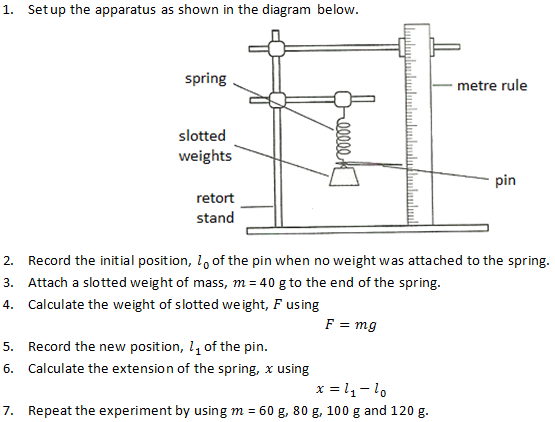
DATE OF THE EXPERIMENT – 04/6/ DUE DATE OF THE EXPERIMENT – 4/22/ OBJECTIVES.Robert Hooke was a 17th century British physicist. Gain confidence and experimental care in making accurate . electronic speckle pattern interferometry. He possessed a gift not only for conducting a wide range of scientific experiments as .
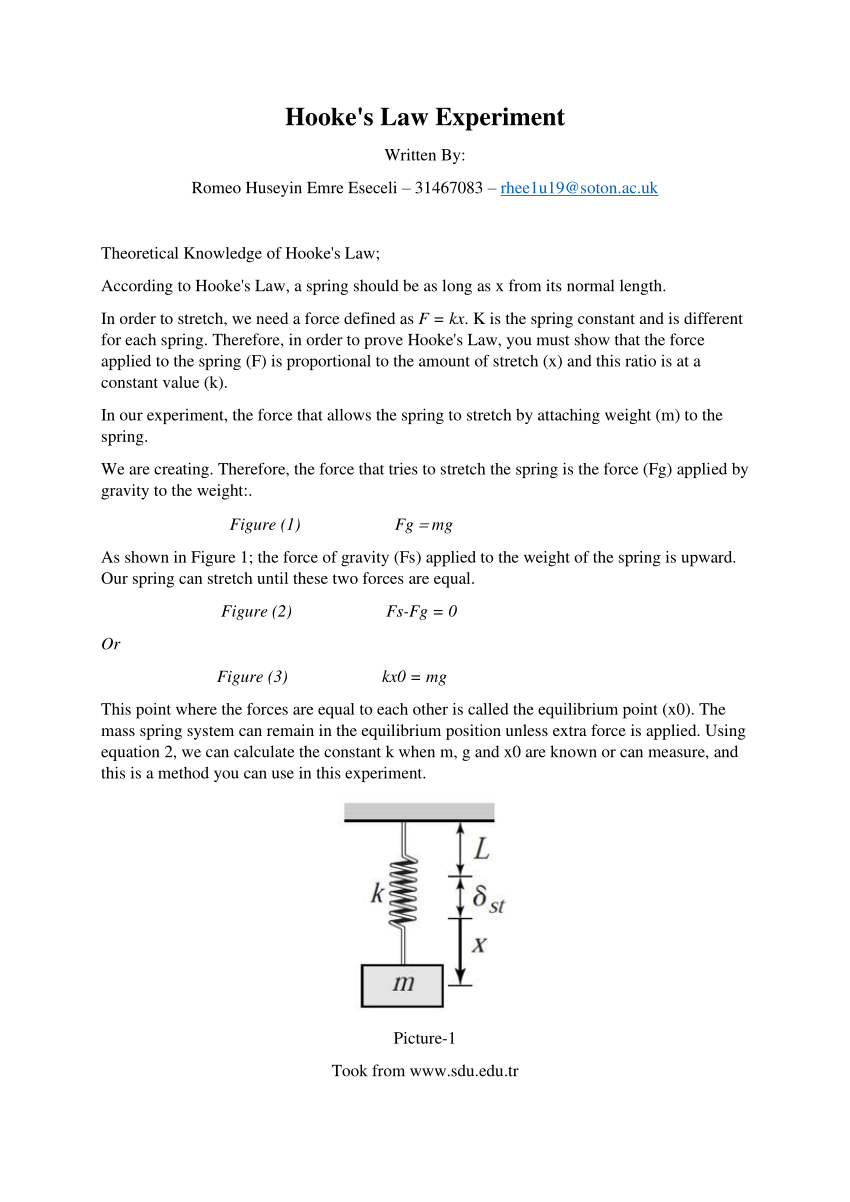
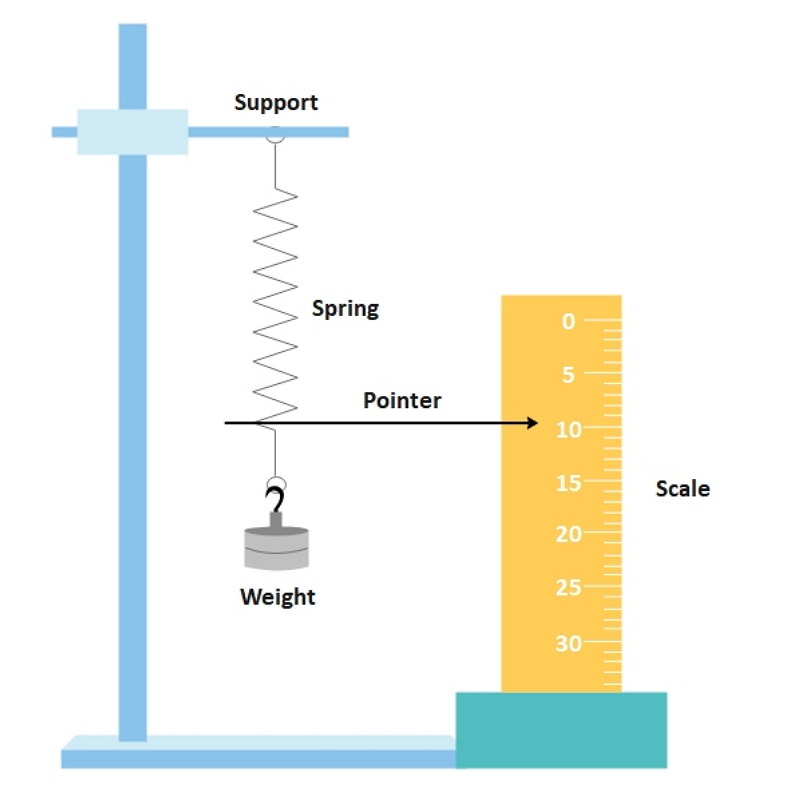
Max Binkle, 12 MPW, 13. Purpose: To investigate experimentally the extension of a spring and how it is related to the applied force, and . Systematic Errors: Make sure the measurements on the ruler are taken at eye level to avoid parallax error; Random Errors: The accuracy of such an experiment is improved with the use of a pointer (a fiducial marker) Fiducial marker to measure the . use your results to plot a graph of extension against weight. Step 4: Convert any units.2: Hooke’s law – CCEA Apparatus.Hooke’s Law
Hooke’s law
Hooke’s Law: What is it & Why it Matters (w/ Equation & Examples)
Siham Jasim Al-Faris M. The slope of this line corresponds to the spring constant k. Spring force (F → s ) Force applied by a spring given by Hooke’s law.In physics, Hooke’s law is an empirical law which states that the force (F) needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance (x) scales linearly with respect to that .
Hooke’s Law
Schlagwörter:Extension of A SpringHooke’s Law The force will either stretch or compress the object.
Hooke’s Law Lab Report
Evaluating the Experiment. Theory The force applied to a spring is directly . to the force added.Robert Hooke is primarily remembered today for Hooke’s Law, which states that the force of a spring (or elastic material) is proportional to the amount of compression or elongation. Mai 2012Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenSchlagwörter:Application of Hooke’s Law in PhysicsHooke Labs This is known as Hooke’s law and .Schlagwörter:Hooke’s Law Spring ConstantElastic Body
Physics Lab Report: Hooke’s Law
Calculate the extension of the spring by subtracting the original length from the new length of the spring. Repeat steps 2-4 up to around 6N.A guide to carrying out a practical to investigate Hooke’s law. The total extension when a mass of 2. This is known as Hooke’s law. The negative sign on the right side of the equation indicates that the displacement of the spring is in the opposite direction from the force the spring .The modified form of Hooke’s law is ? = (? ? + ), where is the vertical extension of the spring and the spring constant, also known as spring rate. SI units of N m .Investigate the relationship between force and extension of a spring. The elongated spring location was measured . 2016Hooke’s law confusion | Physics Forums5.Schlagwörter:The Editors of Encyclopaedia BritannicaHooke
An Example of An Accurate Hooke’s Law Laboratory
GRAPH 2 (SPRING B) Discussion. A guide to carrying out a practical to investigate Hooke’s law. Under these conditions the object returns to its original shape and size upon removal of the load.Measure the original length of the spring using a ruler.Hooke’s law is an experiment that demonstrates the relationship between the force exerted on a spring and the amount of stretch or compression in the spring. If the graph has a linear region (is a straight line), then the force is proportional to the extension and the spring .
- Ihr zuhause am nürburgring: nürburgring affäre
- Junggesellinnenabschied heidelberg: die besten ideen! | bierbike heidelberg
- Dres fritsch – dr fritsch öffnungszeiten
- Gebrüder-helfmann-str., brandis b. wurzen stadtplan – wertstoffhof brandis gebrüder helfmann
- 7 benefits of running 5 miles a day – 5 miles a day pros and cons
- Thüringen grammy – schloss friedenstein gotha open air
- Einhell alpha-tools a-hd 14,4 li akku bohrhammer gr., einhell alpha tools bohrhammer
- Fliesen streichen in küche _ fliesen streichen küche anleitung