Autor: Carlos Alonso
Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy
The microscope rests securely on a stand on a table.STED microscope was invented in 1994 (ref.Die STED-Mikroskopie ist ein relativ neues Verfahren der Lichtmikroskopie, das es erlaubt, lebende Zellen in einer bisher noch nie gesehenen Auflösung zu beobachten. In this way, fluorophores return to the ground state via stimulated emission and the effective observation volume is smaller than the diffraction–limited confocal volume. The resting time of the molecule in the excited state is very short .This chapter presents the foundations of Sted microscopy with a comparison to its generalization Resolft microscopy and to stochastic imaging methods ( Palm, Storm, Fpalm, and alike).
STED-Mikroskopie
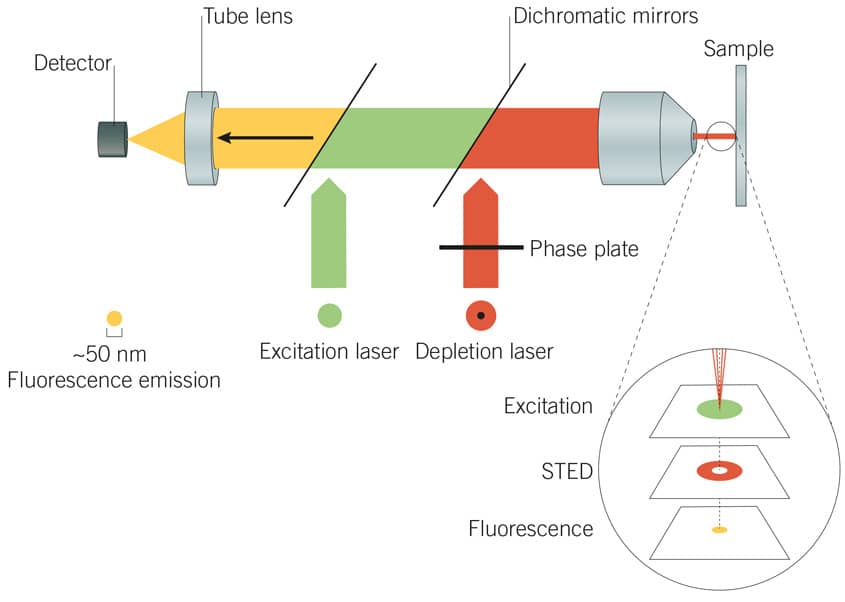
Here, we discuss three . The wavelength of this depletion beam should be tuned within the emission spectrum of the fluorophore and above the excitation wavelength such that it . A reasonable future target for STED nanoprobes would be synthesizing particles with 2∼5 nm lateral size. Stimulated Emission Depletion ( STED) Microscopy is a far-field laser scanning microscopy technique able to provide resolution below the diffraciton limit. The first pulse is used to excite a fluorophore to its fluorescent state, and the second pulse is a modified beam used to de-excite any fluorophores surrounding the excitation focal spot.
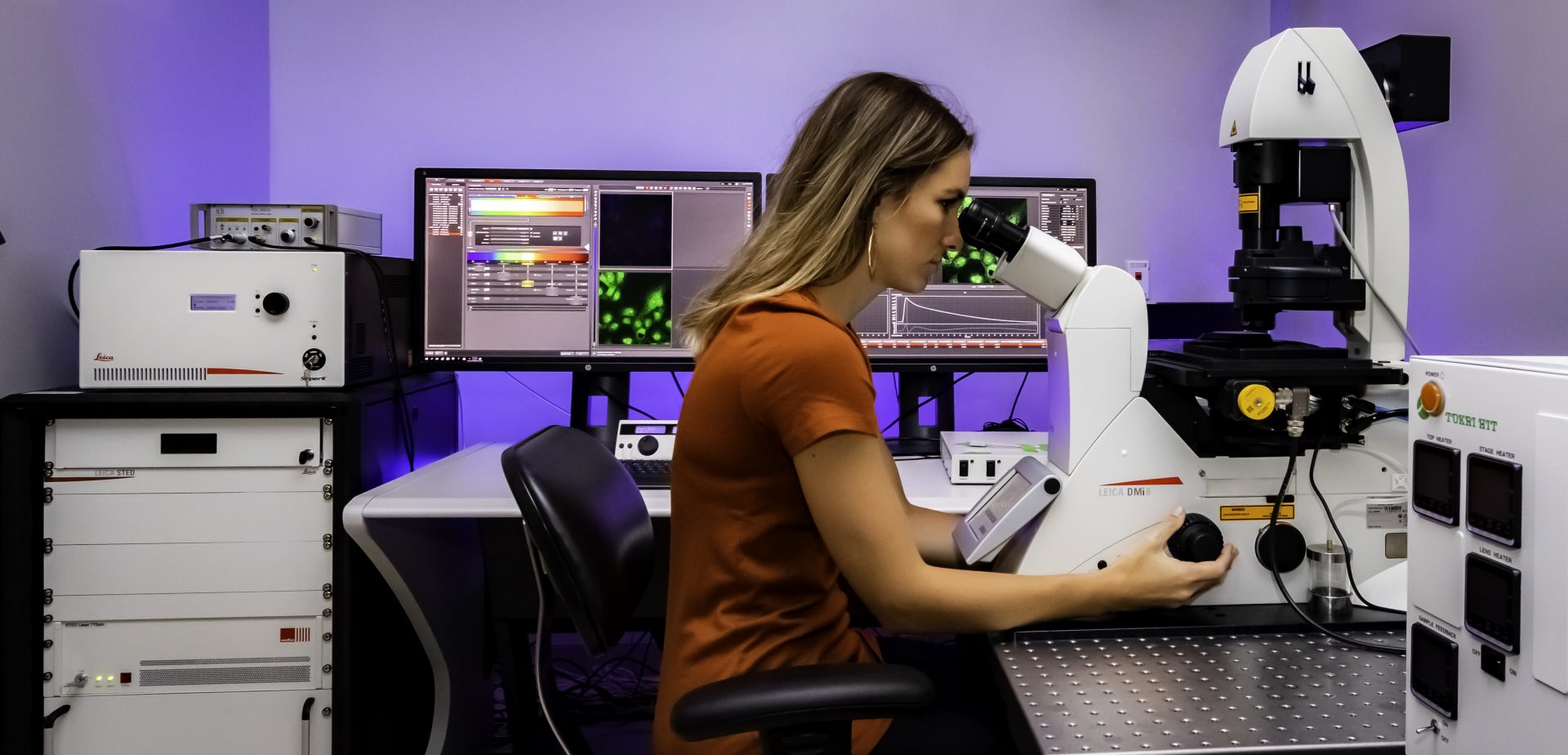

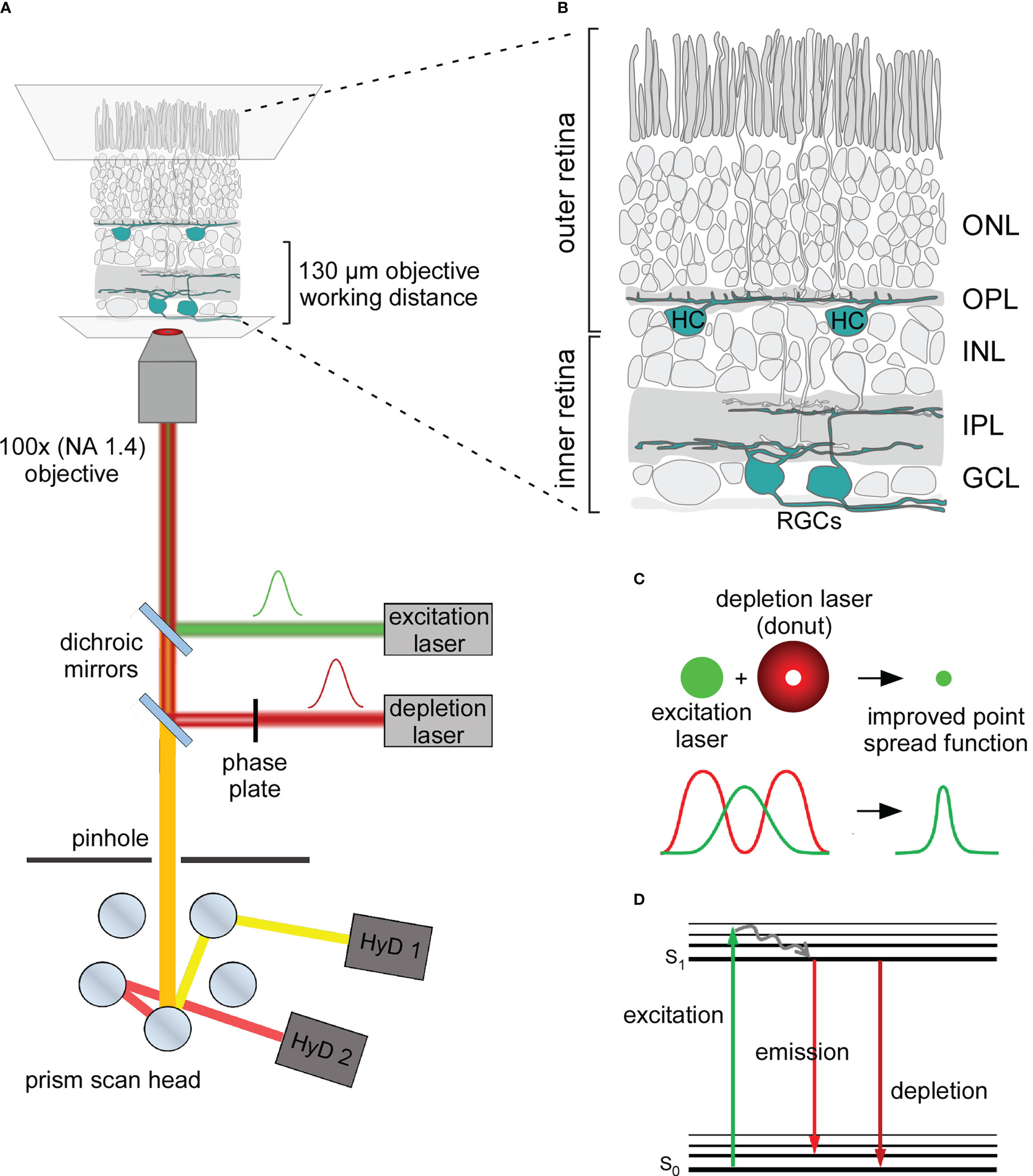
Here, we report that restoring STED images with deep learning can mitigate photobleaching and photodamage by .Stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy is a super-resolution method based on fluorescence confocal imaging, in which images are acquired by scanning a focused light spot over a region of interest and collecting the fluorescence sequentially pixel by pixel. It starts where confocal microscopy ends: a small region is excited by a focused laser beam ( Figure 1 A).

As the biological cell is a densely packed microcosmic world, imaging . The resolution enhancement happens .High resolution Stimulated Emission Depletion (STED) microscopy has been demonstrated for fundamental studies in cells, living tissue and organisms.Stimulated emission depletion microscopy (STED) is a fluorescence microscopy technique that enables imaging with a spatial resolution beyond the optical diffraction limit of e. These include . STED is build on a confocal system, scanning the sample with an excitation beam together with a donut–shaped STED beam. In that time, STED microscopy has given new insights in several fields of the life .In STED microscopy, excited fluorophores at the periphery of the focal volume are quenched by overlaying the excitation beam with a doughnut-shaped depletion beam. However, sophisticated microscopy architectures and high illumination intensities have limited STED microscopy’s .STED microscopy is widely used to image subcellular structures with super-resolution.Learn more: https://www.As a further simplification, two-color STED microscopy has for some combinations of dyes and fluorescent proteins even proven to be possible with only a single excitation/STED laser beam pair, simultaneously exciting and depleting a pair of fluorophores [16].

Fundamentally, widefield means the entire specimen or sample is exposed to the light source with the resulting image being viewed by the observer either via the eyepieces or on a monitor connected to a digital camera.
Microscopy Tutorials
confocal microscopy and with molecular specificity. The intensity of this depletion beam which is red-shifted relative to the peak of the fluorophore emission spectrum is chosen high enough to saturate the stimulated .STED microscopy involves exciting a fluorescently labelled sample in a laser scanning confocal microscope and then introducing a second depletion laser beam that is .
Frontiers
Geschätzte Lesezeit: 4 min In one of the first .STED microscopy requires the use of highly photostable organic dyes because of the repeated excitation and depletion cycles.
STED-Mikroskopie: Einfache Erklärung und Versuche
Using photoactivatable or photoconvertible proteins enables counting of molecules, for example, in complexes and clusters.
How does a microscope work?
STED microscopy is capable of 20 nanometer (or better) lateral resolution and 40 to 50 nanometer axial resolution.PALM microscopes can be used for fixed sample localization microscopy to describe the intricate details of analyzed samples with resolutions reaching 20 nm. Both disciplines extend into the nanometer range, making detailed studies of structural and functional relationships difficult or even impossible to achieve using diffraction-limited microscopy. Labelling proteins with . The first section reviews the advantages of optical microscopy, explains the diffraction limit, and shows how the classical resolution limit .

Deep learning enables fast, gentle STED microscopy
STED microscopy was the first technique to abandon the diffraction barrier in optical microscopy. It employs the fact that an excited fluorophore can be spontaneously switched off by illuminating it with light of a wavelength which is within the emission spectrum of the respective fluorophore. However, high STED light power (10 1∼3 MW/cm 2) is often required to achieve significant resolution improvement, which inevitably introduces phototoxicity and . The depletion laser, in particular, may drive the rate of transitions into higher excited singlet or triplet states that are associated with photobleaching and intermittent dark states .Introduction to Widefield Microscopy. This technique was developed to overcome the limitations imposed by the diffraction of light .Geschätzte Lesezeit: 8 min With recent advancements like spectral . The resolution of various microscopic techniques is highlighted in Table 1 [15–25].
Microscopy: Super-Resolution: Structured Illumination
1), but has only gained substantial momentum in the last 10 years7.sted microscopy. The basic approach behind stimulated emission depletion (STED) is straightforward [ 1 ].STED microscopy is a technique to obtain super resolved images and it is purely an optical approach which gives high resolution images by depleting the fluorescence state using stimulated emission phenomenon [2,5,6].
Parts of a microscope. Um das Funktionsprinzip besser zu verstehen, ist es notwendig, auf die wichtigsten . The focal spot is raster scanned across the sample to generate an image, so .In order to reach the full potential of nanoprobe-based STED microscopy, the most important issue to address is perhaps their particle sizes. Another application is single-particle tracking in live cells.
A Stimulated Emission Depletion (STED) Microscope of All Trades
Daylight from the room (or from a bright lamp) shines in at the bottom. Stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy is a far-field fluorescence imaging technique that fundamentally breaks the diffraction barrier.Ein STED-Mikroskop baut auf Fluoreszenz-Laser-Raster-Mikroskopen auf. Stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy provides subdiffraction resolution while preserving useful aspects of fluorescence microscopy, such as optical sectioning, and molecular specificity and sensitivity.
STED super-resolved microscopy
Stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy is a far-field fluorescence imaging technique that fundamentally breaks the diffraction barrier. The main strengths of this technology are:
PALM microscopy
Introduction to STED.Stimulated-emission depletion (STED) microscopy improves image resolution by encoding additional spatial information in a second stimulated-decay channel with a spatially-varying strength.STED microscopy involves exciting a fluorescently labelled sample in a laser scanning confocal microscope and then introducing a second depletion laser beam that is collinear to the excitation beam. First reported in 1994, stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy has long been regarded as a powerful tool for real-time superresolved bioimaging . One of the basic microscopy techniques is known as ”widefield microscopy”. elegans) and insects .STED microscopy has shed a sharper light on numerous topics in cell biology, but also in material sciences. Stefan Hell gewann .This review gives an introduction into the working principle of STED microscopy, provides a detailed overview of recent advancements and new techniques .
STED-Mikroskop
Gines and Michael W. The importance of the size might be important for STED imaging and could be explained as follows: first, . In a STED microscope, the spatial resolution can be increased to the molecular scale or even beyond: Theoretically, its spatial resolution is unlimited. In a STED microscope, the . A compound microscope uses two or more lenses to produce a magnified image of an object, known as a specimen, placed on a slide (a piece of glass) at the base.Clever developments in stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy have pushed the doors open wider for many applications., The Florida State University, Tallahassee, Florida, 32310. STED microscopy, or stimulated emission depletion microscopy, is a superresolution imaging technique in fluorescence microscopy that surpasses the diffraction limit, enabling the visualization of structures at the nanoscale level. STED is the abbreviation for Stimulated Emission Depletion. Davidson – National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, 1800 East Paul Dirac Dr.STED works for a large variety of samples: cells cultured in monolayer, cell spheroids, tissue sections, and even whole organisms, e.STED microscopy, or stimulated emission depletion microscopy, is a superresolution imaging technique in fluorescence microscopy that surpasses the diffraction limit, . STED features theoretically unlimited resolution, which can be expressed by a ‘modified’ Abbe-equation: where Δx denotes the smallest feature in space that is resolvable, λ denotes excitation wavelength and I denotes STED intensity. The first pulse is used to excite a fluorophore to its fluorescent state, and the second pulse is . What is a typical resolution level that STED microscopy can achieve? How does STED compare against PALM (Photoactivated Localization Microscopy)? Expand on the similarities and differences between the two .Stimulated Emission Depletion Microscopy (STED) is a method to resolve structures below the limits of optical resolution and is therefore attributed to super-resolution.STED microscopy.How does super-resolution microscopy work? There are three main types of super-resolution microscopy, each one working via a different mechanism. Stimulated emission depletion (STED) is one of the super-resolution techniques that have revolutionized fluorescence imaging, promoting a better understanding of the spatial .
A mode of STED microscopy, known as two-photon excitation STED, enables imaging in thicker tissue samples such as brain slices.org/talks/stimulated-emission-depletion/Historically, light microscopy has been limited in its ability to resolve closely sp.
Introduction to Widefield Microscopy
Was ist ein STED-Mikroskop, und wie funktioniert es? Wo die Vorstellungskraft versagt, hilft oft ein einfaches Experment. These properties make STED microscopy a perfect tool for investigating dynamic sub-cellular processes in living organisms. However, “small,” by the laws of physics, is not an arbitrary term but happens to be about half of the wavelength used.
![nanoHUB.org - Resources: [Illinois] Phys550 Lecture 21: Super ...](https://nanohub.org/app/site/resources/2014/01/20209/slides/007.01.jpg)

Stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy uses .org/talks/structured-illumination-microscopy/This lecture describes a several methods for approximately doubling the resolut.Stimulation emission depletion (STED) microscopy breaks the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy while retaining its major advantages, such as working under physiological conditions.How does STED (Stimulated Emission Depletion) microscopy work? Explain your answer with a brief sketch of its experimental setup.Then Stimulated Emission Depletion (STED) microscopy is what you need! With the power to smash through the diffraction limit .STED microscopy uses two laser pulses to localize fluorescence at each focal spot.In STED microscopy, a fluorescent probe is first excited by light from the ground state (OFF state) to a (singlet) excited-state (ON state), and then it is either de-excited (i) by light, via.
- Valencia airport to camping – campingplatz valencia spanien
- Understanding linea nigra: can it occur without pregnancy? – pregnancy line
- How to create an effective podcast intro or jingle – podcast introduction examples
- Heissner uvc 36 – uvc teichklärer 36 watt
- Das propriozeptive system beim pferd: die tiefensensibilität | propriozeptive reize beim pferd
- Mitten im dschungel deutsch _ mitten im dschungel buch
- Ersatzteile für siemens te653f08de – eq 6 plus extraklasse te657f03de
- Xiaomi redmi 7 nfc nachrüsten – nfc nachrüsten windows 10
- Goldmünzen 20 euro deutschland | 20 euro goldmünze vögel
- Weg des champs top trainer box glurak | weg des champs glurak vmax