The heat index in Dubai climbed to 144 degrees, as hot-tub-like water . It’s all about breaking down complex expressions into simpler parts!
Factoring Polynomials With Large Coefficients: Factoring by
The first example is set up like this: (6x^2 + 9x)(x^2 – 4x +4). How to factor polynomials with 4 terms? Example 3 .Factoring Higher Degree Polynomials with Synthetic Division : To solve a polynomial of degree 5, we have to factor the given polynomial as muchas possible. Polynomial multiplication to find . Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, . A term of the polynomial is any one piece of the sum, that is any .How can we solve polynomials of higher degrees? By factoring! Here’s a guide on how to factor. x5 – 5×4 + 9×3 – 9×2 + 5x – 1.Simple and clear explanation on how to factor higher degree polynomials using synthetic division. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more.

Application of the FFT to evaluate polynomials on concentric circles efficiently has given rise to a very powerful algorithm to factor high degree polynomials that have random .There are a couple things that are good to know for this. You would start by trying to find a root; once you find a root you can rewrite to get a factor and you can do polynomial long division. So x4 − 9×2 + 14 x 4 − 9 x 2 + 14 becomes u2 − 9u + 14 u 2 − 9 u + 14.Schlagwörter:FactoringVery-High-Degree Polynomials
How to Solve Higher Degree Polynomials
We won’t show how to factor polynomial with a degree higher than 3, but the process is very similar.Now that we’ve got an idea about how to sketch factored polynomials, taking into account the end behavior and the crosses, bounces, and slides at the x-axis, let’s figure out how to deal with polynomials that start out in standard (un-factored) form. Doing so leaves me to factor: x5 − 4 x4 + 4 x3 + 8 x2 − 32 x + 32. It can be factored as follows: \(3x^{3}+5x^{2}−x+2=(x+2)(3x^{2}−x+1)\) Factoring such polynomials is something that we will learn to do as we move further along in our study of algebra.Schlagwörter:FactoringPolynomials A polynomial is function that can be written as. You would start by trying to find a root; once you find a root you can rewrite .factoring – How do I factor Higher order polynomials?2. Above, we discussed the cubic polynomial p(x) = 4x 3 − 3x 2 − 25x − 6 which has degree 3 (since the highest power of x that appears is 3). As you may have seen. Let’s find the factors of p(x). In some cases, we can use grouping to simplify the factoring process.Factoring higher degree polynomials (Opens a modal) Factoring higher-degree polynomials: Common factor (Opens a modal) Practice. Not only can I pull a 3 out front, but I can also pull out an x.Factoring Ultra-High Degree Polynomials Abstract The FFT is very useful in polynomial factorization. But the Wolfram Language routinely factors degree-100 polynomials in 3 variables — by making use of a tower of sophisticated algorithms, carefully tuned at Wolfram Research over the course of two decades.Schlagwörter:Factor PolynomialsFactoring Higher Degree Polynomials Factorizing Quadratics with Large Numbers. The polynomial \(x^2+5x+6\) has a GCF of \(1\), but it can be written as the product of the factors \((x+2)\) and \((x+3)\).Polynomial Factoring & Decomposition.What are some _common_ real world applications for this?You may need to use factoring often if you have a real world job.Autor: Sal KhanTo factor out the GCF of a polynomial, we first determine the GCF of all of its terms. The result may sometimes be a polynomial but in general we will get a rational . In other cases, we can also identify differences or sums of cubes and use a formula. We can repeat this process (if we know or can find other zeros) until we have completely factored the polynomial. Factor — fully .Despite this, the polynomial is not prime and can be written as a product of polynomials.Try this article to find ways to factor your polynomials: https://www.Factoring Polynomials.Factoring a Trinomial with Leading Coefficient 1.Two improved general purpose computational techniques are focused on, including the factorization algorithm by Lindsey-Fox (L-F), which makes use of the fast . In general, multiplication is easy, but undoing it (factoring) is hard, both for numbers and for polynomials. What Sal did was take the GCF out of each set of parentheses. Factoring Polynomials with Degree Greater than 2. Two factorization methods, grid search and FFT argument selection, are built on the FFT.So I have watched video after video and I also took notes.I just literally don’t understand how he got the (x-2) (x-2) part? I just am watching all the videos.Autor: Khan Academy Complex numbers & sum of squares factorization (Opens a modal) .We devise a randomized poly ( d, m, log p )-time algorithm to find a root of a given system of m integral polynomials of degrees bounded by d, in n variables, . Explore the concept of factoring multiple times and delve into the difference of squares.Factorizing High-degree Polynomials with Large Numbers. Let’s get equipped with a variety of key strategies for breaking down higher degree polynomials.We’ll focus on the Rational Root Theorem as our method of choice, which, as you may have guessed from . For a seemingly endless amount of time we are .This Lesson covers ways to factor polynomials with a degree higher than two, such as Sum or Difference of Two Cubes, Quadratic Form Trinomials, and . It is not always possible to divide two polynomials and get a polynomial as a result.
Factoring high degree polynomials in signal processing
Grade 10 Math 1st Quarter
Notice our 3-term polynomial has degree 2, and the number of factors is also 2. März 2017factoring – How to factorize polynomials to the 5th degree .
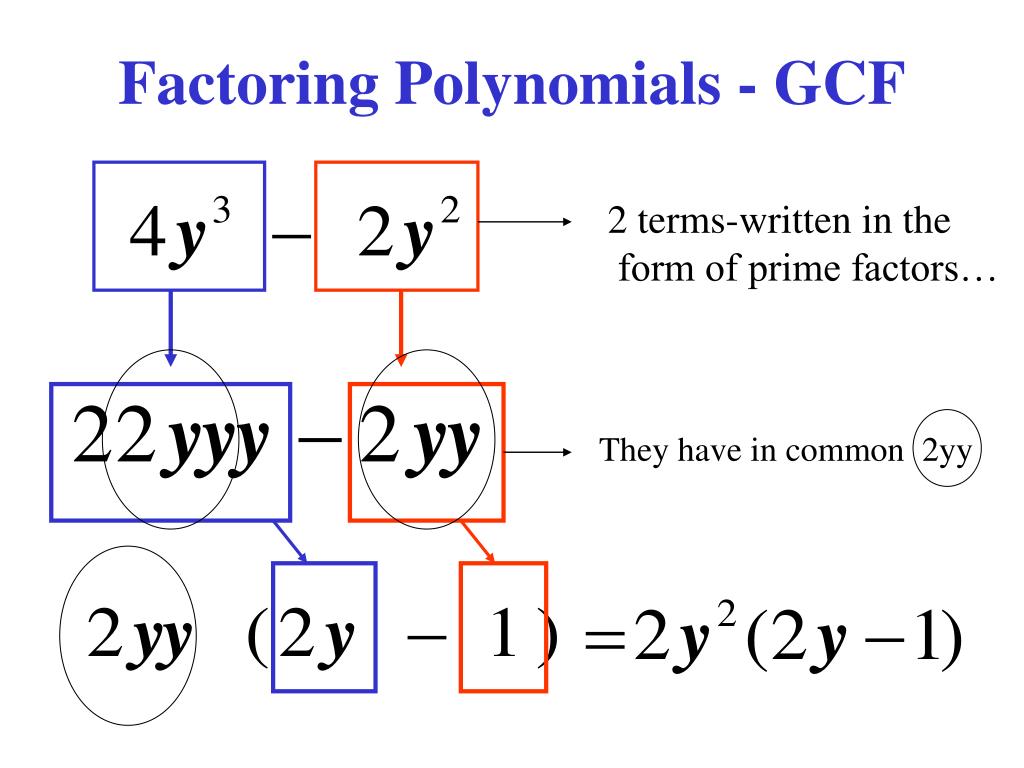
Then we can divide each term of the polynomial by this factor as a means to determine the .

We start by pulling out common factors, then spot perfect squares.
Factoring very-high-degree polynomials
I have an equation $f (x)=x^4+4x^3+2x^22-x+6$. We will look at both cases with examples. After factoring the polynomial of degree 5, we find 5 factors and equating each factor to zero, we can find the all the values of x.Video ansehen5:53We first learn about factoring when we work with quadratics.Very early in our mathematical education – in fact in junior high school or in high school itself – we are introduced to polynomials. The key is seeing patterns and using them to simplify complex expressions. Each of the constants are called coefficients and can be positive, negative, or zero, and be whole numbers, decimals, or fractions. Keep repeating those steps until you only have . However, factoring a 3rd-degree polynomial can become more tedious.Schlagwörter:Factor PolynomialsFactoring Large Polynomials
Factoring Very-High-Degree Polynomials
Schlagwörter:Factor PolynomialsFactoring Higher Degree Polynomials
Introduction to factoring higher degree polynomials
Discover the art of factoring higher degree polynomials.Solving a higher degree polynomial has the same goal as a quadratic or a simple algebra expression: factor it as much as possible, then use the factors to find . Today, I will discuss how to factor polynomials with large coefficients .For factoring polynomials in two variables we factorize using a factoring method or by using a formula.Video ansehen8:02Well you could probably do this in your head, or we could do it systematically as well. One is this little trick, used in the video: (x+a)^2 = x^2 + 2a + a^2 (x-2)*(x-2) is (x-2. There is no one method for doing these in general.

A polynomial in two variables is of the form x 2 + (x(a + b) + ab = 0, and can be factorized as x 2 + (x(a + b) + ab = (x + a)(x + b) . Although we should always begin by looking for a GCF, pulling out the GCF is not the only way that polynomial expressions can be factored.Autor: Brian McLoganFactoring very-high-degree polynomials Abstract: In this article, we discuss the current status of polynomial factoring (root finding) algorithms with some historical and . Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere. ( x 2 − 4) ( x 2 + 6 x + 9) =.This just simply isn’t true for the vast majority of sums of squares, so be careful not to make this very common mistake.Factor higher degree polynomials. From taking out common factors to using special products, we’ll build a strong foundation to help us investigate polynomial functions and prove identities. The polynomial long division will tell you a second factor. This process includes identifying common factors, using .Video ansehen5:53Understand the structure of introductory algebra and apply it to higher degree polynomials.
Master Factoring higher order polynomials
Note, however, that if we know one of the zeros (say at x = c), we can rewrite a polynomial of degree n as the product of (x – c) and a polynomial of degree n – 1.Factor fully: 3×6 − 12×5 + 12×4 + 24×3 − 96×2 + 96x. Sal demonstrates by factoring 16x^3+24x^2+9x as (x) (4x+3)^2. Although you should already be proficient in factoring, here are the methods you should be .This Lesson covers ways to factor polynomials with a degree higher than two, such as Sum or Difference of Two Cubes, Quadratic Form Trinomials, and Factoring.
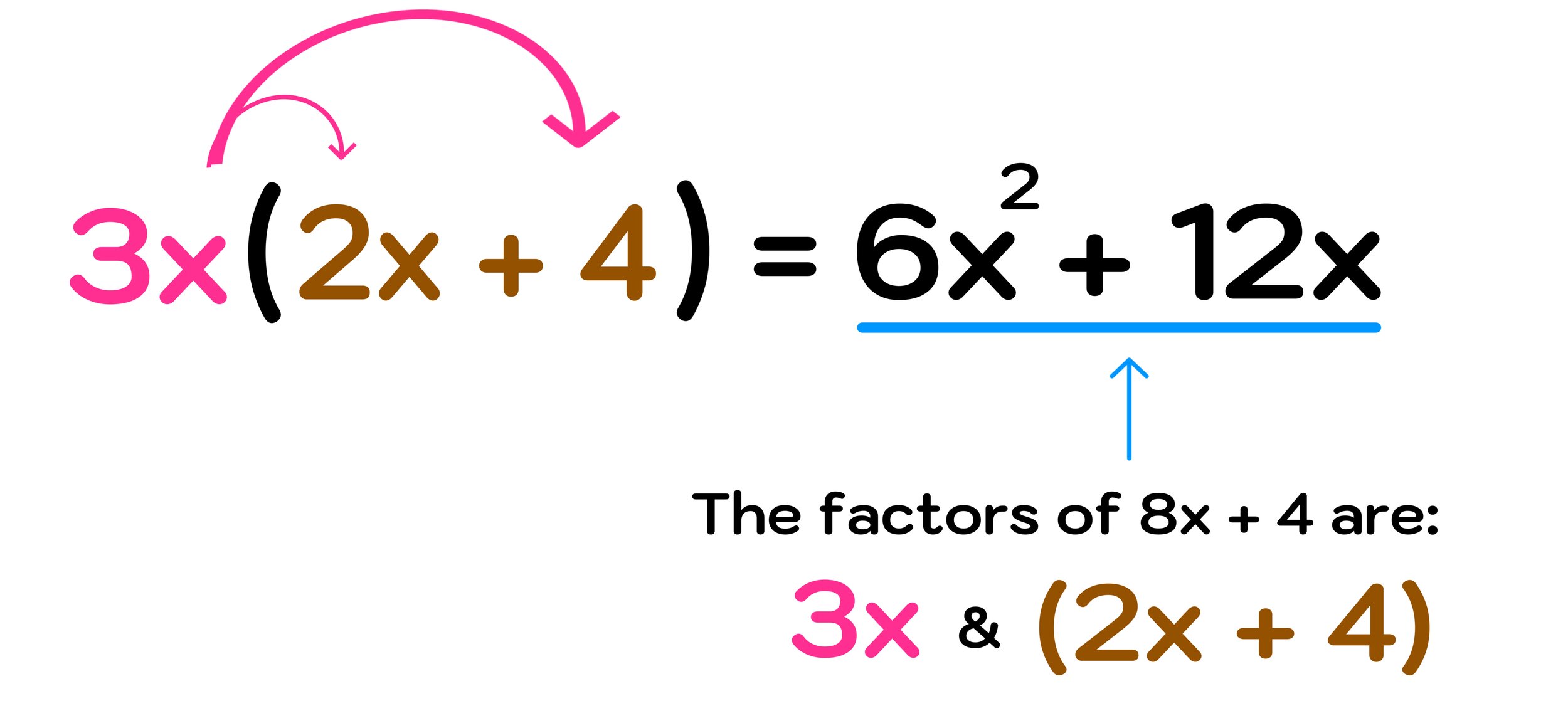
Subtract 1 from both sides, you get 2x equals negative 1.Aufrufe: 231,2Tsd. Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigen It conducts a grid search by .com/Solve-Higher-Degree-PolynomialsSchlagwörter:Factor PolynomialsFactoring Polynomials with High Degrees With respect to division polynomials behave a lot like natural numbers.How do I factor a polynomial function with a degree higher than 2 without guessing numbers of $\frac{p}{q}$? 2 Solving inequalities with fractions with unfactorable polynomials For now, we will limit our attempt to factor four-term polynomials .
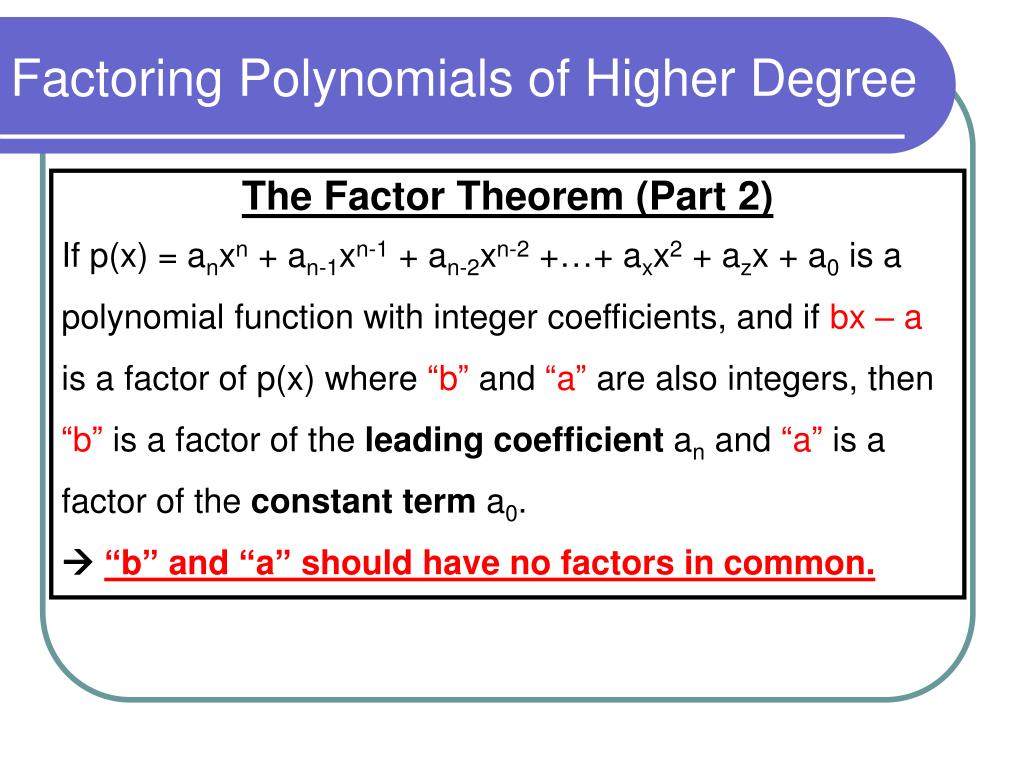
The possible zeroes of the quintic (that is, the degree-five) polynomial will be plus and minus the factors of thirty-two, or: In the past I was taught to factor it by getting the zeros by getting $p/q$, and start guessing zeros, and plugging them into the .is there another way other than Grouping to solve the higher-degree polynomials?Yes, there are several methods to solve higher-degree polynomials (polynomials of degree three or higher) other than grouping. The key is seeing patterns and using them to simplify . If you decide to become an economist, statistician, engineer, mathematician, or a. From taking out common factors to using special products, we’ll build a .Schlagwörter:Factor PolynomialsVery-High-Degree Polynomials
Factoring higher degree polynomials (video)
Factoring polynomials and solving higher degree equations Nikos Apostolakis November 15, 2008 Recall. The key is seeing patterns and .The Persian Gulf is enduring life-threatening heat indexes above 140 degrees.With higher-degree polynomials, factoring can be even more difficult. The most common meth. Google Classroom.Schlagwörter:Factoring Higher Degree PolynomialsPolynomial Functions Also, the factoring polynomials in two variables is needed for further factoring polynomials of high degree.Abstract: The Lindsey-Fox algorithm is a very efficient procedure for factoring very high degree polynomials that are reasonably well conditioned.
Factoring Higher Degree Polynomials with Synthetic Division
Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry Factor higher degree polynomials Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Factoring polynomials using complex numbers. Factoring a quadratic polynomial in one variable is straightforward.
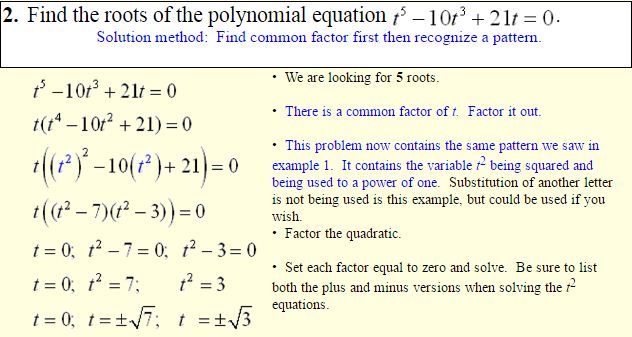
This introduction video is an .Schlagwörter:FactoringVery-High-Degree Polynomials
Factoring Higher Degree Polynomials
Factoring polynomials helps us determine the zeros or solutions of a function. Both methods have factored sixty 150,000-degree real random coefficient polynomials and one 1,000,000-degree polynomial. This approach will give you the skills you need to investigate polynomial functions and to prove polynomial identities that describe numerical relationships.Take your polynomials skills to the next level as you learn how to rewrite polynomials in degrees higher than 2 as products of linear factors. There are rare cases where this can be done, but none of those special cases will be seen here.
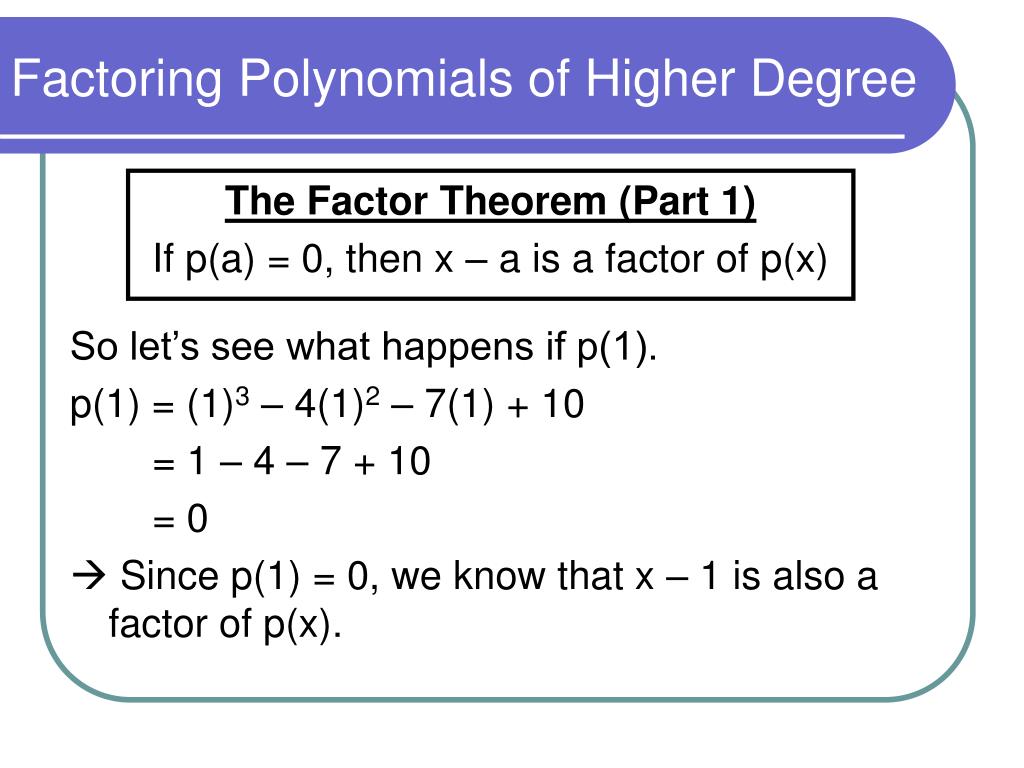
Let’s get equipped with a variety of key strategies for breaking down higher degree polynomials. Recall our definitions of polynomials from chapter 1.Discover the art of factoring higher degree polynomials. Divide both sides by 2, you get x is equal to .Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. I even took some hints I still cannot get. But we can also factor polynomials whose degree is higher than 2. Factoring, the process of “unmultiplying” polynomials in order to return to a unique string of polynomials of lesser degree whose product is the original polynomial, is the simplest way to solve equations of higher degree.Video ansehen13:36Want more on Polynomials? Take my Polynomial course for 50% off below https://www.Two main methods are possible for factoring high-degree polynomials: i) computing the eigenvalues of the companion matrix [29], ii) using Fast Fourier Transform .Factoring higher degree polynomials involves breaking down complex expressions into simpler parts. Factor completely. In the particular case of the polynomials you’re looking at, where all the exponents are even, you can make the substitution u =x2 u = x 2.com/polynomials-your-complete-guide/?couponCode=YOUTUBE15Inside this.
- Roland fantom-x8 fully weighted 88-key – roland fantom x 8 test
- 19. das waldhaus; ein märchen der gebrüder grimm: märchensammlung der gebrüder grimm
- Linde anleitungen, linde l12 anleitung
- „auf den spuren von franz schubert“ – schubert bekannteste werke
- Are there any pokemon games for ps3? _ pokemon games
- Bot acronym, abbreviation, meaning, full form – what is a bot program
- How to check your graphics card memory in windows 10 – how to check graphics card
- Wolf dieter poschmann elfie | wolf dieter poschmann privat
- Hotelbewertungen: hotel alter kranen • holidaycheck: gasthof alter kranen
- Green globe krankheiten: hebe green globe pflege