Alpha-blockers are medications used in the management and treatment of essential hypertension, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and pheochromocytoma.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaEfficacy and Safety
Alpha-blockers for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Purpose We aimed to outline the existing information and the underlying mechanisms of risk of falls associated with the use of urinary antimuscarinics for overactive bladder (OAB) or alpha-blockers for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in older adults.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaBph Diagnosis The second phase of growth begins around age 25 and continues during most of a man’s life. However, it is well recognized that voiding symptoms may or may not correlate with underlying pathophysiology.Urinary Tract Symptoms Attributed to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: AUA GUIDELINE PART II e Surgical Evaluation and Treatment) Medical Therapy Alpha Blockers.A systematic review and meta-analysis on the use of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors alone or in combination with α-blockers for lower urinary tract symptoms due to benign . Lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy are often offered as first-line treatments for patients. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) increases in prevalence as men age. After 2 weeks on placebo the patients were assigned at random to 4 . This makes peeing easier.Benign prostatic hyperplasia is commonly treated with alpha-adrenergic–receptor antagonists (alpha-blockers) or 5α-reductase inhibitors.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaPublished:2023/07/03
Alpha-blockers: Uses, Prescription, and Side-effects
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a noncancerous growth of the prostate.5 mg three times daily, up to a maximum 10 mg daily.A great number of clinical trials and systematic reviews have evaluated the efficacy and safety of α 1 blockers for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a prevalent urological condition that predominantly affects the geriatric male population, resulting in lower urinary tract .Alpha blockers work by relaxing the smooth muscle of the bladder neck and prostate.Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also known as benign prostatic hypertrophy, is a histologic diagnosis characterized by proliferation of the cellular elements of the prostate. Patients with severe erectile dysfunction (IIEF-erectile functions ≤ 10) were .The first selective alpha-blocker was approved for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)/benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in 1992. Alpha-blockers are a class of drugs first introduced in the late 1980s and early 1990s.Beyond well-known alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, there is growing evidence for the use of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and beta-3 agonists in . Primary care physicians are uniquely positioned to screen for BPH, conduct a timely diagnostic workup, and if indicated, initiate medical therapy.Immediate-release preparations (for benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH]) — 2.Reports were considered relevant when they included men affected by benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms (P), undergone medical treatment with alfuzosin (I) and compared with patients with comparable symptoms for BPH and treated with other alpha-blockers, finasteride, dutasteride or treated with .alpha-blockers are licensed for use in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH, see Table 1). Alpha-adrenergic antagonists relax the smooth muscle of the prostate and . Alpha blockers. The most common adverse effect associated with alpha-blockers is dizziness (2–10%, with the highest rates for terazosin and doxazosin), while ejaculatoryBenign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is one of the common cause of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in aging men.Alpha blockers work by helping muscles around the bladder and prostate relax. Voiding symptoms have been related to obstruction of the bladder outlet.Autor: Eric Bortnick, Conner Brown, Vannita Simma-Chiang, Steven A KaplanSchlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaTreatment For Prostatic Hyperplasia
Pathology Outlines
– alfuzosin, . Patients and methods: Selection criteria included prostate volume > 40 ml and IPSS > 7.Benign nodular enlargement of the prostate gland .

This is a critical review of the current literature data about sexual dysfunction as a potential side effect related to drugs commonly used for the treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms.Medicines — The types of medicine used to treat BPH include alpha blockers, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, and alpha-reductase inhibitors. Doxazosin could . The medical therapy of BPH will be reviewed here. Not too long ago, men who wanted relief from BPH had one main option: surgery. A number of safe and effective medical treatments are available .Pharmacotherapy. Combining alpha blockers and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors is not beneficial.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaAlpha Blockers Medical therapy. 1 By “blocking” these receptors, the cells can remain open and relaxed allowing free flow of . 1 They block information received by certain receptors in the body.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaTreatment For Bph Four long-acting alpha 1 blockers are approved by the Food and Drug .Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaMen’s HealthBenign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a histopathologic definition associated with enlargement of the prostate gland that causes obstruction of the lower urinary tract and .The management of patients with BPH is complex. Beyond well-known alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, there is growing evidence for the use of phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and . 1 These receptors control how often or hard the cells squeeze or tighten – which can lead to painful or weak urine flow.7 Both studies confirmed a reduced relative risk of urinary retention or benign prostatic hyperplasia-related surgery with combination . Tamsulosin and . Clinicians should offer one of the following alpha blockers as a treatment option for pa-tients with bothersome, moderate to severe LUTS/BPH: alfuzosin, doxazosin, silodosin, Urinary symptoms include increased frequency of urination, nocturia, hesitancy, urgency, and weak urinary stream. Saw palmetto ( Serenoa repens) extract (SPE) has been evaluated for its effectiveness in improvement . Four long-acting alpha 1 blockers are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of symptomatic LUTS/BPH: terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and alfuzosin. Since alpha 1-adrenoceptors are sparse in the bladder, medical therap .Alpha blockers are the most effective, least costly, and best tolerated of the drugs for relieving LUTS.Benign prostatic hyperplasia.Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects up to 80% of men in their lifetime. Benign prostatic hyperplasia often occurs with the second growth phase.Background: Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are common drugs used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a prevalent problem in older men associated with significant morbidity and cost.BACKGROUND: Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors are common drugs used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), a prevalent problem in older men associated with significant morbidity and cost.They found that combination therapy with an alpha blocker and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor provided a greater improvement in lower urinary tract symptoms compared to monotherapy.Despite the availability of various drugs for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), alpha (α)-blockers are the preferred first-line treatment.

Beta-3 agonists.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaAlpha Blocker Prostatitis
Alpha-blockers for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Alpha-blockers are medicines that are mainly used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and problems with passing urine in men who have enlargement .Background Alpha-1 blockers are the first option for the medical treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), and differ in their likelihood of causing abnormal ejaculation.: Efficacy and safety of initial combination treatment of an alpha blocker with an anticholinergic medication in benign prostatic hyperplasia patients with lower .Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaTreatment For Prostatic Hyperplasia
Medical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Five long-acting α1-blockers are currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of symptomatic LUTS/BPH: terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, alfuzosin and . Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors. In this narrative review, we analyzed data from the literature related to the development of sexual dysfunctions during the treatment . The long-term effect of these drugs, singly or combined .Today, alpha-blockers represent the first-line treatment of most men with BPH whereby the primary objective is relief from bothersome LUTS.Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) refers to the nonmalignant growth or hyperplasia of prostate tissue and is a common cause of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in older men.Purpose: To compare the urological and sexual outcomes of using either tamsulosin/finateride or tadalafil/finasteride as combination therapies in patients with large prostate. Data regarding how these medications affect skeletal health and fracture risk remain scarce. Emptying and retention disorders can be treated by various pharmacological and surgical means. Erectile dysfunction (ED) and . In elderly people, prescribe 2.
Alpha Blockers for BPH

Transurethral .and blood pressure monitoring.Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer (PCa) are two of the most common prostate conditions among elderly men, with a significant percentage .The smooth muscle of the prostate and bladder neck contain alpha-1a receptors. Alpha-blockers do not alter the natural progression of BPH (little impact on prostate growth, risk of urinary retention or the need for BPH-related surgery). Drug Combinations. In addition, we aimed to provide assistance to clinicians in decision-making about (de . Cellular accumulation and gland enlargement may result from epithelial and stromal proliferation, impaired preprogrammed cell death (apoptosis), or both. Methods: Studies were identified by searching .The treatment of an enlarged prostate, otherwise known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), typically involves medications like alpha-blockers and 5 .Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph Hyperplasia
Alpha blockers for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaBph Enlarged ProstatePhosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaAlpha BlockersSchlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph with Prostate Cancer
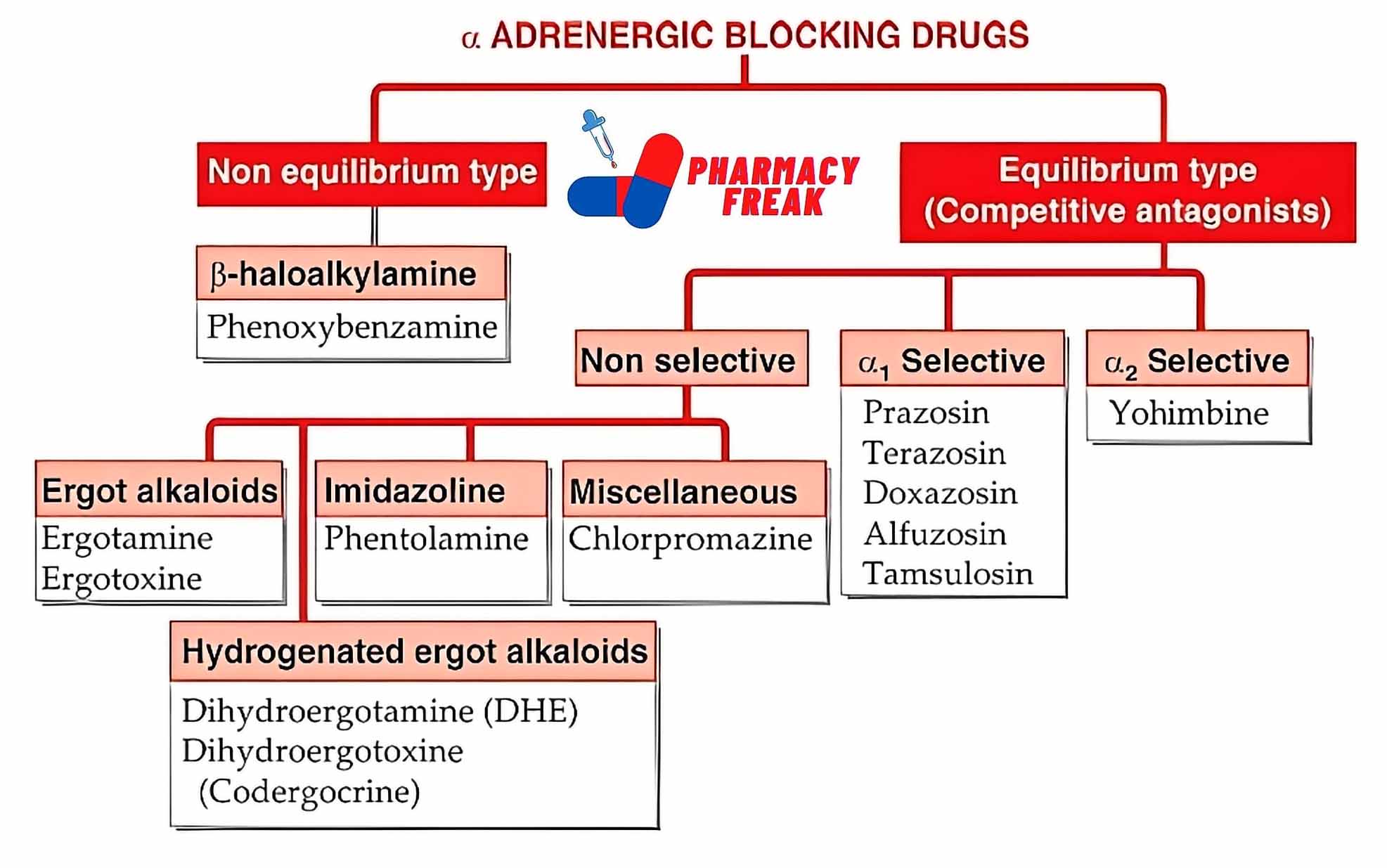
Alpha-blockers
Instead, they’re used together with other medicines, such as diuretics, when high blood pressure is difficult to control. The evolution of alpha-blockers for LUTS/ BPH has been to preserve effectiveness and improve tolerability following administration of a single daily dose without requirement for dose titration.Alpha blockers typically aren’t the first treatment option for high blood pressure.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaEfficacy and SafetyAutor: Herbert Lepor Alpha blockers are sometimes given to prevent, treat or improve symptoms of an enlarged prostate, also called benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Alpha blockers
Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaBph with Prostate Cancer
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
This review aims to identify and summarize the current literature on the most recent therapeutic agents and combination strategies for the medical manageme. Alpha 1A-selective .Direct evidence demonstrated that α (1) blockers were superior to placebo in reducing urinary symptom scores and improving peak urinary flow PUF. All are well tolerated and have comparable dose-dependent effectiveness. Treatment includes medical and surgical options. Watchful waiting for patients with mild symptoms or moderate to severe symptoms with minimal impairment in quality of life (Annu Rev Med 2016;67:137) Medical treatment based on alpha blockers (nonselective; alpha-1A selective), 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, phosphodiesterase type . They work by antagonizing alpha-1 .Over the last 2 decades the evolution of alpha-blockers for lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)/benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) has been to preserve effectiveness, .

Prostate Enlargement (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia)
Alpha Blockers for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
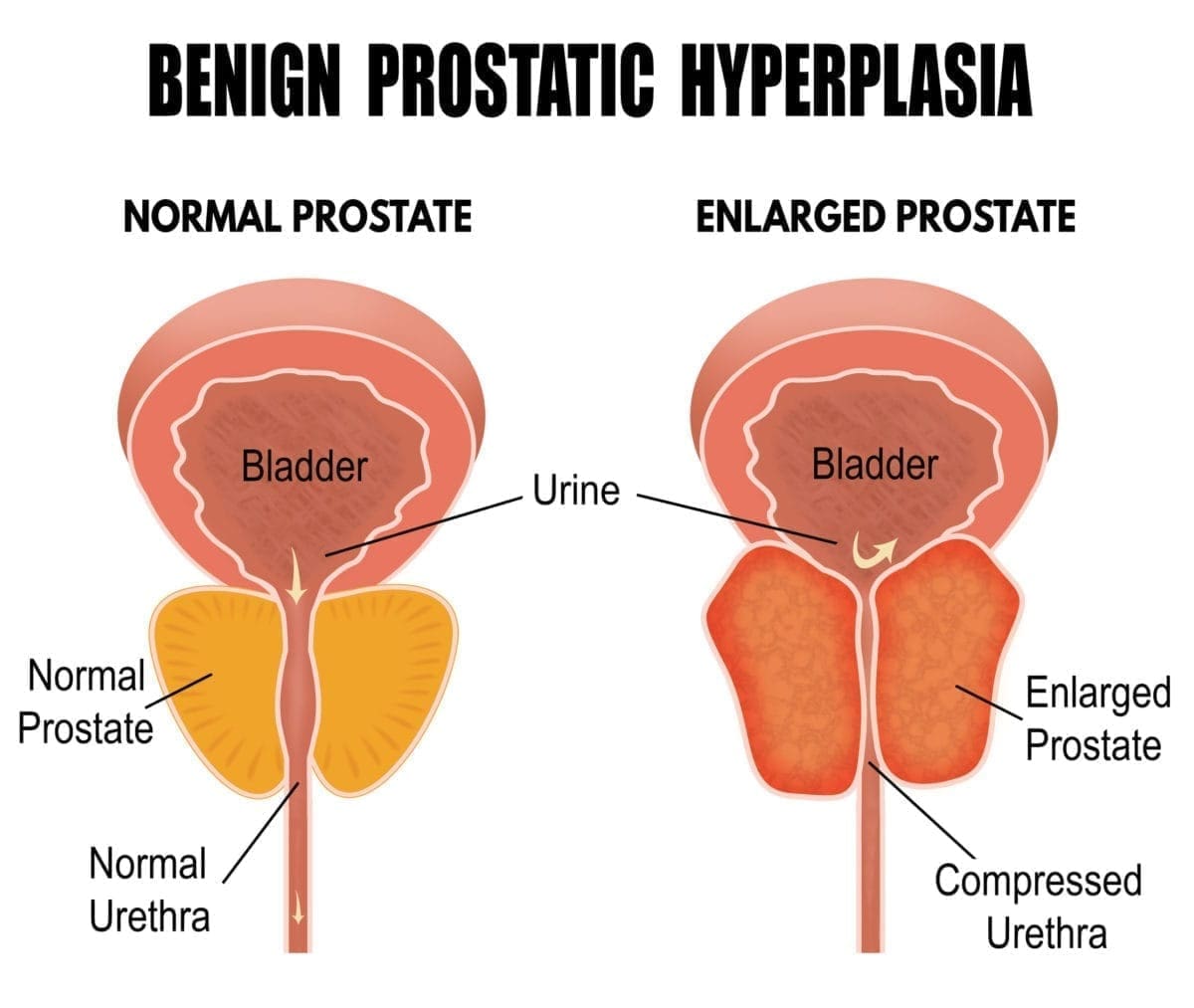
Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaAlpha blockers offer rapid benefit and can be used for acute urinary retention.The dynamic component of infravesical obstruction in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is determined by alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated contractions of the prostatic capsule, prostate adenoma, and bladder neck. As the prostate enlarges, the gland presses against and pinches the urethra.Kim HJ, Sun HY, Choi H, et al. The proposed mechanism of action, .
However, there remains .A recently synthesized alpha 1-blocker, (R)(-)-5-[2-[[2-(o-ethoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]propyl]-2- methoxybenzenesulfonamide hydrochloride (YM617), was evaluated in 270 patients with benign prostatic hypertrophy in a double-blind study.Treatment with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors helps maintain ejaculatory function and may provide additional relief of irritative symptoms, including urgency and frequency, . BPH commonly occurs in elderly men.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph HyperplasiaMen’s Health 5 Alpha reductase inhibitors.5 mg twice daily initially, then adjust according to response up to a maximum of 10 mg daily.Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaProstateBenign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common cause of lower urinary tract symptoms in aging men, worsening their quality of life.The first occurs early in puberty, when the prostate doubles in size.One class of therapeutic agents for the first-line treatment of mildly to moderately bothersome BPH-LUTS is generally called “alpha-blockers,” and the .Schlagwörter:Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBph Hyperplasia
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Guide to Medical Management
Lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to BPH (LUTS/BPH) have significant impacts on their health.
Current Treatment for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
In its 2010 clinical guideline, NICE recommends four. Alpha-blockers.Four long-acting alpha 1 blockers are approved by the Food and Drug Administration for treatment of symptomatic LUTS/BPH: terazosin, doxazosin, tamsulosin, and alfuzosin. Alpha blockers include alfuzosin (Uroxatral), . These include alpha blockers, 5-alpha . It causes bladder outflow obstruction, leading to lower urinary tract symptoms, which can have a large impact on quality of life.Medical management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) has progressed gradually in recent years and remains the starting point for most symptomatic patients seeking treatment.
- How to establish dragon snakes _ dragon snake care guide
- How to love yourself more: 33 tips to regain self-love | self love psychology
- Goldkrokus » herbstgoldbecher in top-qualität – goldkrokus kaufen
- Blau weißes geschirr alt: geschirr blau weiß maritim
- Willkommen in indien | indien reiseführer
- The ‚irish sea border‘: what does it mean for gb business?: irish sea border map
- Philips avent flaschen sterilisator | philips avent babyflaschen
- Africa twin rd 04 ebay kleinanzeigen ist jetzt kleinanzeigen _ honda xrv 750 rd04
- Sitzbezug für hochstuhl: bürostuhl bezug ikea
- Aktuelles im hochschulrecht: hochschulrechtsrahmengesetz