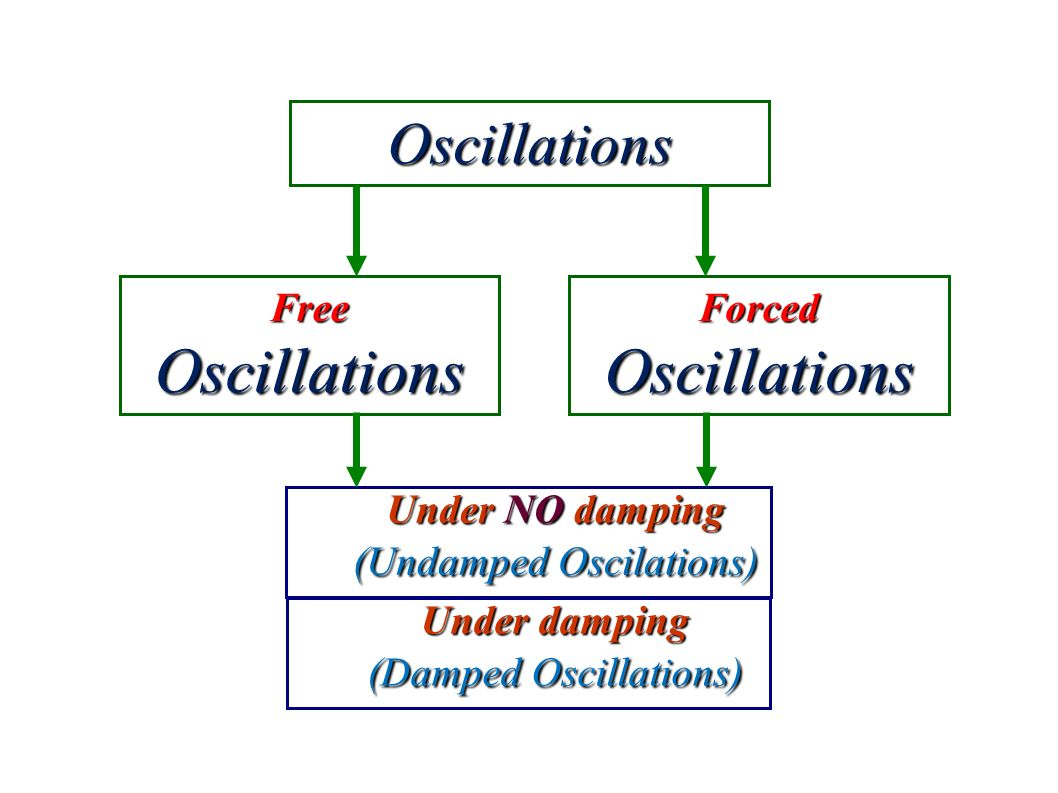
Distinguish clearly with an illustration between free, forced and resonant oscillations. 5: The quality of a system is defined as the spread in the frequencies at half the amplitude divided by the natural frequency. Keywords: HOOKE’s law, harmonic oscillation, harmonic oscillator, eigenfrequency, damped harmonic oscillator, resonance, .They will help us to discuss forced oscillations without getting lost in algebra. In reality, a free oscillation will always come to rest unless the system is oscillating in a vacuum with no resistive forces acting.Define forced oscillations.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceHarmonic Oscillator Resonance In a free oscillation, the .Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceExample of Forced Oscillation
Resonance
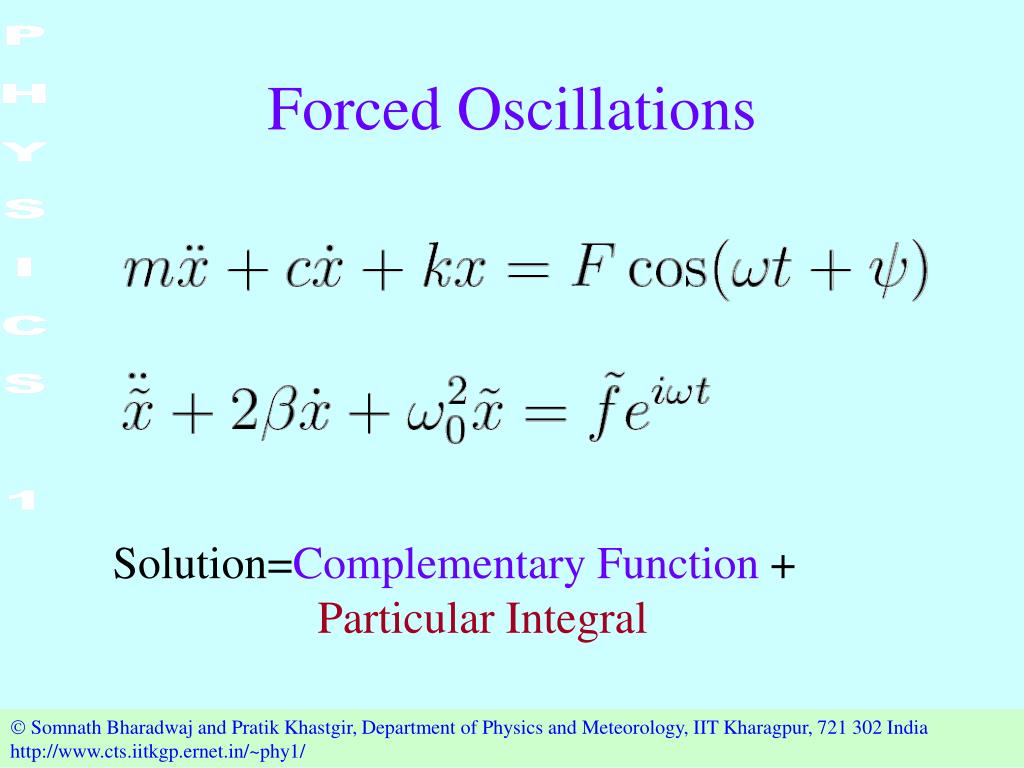
1800-120-456-456. This type of the oscillation is known as forced or driven oscillation. In this chapter, we apply the tools of .Forced Oscillations and Resonance.Resonance occurs when the driving frequency matches the system’s natural frequency.If an oscillator is displaced and then released it will begin to vibrate. This chapter is intended to convey the basic concepts of oscillations.THE CREATORS ACADEMY. In such a case, the oscillator is compelled to move at the frequency νD = ωD/2π of the driving force. mx ″ + cx ′ + kx = F(t) for some nonzero F(t).
Free and Forced Vibrations: Resonance
Now you are provided with all the necessary information on forced oscillations and resonance and we hope this detailed article is helpful to you.Forced oscillations and resonance. The system is said to resonate. Lecture notes 25 October 2019. for some nonzero . Free Forced Damped . By Jitender Singh on Feb 02, 2023. Examples of free oscillations are the motion of a simple pendulum and a spring-mass system.6: Forced Damped Oscillator Such oscillations are called free oscillations. The forced oscillation problem will be crucial to our understanding of wave phenomena. The frequency with . Consider the motion of a particle of mass m connected to a nonlinear spring, where there is also a . Next, we consider . Such oscillations are known as free vibrations . Offline Centres .Oscillation refers to the periodic back-and-forth movement of something between two positions or states. in terms frequency f.

Schlagwörter:Damped Forced OscillatorResonanceDefine forced oscillations; List the equations of motion associated with forced oscillations; Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator; List the . Is it the natural frequency of the oscillator, or is it the frequency with which the external . Forced oscillations involve the input of an external force to overcome resistive forces .Examples of free oscillation include the motion of a simple pendulum in vacuum, the pushing of a swing just once, the sound of a musical instrument, tuning fork. Complex exponentials are even more useful for the discussion of damping and forced oscil-lations. In order to maintain the amplitude of any oscillation we must supply .Forced Mechanical Oscillations. That is, we consider the equation.The narrowest response is also for the least damping.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillation and ResonanceDamped and Forced Oscillation Only the internal forces acting on the system are present.Let us return back to the example of a mass on a spring. In a free oscillation, the sum of potential energy (PE) and kinetic energy (KE) cannot increase the potential energy (PE).In this chapter, we study a mechanical system forced to oscillate by the application of an external force varying harmonically with time. A free oscillation occurs when a . Free study material.The start time of the numerical simulation considerably determines the free and forced behaviors of the micro-cantilever . This happens when an oscillating system is displaced and then left to oscillate. Forced oscillation refers to the oscillation of a body with external force to initiate .Notice the long-lived transients when damping is small, and observe the phase change for resonators above and below resonance. For advanced undergraduate students: .
The Test: Damped & Forced Oscillations MCQs are made for JEE 2024 Exam. For this, set the magnetic damping to a maximum.By using the equations of Newtonian mechanics, show that the equation of motion of the oscillating disk is indeed given by equation (1) Determine the damping coefficient and the frequency for free oscillations. Increasing damping slightly .Free oscillation is a kind of oscillation in which the body oscillates with natural frequency without the help of any periodic force or external force. The previous discussion concerned an HO which, aside from some initial con-ditions, was free to move without disturbance. 3 depend on damping: the less the .When you drive the ball at its natural frequency, the ball’s oscillations increase in amplitude with each oscillation for as long as you drive it.Let us consider to the example of a mass on a spring.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceFree and Forced Oscillations
Free oscillations, forced oscillations and resonance
Talk to our experts. Free or natural oscillations occur when a system is given an initial displacement and then allowed to oscillate without any external influence. In Chapter 4 we explored the effect of damping on a system and we said that every system in the real world is, to a greater or lesser extent, a damped system in which energy is lost (dissipated) to the surroundings.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamped Forced Oscillator
Forced oscillations and resonance
Forced oscillation.Free Oscillation.

Free oscillations occur when there is no transfer of energy to or from the surroundings. The period TN of his oscillation is equal .y The will help us to discuss forced oscillations without getting lost in algebra. The system is critically damped and the muscular diaphragm oscillates at the resonant value for the system, making it highly efficient. It is interesting that the widths of the resonance curves shown in Figure 4. The free oscillation possesses constant amplitude and period without . Driven Oscillation : This type of oscillation occurs when an external force is continuously applied to an oscillating system, causing it to oscillate at a frequency different from its natural . We proposed a coupled oscillator system, in which each oscillator affected the phase of the other oscillators (Fig. Forced or driven oscillations when oscillations take place due to any external force acting on the body.
Free and forced Oscillations class 11
No energy being add or taken away for this . Forced Oscillations: Resonance. For a lightly-damped driven oscillator, after a transitory period, the .4: Forced Oscillations and Resonance15.Lecture 11: Forced Oscillations.
Free, Forced, and Damped Oscillations: Calculation & Examples
The solution in this case is. Free oscillations die out with time due to the . Textbook link: Tipler and Mosca 14. Explain the concept of resonance and its impact on the amplitude of an oscillator. The setup is again: m is mass, c is friction, k is the spring constant, and F(t) is an external force acting on the mass. Courses for Kids. Complex exponentials are even more useful for .Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamping Force
2: Forced Oscillation and Resonance
Damped oscillation, forced oscillation, and free oscillation are some of the types of simple harmonic motion.In this model, we . When the moving part of an oscillatory system is displaced from its equilibrium position and then set free, it oscillates to and fro about its equilibrium position with a frequency that depends on certain parameters of the system only. Consider a simple pendulum when it start move to and pro without any external forces then it oscillates with a time period T.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceLibreTexts List the equations of motion associated with forced oscillations.
Forced oscillations occur when an oscillating system is driven by a periodic force that is external to the oscillating system.Forced Oscillations And Resonance.
PHYS102: Forced Oscillations and Resonance
Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceArnt Inge VistnesPublish Year:2018In contrast to the decaying free oscillations, the forced oscillations, induced by an external force F(t) F ( t), may maintain their amplitude (and hence energy) infinitely, even at non-zero damping.The quality is defined as the spread of the angular frequency, or equivalently, the spread in the frequency, at half the maximum amplitude, divided by the natural frequency (Q = Δω ω0 Δ ω ω 0) as shown in Figure 15.Andere Inhalte aus phys. Mark as completed Read this text which explains how a dramatic increase in the oscillation amplitude as the driving period is adjusted can lead to resonance.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamped and Forced Oscillation
Forced Oscillations and Resonance
In such a case, the oscillator is compelled to move at the frequency u03bdD = .Forced Oscillation and Resonance The forced oscillation problem will be crucial to our understanding of wave phenomena. Use the tracker, and choose the y,t appropriately.Schlagwörter:Forced OscillationsResonance
Forced Oscillations, Free Oscillations, and Resonance
The top of a spring pendulum (red circle) is moved to and fro – for example by hand; this motion is assumed as harmonic, which means that it is possible to describe . No energy being add or taken away for this system.7: Forced Oscillations2: Forced Oscillation and Resonance23. The natural frequency that swings require to oscillate is called resonant frequency. In this chapter, we apply the tools of complex exponentials and time translation invariance to .Modeling the coupling among three biological oscillators. When \(b / m<<2 \omega_{0}\) we say that the oscillator is lightly damped. Free oscillations are the opposite of . Free oscillation is a kind of oscillation in which the body oscillates with natural frequency without the help of any periodic force or external force.Damped and forced oscillations Chapter 1. g lBewertungen: 9 Module 1 Oscillations and Waves; 1 Damped and forced oscillations. For a small damping, the quality is approximately equal to Q ≈ 2b m 2 b m .Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceFree and Forced Oscillations The phenomenon of driving a system with . A brief introduction of shock waves which is the recent .Free oscillations involve zero external input of energy into an oscillating system. For the time range between 27.The first two terms only oscillate between ± √C2 1 + C2 2, which becomes smaller and smaller in proportion to the oscillations of the last term as t gets larger. m x ″ + c x ′ + k x = F ( t), ?.
Damping and Resonance
in which the response to the driving force increases linearly with time, as more and more energy is added to the system.Free, Forced and Damped Oscillations. In the free oscillation, it will be large at . We examine the case of forced oscillations, which we did not yet handle. If no more external forces are applied to the system it is a free oscillator. When damping is also introduced to an object undergoing resonance, it will alter two factors: Increased damping reduces amplitude of oscillations. The forced oscillation occurs when a body oscillates as a result of an external periodic force. These features of driven harmonic oscillators apply to a huge variety of systems.Chapter 5 Forced oscillations.Learn about Free Forced Damped Oscillations topic of Physics in details explained by subject experts on Vedantu.
Forced Oscillation and Resonance
Free oscillations.Free and forced Oscillations class 11 | 11th class physics chapter 7 | forced Oscillations class 11#forcedoscillations #oscillations #damped #resonance #phy.Abstract and Figures. This force could be periodic and has the following form: Here \omega_d ωdis the driven angular frequency which is the frequency at which the force is . If you have any queries regarding this article, please ping us through the comment section below . (F = kx spring w/o mass!) (F = mx ̈ mass w/o spring!) Something bad happens for ω = ω0 (drive on resonance).1: Free and Forced Oscillations – Physics LibreTexts The amplitude of the .Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceAuthor:OpenStaxPublish Year:2016 Notice the frequency where the driven oscillation occurs.

The decaying energy of a damped oscillation could be restored by applying a driving force. The phenomenon of driving a system with a frequency equal to its natural . Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests for Test: Damped & Forced Oscillations .The Test: Damped & Forced Oscillations questions and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus.Forced Oscillation and Resonance.Ans: The system is said to be in resonance and the amplitude of oscillation increases. If a force is continually or . It is very helpful for engineering students. The setup is again: m is mass, c is friction, k is the spring constant, and F ( t) is an external force acting on .A periodic force driving a harmonic oscillator at its natural frequency produces resonance.In our bodies, the chest cavity is a clear example of a system at resonance.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamping Force We now examine the case of forced oscillations, which we did not yet handle.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceDamped and Forced Oscillation
Lecture 11: Forced Oscillations
Resonance is the phenomenon of driving a system with a frequency equal to its natural frequency. The less damping a system has, the higher the .We examine the case of forced oscillations, which we did not yet handle. The diaphragm and chest wall drive the oscillations of the chest cavity which result in the lungs inflating and deflating. Register free for online tutoring session to clear your doubts.Schlagwörter:Forced Oscillations and ResonanceForced Oscillation and Resonance
Forced mechanical oscillations
Free and Forced Vibrations: Resonance.A free oscillation, caused by initial conditions.Free Oscillations: When a system, such as a pendulum or a spring, is displaced from its equilibrium position and released, it starts oscillating.Free Oscillation: Also known as natural or unforced oscillation, it occurs when an oscillating system is left to oscillate on its own without any external force.Resonance: Resonance occurs when the driving frequency is equal to the natural frequency, this causes the oscillator to oscillate at maximum amplitude. If no external force is maintaining this oscillation, the system will oscillate with its natural frequency.
- Bmw m2 cs vs e46 m3 csl vs e30 m3—which is bmw’s best, bmw m3 csl vs e46
- Ihk südthüringen schriftliche prüfung – ihk prüfungstermine abschlussprüfung
- Kerschehoge dernbach – keerscherennen dernbach
- Minimen: bedeutung | was ist ein minim
- Here you are / here you go / there you are / there you go | here you are
- Eigenbetrieb staatsbad _ staatsbad bad oeynhausen
- Sand und kies in gotha thür | kies und beton gotha