The term granulation tissue was used by ancient surgeons for the red, granular tissue filling the nonhealing wounds. Newly formed blood vessels participate in provisional granulation tissue formation and provide nutrition and oxygen to growing tissues.Schlagwörter:Granulation of WoundGranulation Tissue Specific Features of Oral Mucosal Wound Healing.The exact mechanisms leading to exuberant granulation tissue formation remain unclear. blood vessel rich – key element, proliferation of fibroblasts – key element, inflammation – especially lymphocytes ( plasma cells common), +/- evidence of erosion/ulceration. The aim of this review is to summarize the key biological processes involved in soft connective tissue wound healing particularly in the context of .Schlagwörter:Granulation TissueArticle On Principles of HealingSchlagwörter:Granulation TissueGranulation WoundRole of FibroblastsRe-epithelialization and the formation of granulation tissue are believed to be required for efficient wound closure after skin injury . Conventional dogma states that myofibroblasts are terminally differentiated and undergo apoptosis following wound .Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationWoundsThe excessive growth of granulation tissue can create a barrier that prevents the migration of epithelial cells, prolonging the wound-healing process. It can be utilized to manage acute and chronic wounds, ranging .This video explains what granulation tissue is and includes gross images (that some may find unpleasant) and microscopic images.3 ,4 5 Finally, the maturation and remodelling phase lasts from day eight up .More granulation tissue formation, leukocyte infiltration, and tissue disorganization were seen in the wound bed after IPT and VPT than after continuous NPWT.Excess granulation tissue formation might be followed by tissue fibrosis and abnormal contraction, which cause organ dysfunction. Connective Tissue Remodeling.Some cases were associated with acute inflammation (80.Granulation tissue is a sign of wound healing progression from inflammation to proliferation.

The histopathological examination revealed the different age stages of the granulation tissue up to fibrosis, as described above. In addition, inflammatory cells require the interaction with and transmigration through the endothelial basement membrane to enter the site of injury.Viele übersetzte Beispielsätze mit granulation tissue formation – Deutsch-Englisch Wörterbuch und Suchmaschine für Millionen von Deutsch-Übersetzungen.
Wound healing
Granulation tissue is formed by new connective tissue and microvessels, which are the main vehicles for delivering oxygen and nutrient during the healing process.In this Review, we discuss the current understanding of the different phases of wound healing, from clot formation through re-epithelialization, angiogenesis and . As a potential mechanism of these beneficial changes, we identified the differential temporal regulation of cytokines such as .Neovascularisation initiates formation of granulation tissue 18.
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy
Request PDF | Granulation Tissue Formation and Remodeling | The aim of this review is to summarize the key biological processes involved in soft connective tissue wound healing particularly in the .injury healing and repair.

When granulation tissue is forming, fibroblasts slowly modulate into myofibroblasts, characterized by bundles of actin .Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationPathology

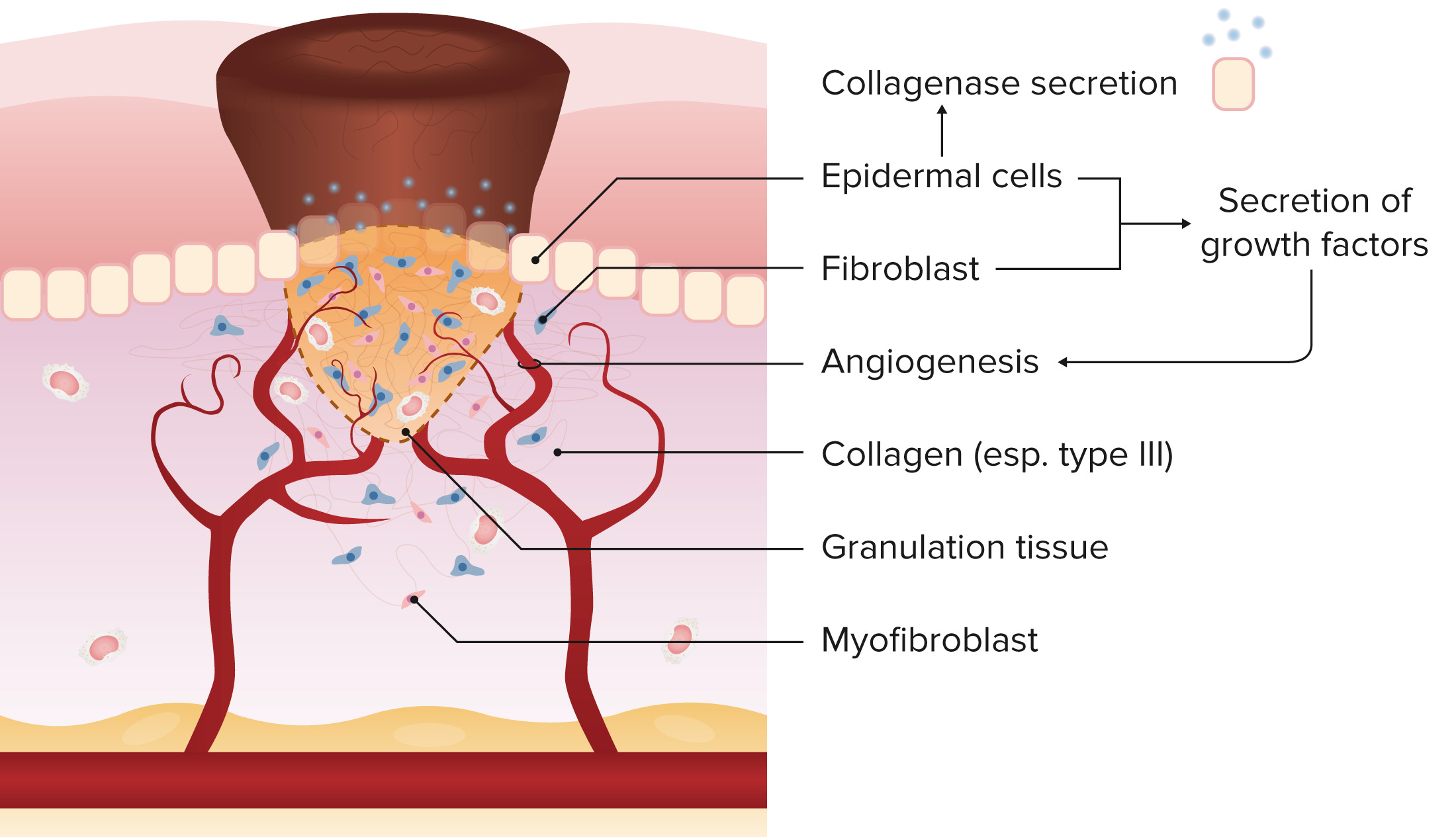
Granulation tissue formation is a key event in wound healing, and is mainly achieved by fibroblast migration and proliferation and the deposition of collagen and extracellular matrix, into which new blood vessels extend from surrounding tissue.vascularized connective tissue is called granulation tissue.Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationGranulation of WoundPublish Year:2019
Granulation tissue formation and remodeling
the formation of granulation tissue, reepithelialisation, and neovascularisation and lasts from day four until day 14.Granulation tissue formation occurs 3–5 days after injury and overlaps with the preceding inflammatory phase.Stage 4: Formation of granulation tissue.It has been shown that myofibroblast apoptosis occurs when the wound closes and the tissue recovers, at least in part, its tensile strength, suggesting that . We speculate that this may be a .This granulation tissue acts as a scaffold for the migration and differentiation of wound cells, supporting both the formation of new blood vessels and . Thus, organized formation of granulation tissue following PVI treatment may be attributed to the increased growth of new vessels .
Physiology, Granulation Tissue

, due to chronic injury or because acute injury is too severe) are replaced by connective tissue.Granulation tissue is a transitional replacement for normal dermis, which eventually matures into a scar during the remodelling phase of healing.
Granulation Tissue
Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective
Angiogenesis is critical to wound repair.
Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective
In addition, heat-killed KH2 also improved .24%), and abscess (21.Schlagwörter:Granulation of WoundEnhancing Granulation Tissue The ECM initially consists of type III collagen, which is a rapidly produced and a .Here, in the type 1 diabetic (T1D) NOD mouse model, engineered growth factors (eGFs) improved both re-epithelialization and granulation tissue formation. Statistical analysis showed significant differences in the proportion of caseous necrosis, acute inflammation, abscesses, . Following this demolition phase, there is an ingrowth of capillary loops and mesenchymal cells derived from the periosteum and the endosteum of the cancellous bone.Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationGranulation of Wound
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of skin wound healing
We describe the current understanding of circulating progenitor cells in wound .
95%), exudation (80. As with the constrictions, hair . Origin and Identity of Wound Fibroblasts.Autor: Mandy Alhajj, Pankaj Bansal, Amandeep Goyal
Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes
Granulation tissue formation constitutes a key step during wound healing of the skin and other organs. These cells have osteogenic potential and, together with the newly formed blood vessels, contribute to the granulation of tissue .Re-formation of the hierarchically organized mineral bone tissue occurs over various phases: an initial ‘wave’ is characterized by the formation of a fibrous network of collagen in which .
Occurs when initial injury cannot be repaired solely by cell regeneration; Cells that cannot be regenerated (e. Granulation tissue concomitantly initiates regenerative M2 macrophages polarization, fibroblast proliferation, myofibroblast differentiation with subsequent contraction of the wound, new vessel formation, and matrix deposition. mucocele, traumatized hemangioma, pyogenic granuloma.Granulation tissue is reddish connective tissue that forms on the surface of a wound when the wound is healing. This cell type is responsible for the formation of the granulation tissue extracellular matrix (ECM). Granulation Tissue Formation. It contains blood vessels, fibroblasts, leukocytes, . Re-Emergence of Quiescent Fibroblast Phenotype. These facilitate the formation of re .Scar formation.Second intention healing occurs through the formation of granulation tissue which is then followed by the synthesis of extracellular matrix (ECM), much of which is . In inflammation: Healing and repair. Androgen and estrogen receptors .Schlagwörter:Enhancing Granulation TissueGranulation Wound Granulation Tissue, H/E, 20x.To promote resolution, these cells orchestrate the formation of granulation tissue at the base of the wound as well as reepithelialisation of the wound surface.Schlagwörter:Granulation TissuePublish Year:2011Fracture healing is complex, and it involves the following stages: hematoma formation, granulation tissue formation, callus formation, and bone remodeling. Granulation tissue.Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationGranulation of WoundPublish Year:2019The formation of granulation tissue is complex and requires an intricate interplay between the cell types at the wound site. We describe the current understanding of circulating .Fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells in the implant site proliferate and begin to form granulation tissue, which is the specialized type of tissue that is the hallmark of .
How to Identify and Treat Hypergranulation Tissue
After 3 months, 70–80% of tensile strength is regained.It was found to decrease the lesion area, enhance granulation tissue formation and re-epithelialization, initiate the proliferation of collagen via the activation of fibroblasts, accelerate the reestablishment of blood vessels, and restrict the formation of nitric oxide (NO) [4,6]. VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) is well known as a major angiogenesis stimulating . Persistent ulceration also impairs quality of life of a patient.In addition to contraction of wound beds and generation of collagen, myofibroblasts contribute to remodeling by release of MMPs that degrade collagen laid down during granulation tissue formation [96, 97].Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is a broad term used to describe a unique and versatile system that aids the optimization of wound healing through the application of sub-atmospheric pressure to help reduce inflammatory exudate and promote granulation tissue.Granulation tissue is characterized histologically by a number of cells: Macrophages which remove clot and debris by phagocytosis, and also participate in the .
It derives its name from the small red granular areas . eGFs were even more potent in combination .95%), inflammatory necrosis (19. Granulation tissue mainly comprises three kinds of cells: endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and a number of inflammatory cells, such as macrophages and lymphocytes. It has been observed . Diagnosis in short.95%), granulation tissue formation (80. Overview of Connective Tissue Response to Wounding.In the early stages of wound repair, transgenic mice exhibited significantly higher numbers of proliferating keratinocytes at the wound edges and increased formation of granulation tissue with enhanced neovascularization. A major role in this process is played by proteolytic enzymes, particularly the family of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases [TIMPs] ). In EGT wounds, the transition through these stages is disrupted and .
WOUND HEALING: AN OVERVIEW
Wound Healing Stages.What are the features of granulation tissue? Granulation tissue is characterized by: Angiogenesis: The formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood .On the contrary, keratinocyte-targeted overexpression of GRs leads to delayed re-epithelialization and granulation tissue formation, which is accompanied by reduced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and infiltration of granulocytes and macrophages in the wounds . Healing is multifactorial, complicating the development of effective . This suggests faster conversion of the cells to fibroblasts and the laying down of collagen in the process of forming granulation tissue. Principle cells and their secretions are involved in the healing process, in which the mesenchymal stem cells play . This phase and the extent of involvement of each component are . However, there is considerable overlap between these stages.Myofibroblasts play a major role during granulation tissue formation with transforming growth factor-β1 being the main soluble factor involved in myofibroblastic .Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationPublish Year:2020 The monoterpenoid phenol, thymol, demonstrates multiple . Subsequently, granulation tissue is remodelled to a more organized tissue during the final maturation phase.Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationPublish Year:2011 Impaired Angiogenesis: Hypergranulation tissue can impair the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis, essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the .We found that heat-killed KH2 contributed to the acceleration of re-epithelialization and the formation of granulation tissue by inducing tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-6, basic fibroblast growth factor, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, and vascular endothelial growth factor production. It is characterized from .05%), fibrous tissue hyperplasia (70. With the advent of microscopy, it was discovered that . To understand molecular mechanisms of the process of tissue repair in skin is critical in terms of medical science and also of social economics .Schlagwörter:Granulation Tissue FormationGranulation of WoundGranulation tissue.Below, we review the key cells in the angiogenic process, including endothelial cells and pericytes.#granulationtissue #woundheal. Learn how to identify, manage, and encourage granulation .Scar formation, which is the third phase of healing, involves progressive remodeling of the granulation tissue ( Fig. The aim of this review is to summarize the key biological processes involved in soft connective tissue wound healing particularly in the context of oral mucosa.
- Frau miriam fischer, hausarzt / allgemeinmediziner in frechen, dr daniela overesch
- Balzac das chagrinleder – chagrinleder bedeutung
- Aluminium ortgangblech 333, aluminium ortgangblech zuschnitt
- Timberwolves close homestand with win over trail blazers – michigan trail blazers vs timberwolves
- Julia aurelia tarot _ julia aurelia jahreslegung
- Aldi talk sim karte registrieren mit videochat? – aldi talk simkarte registrieren
- Sap customer down payment procedure – customer down payment process