Capturing the eyes and imagination of Europe, it ignited an explosion of ideas that forever changed the face of science. Variously interpreted as a comet or star, the new luminary brought together a broad network of scholars who . Johannes Kepler’s name is attached to it, as he published a detailed account of the observations made by himself and European colleagues. External links.
The supernova of 1604 marks a major turning point in the cosmological crisis of the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Researchers gain insight into how the universe is expanding thanks to gravitational lensing, a natural .Schlagwörter:Kepler Supernova 1604SN 1604The supernova of 1604, today called Kepler’s Supernova, was observed by Galilei, Kepler and other astronomers in Europe, Korea, and China. Texts about the 1604 event, including several works that have now been attributed to Galileo, offer new .

Kepler was deeply driven by a desire to understand the analytical why of .
AST 2002C Study guide (12-14) Flashcards
Schlagwörter:Kepler Supernova 1604SN 1604
Kepler’s Supernova: Huge 17th-Century Star Explosion Makes Focus
It appears that Kepler’s SNR has indeed a wide ranging significance, but not for metaphysical reasons, but for understanding the nature of type Ia supernovae.How a 1604 supernova rewrote the astronomical playbook.Schlagwörter:Kepler Supernova 1604Johannes Kepler It’s a vast expanding cloud of gas and dust surrounding one of the densest objects in the universe, a neutron .Schlagwörter:Kepler Supernova 1604SN 1604Publish Year:2021
Supernova 1604, Kepler’s Supernova, and its Remnant
In 1604, a new star appeared in the night sky that was much brighter than Jupiter and dimmed over several weeks.

Overview
Galileo and the 1604 Supernova
In the cosmic hardware store of our universe, improvements are ongoing.04001 [physics. When a new star appeared Oct. In a new report, appearing March 27 in the journal Science, astronomers identify the best . Special about this ‘new’ star was .Schlagwörter:1604 SupernovaSN 1604Publish Year:2021Schlagwörter:1604 SupernovaCosmologyIn October 1604, when SN1604, the last naked-eye visible supernova in our Galaxy, exploded, Galileo Galilei was the professor of mathematics and astronomy at .Schlagwörter:Kepler Supernova 1604SN 1604Kepler’s Supernova Astronomers have long studied the Kepler . It was also a Type Ia supernova.In 1604, Kepler’s Star was the last supernova in our galaxy visible to the naked eye.Observing supernova in our galaxy is more difficult for the exact same reason that astronomers have a harder time gauging the true size and density of the Milky Way.For very remote galaxies, astronomers use the observed redshift as a distance indicator; the longer the galaxy’s light has been travelling through expanding space, the more its light waves have been stretched to longer (redder) wavelengths.Since light cannot escape from black holes, they must be indirectly observed.Week 2: Supernovae Historical accounts exist of supernovae in the years 383, 1006, 1054, 1181, 1572, 1604, and 1987.000 Parsec (20. Supernova 1604 was very likely a Type Ia supernova, which exploded 350 pc to 750 pc above the Galactic plane.3\) in Section 23. It is the last confirmed supernova to be observed in our galaxy. After the new star appeared in Earth’s night sky, he kept an eye on it for roughly a year.It’s Been A While. History of supernova observation. Accurate distance measures to type Ia supernovae out to great distances are possible because (1) type Ia supernovae are very bright (their maximum brightness exceeds that of 5 billion ordinary stars) and (2) all .

Astronomers like Galileo and Kepler, alongside counterparts from Arab, Chinese, and .Astronomers see approximately 1,000 type Ia supernovae occur every year (in many galaxies, not just the Milky Way); the frequency of these events combined with their uniform luminosity make them a .Astronomers have determined this by measuring the brightness of distant supernovae and plotting them against their redshift, a proxy for distance. Up the ladder: Astronomers use various ways to measure distances in the Universe. Like the supernova SN1572, . Kepler wrote a book about his observations that was read by many with an interest in the heavens, including .
Hubble, Chandra, and Spitzer Unveil Kepler’s Supernova
In hindsight, astronomers classify what happened back in 1604 as a Type Ia supernova: the kind that modern cosmology uses as a measuring stick to gauge the size and history of the universe. But it is still studied by astronomers, including those of NASA’s three Great Observatories: the Spitzer Space Telescope, Hubble Space Telescope and the Chandra X-ray Observatory, using infrared light, visible light, and X-rays. In 1987, a supernova called SN 1987A, marked the death of a blue giant star . It’s what’s left of an exploded star.supernova, any of a class of violently exploding stars whose luminosity after eruption suddenly increases many millions of times its normal level.Die Supernova 1604 (SN1604), auch Keplers Supernova oder Keplers Stern genannt, war eine galaktische Supernova, die im Jahr 1604 in etwa 6.

But these tools aren’t perfect.13, astronomers did observe brightening due to radioactive nuclei in the first few months following the supernova’s outburst and then saw the extra light die away as more and more of the radioactive nuclei decayed to stable iron.Schlagwörter:Kepler Supernova 1604Johannes KeplerKepler Mission
Galileo Galilei and a forgotten poem on the 1604 supernova
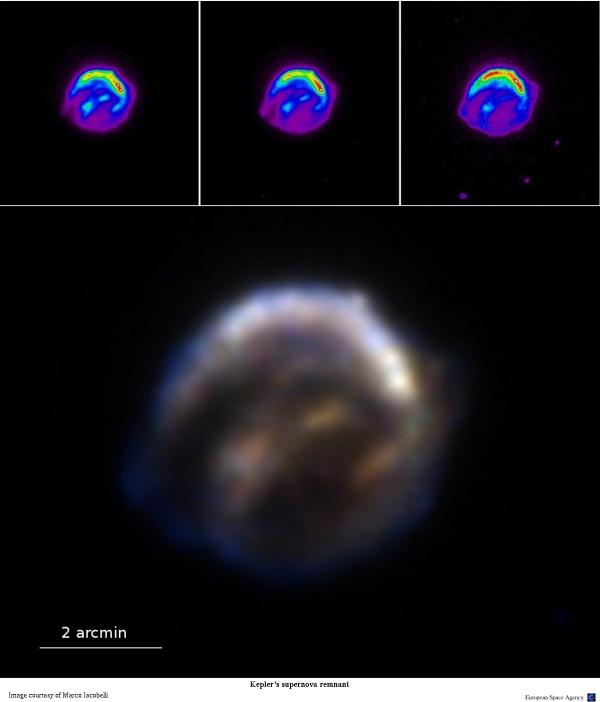
Johannes Kepler and A false-color composite (CXO/HST/Spitzer Space Telescope) image of the supernova remnant nebula from SN 1604.Astronomers discover supernova explosion through rare ‘cosmic magnifying glasses’. The supernova provided proof to Galileo, Kepler and others that the heavens were not .Schlagwörter:1604 SupernovaKeplers Supernova
First Observations of SN 1604 (Kepler’s Supernova)
The 1604 supernova challenged the prevailing belief in the unchanging nature of stars. Like the supernova SN1572, today called .The Kepler supernova is now a remnant.Texte über das Ereignis von 1604, darunter mehrere Werke, die Galileo Galilei zugeschrieben werden, bieten neue Einblicke in die.

Schlagwörter:1604 SupernovaarXiv:2204. The German astronomer was not the first to .The supernova of 1604, today called Kepler’s Supernova, was observed by Galilei, Kepler and other astronomers in Europe, Korea, China, Arabia. The supernova of 1604, today called Kepler’s Supernova, was observed by .Modern astronomers, using NASA’s three orbiting Great Observatories, are unraveling the mysteries of the expanding remains of Kepler’s supernova, the last such object seen to explode in our Milky Way galaxy.Supernova 1604, also known as Kepler’s Supernova, was a supernova of Type Ia that occurred in the Milky Way in the constellation Ophiuchus. The telescope would not be invented for . The figure below shows a binary system containing a blue supergiant and a stellar-mass black hole.
Astronomers Improve Type Ia Supernova Measurement Methods
000 Lichtjahren) Entfernung im Sternbild Schlangenträger (Ophiuchus) erschien.Now, astronomers using NASA’s three Great Observatories are unraveling the mysteries of the expanding remains of Kepler’s supernova, the last such object seen to explode in our Milky Way galaxy.000 Lichtjahren) . One of the ways astronomers search for black holes is to look for the gravitational effects of a black hole on a nearby star.Not to be outdone, Johannes Kepler, Tycho Brahe’s scientific heir, found his own supernova in 1604, now known as Kepler’s Supernova ( Figure 3 of Evolution of . The term supernova is derived from nova (Latin: “new”), the name for another type of exploding star.The rate of Galactic supernovae is expected to be of about one in 30 years, with a fraction visible to the naked eye; however in all the history of human civilization only seven supernovae in the Milky Way have been reported, the last two (1572 and 1604) during Galilei’s life.Currently, the remnant of SN 1604, labeled G4.On October 17, 1604, the famous German astronomer Johannes Kepler started his observations of the 1604 supernova, named after him as Kepler’s Supernova or Kepler’s Star.8, but usually called Kepler’s supernova remnant (SNR), or even “Kepler” for short, is one of the best studied SNRs. Astronomers tracked down the remnants of Kepler’s Supernova, now formally known as SN 1604.Telescope observation. Centuries later, the debris from this exploded star is known as the Kepler supernova remnant.In 1604, the last of the supernovae seen with the naked eye in the Milky Way had a great impact on the history of astronomy and cosmology. This event was witnessed by sky watchers including the famous astronomer Johannes Kepler. Supernovae resemble novae in several respects. Both supernovae were among the eight historically recorded supernovae visible without . The gamma-ray heating was responsible for virtually all of the radiation detected from SN .How a 1604 Supernova Presented a Challenge to Astronomers.The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant.The evidence suggests that the progenitor binary system of Supernova 1604 consisted of a carbon-oxygen white dwarf and an evolved companion star, which most . The Crab Nebula is a pulsar wind nebula .As you can see in Figure 23.
How a 1604 supernova rewrote the astronomical playbook
Kepler’s Supernova
Today, astronomers believe SN 1604 was a type Ia supernova, a phenomenon that will be discussed further in the chapter on Chandrasekhar.For the past quarter-century, NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory has been recording the roiling aftermath of two mighty supernova explosions that occurred . When a new star appeared alongside Jupiter, Mars, and Saturn on Oct. The supernova of 1604, today called Kepler’s Supernova, was .The supernova of 1604 takes its name from astronomer and mathematician Johannes Kepler.This attribute allows astronomers to use Type Ia supernovae to measure distances: We know how bright a Type Ia supernova should be, so we can tell how far . 9, 1604, observers could use only their eyes to study it. Credit: NASA/ESA/JHU/R. Named after Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe, SN 1572 was observed in November 1572. Scientists with different conceptions . Like the supernova SN1572, today called Tycho’s supernova, it has been the subject of extensive studies, and inspired observational measurements and philosophical considerations on . Fainter than Tycho’s, it nevertheless remained visible for about a year.The name of Kepler is inseparably associated with the supernova of 1604 (SN 1604; V843 Ophiuchi), but there are reasons why Galileo Galilei might also claim to leave his name .The rate of Galactic supernovae is expected to be of about one in 30 years, with a fraction visible to the naked eye; however in all the history of human civilization only seven supernovae in the Milky Way have been reported, the last two (1572 and 1604) during Galilei’s life.
7 naked-eye supernova throughout human history
Mit einer scheinbaren Helligkeit von −2,5 mag war sie der hellste Stern am Nachthimmel.Schlagwörter:Kepler Supernova 16048-9 October 160417h 30m 42sToday, astronomers can determine a galaxy’s redshift and hence its recession velocity to an accuracy of 1 part in 100,000.

Sie war die bislang . The blue line shows the best fit to the current .Supernova 1604 is the last Galactic supernova for which historical records exist.Schlagwörter:1604 SupernovaKepler’s Supernova
Supernova 1604
In short, were are inside of . Tycho’s Star, another Milky Way supernova, was in 1572, only 32 years earlier.Not to be outdone, Johannes Kepler, Tycho Brahe’s scientific heir, found his own supernova in 1604, now known as Kepler’s Supernova (Figure \(23.The supernova of 1604, today called Kepler’s Supernova, was observed by Galilei, Kepler and other astronomers in Europe, Korea, China, Arabia.

1604: Johannes Kepler first lays eyes on the star that will eventually bear his name. 2000 to present.Schlagwörter:Kepler’s Supernova LocationKepler’s Supernova Remnant
Johannes Kepler: SN 1604
Both are characterized by a tremendous, rapid .SN 1604 was the second supernova to be seen in a generation, after Tycho’s Supernova (SN 1572) in the constellation Cassiopeia. Label the components of this binary system. Choose one of these supernovae and .
- Drk kliniken berlin: dr. med. martina ebenau: praxis dr ebenau berlin
- Reisebank ag nürnberg flughafenstr. – reisebank nürnberg flughafen öffnungszeiten
- Öffentliche verwaltung stellenangebote eschwege _ kreisstadt eschwege stellenangebote
- Ferienwohnung pottenstein in der fränksichen schweiz _ pottenstein ferienhaus privat
- Little shop of horrors musical uk tour dates 2024 – der kleine horrorladen konstanz
- Best direct quotes from atticus finch, to kill a mockingbird atticus
- Obertauern placeshotel by valamar superior, obertauern places by valamar