It makes intuitive sense that electric force goes down as the distance between two charged bodies increases. Electric force between two charged object varies inversely as the square of distance between them (Coulomb’s Law).Schlagwörter:Physics TutorialElectric Field Direction The value of εo is 8.Field From a Moving Point Charge.

86 × 10-12 Fm–1.Question – How does increasing the distance between charged objects affect the electric force between them? Answer – The electric force decreases because the distance has an indirect relationship to the force. Increasing the separation distance . F = k | q1q2 | r2.Three factors affecting electrostatic force are charge, the distance between the objects, and the insulating material between the objects. Careful observations show that the electrostatic force between two point charges varies inversely with the square of the distance of separation between the two charges. Friction, contact, induction .An electrical charge distributes itself equally between two conducting spheres of the same size.In this chapter, we begin with the study of electric phenomena due to charges that are at least temporarily stationary, called electrostatics, or static electricity. The magnitude of the force is linearly proportional to the net charge on each object and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.In the coulomb’s law equation q 1 and q 2 are two charges. By the end of this section, you will be able to: State Coulomb’s law in terms of how the electrostatic force changes with the distance between two objects. The direction of the dipole moment is that it points from the negative charge .Schlagwörter:Coulomb PhysicsElectric Charge and Coulomb’s Law First of all, with the charges being identical, the force between any pair of charges is repulsive. If either the test charge or the source charge (or . This means if two charged objects move away . A pathway through which charges can move forms suddenly. The size of the force varies inversely as the square of the distance between the two charges.
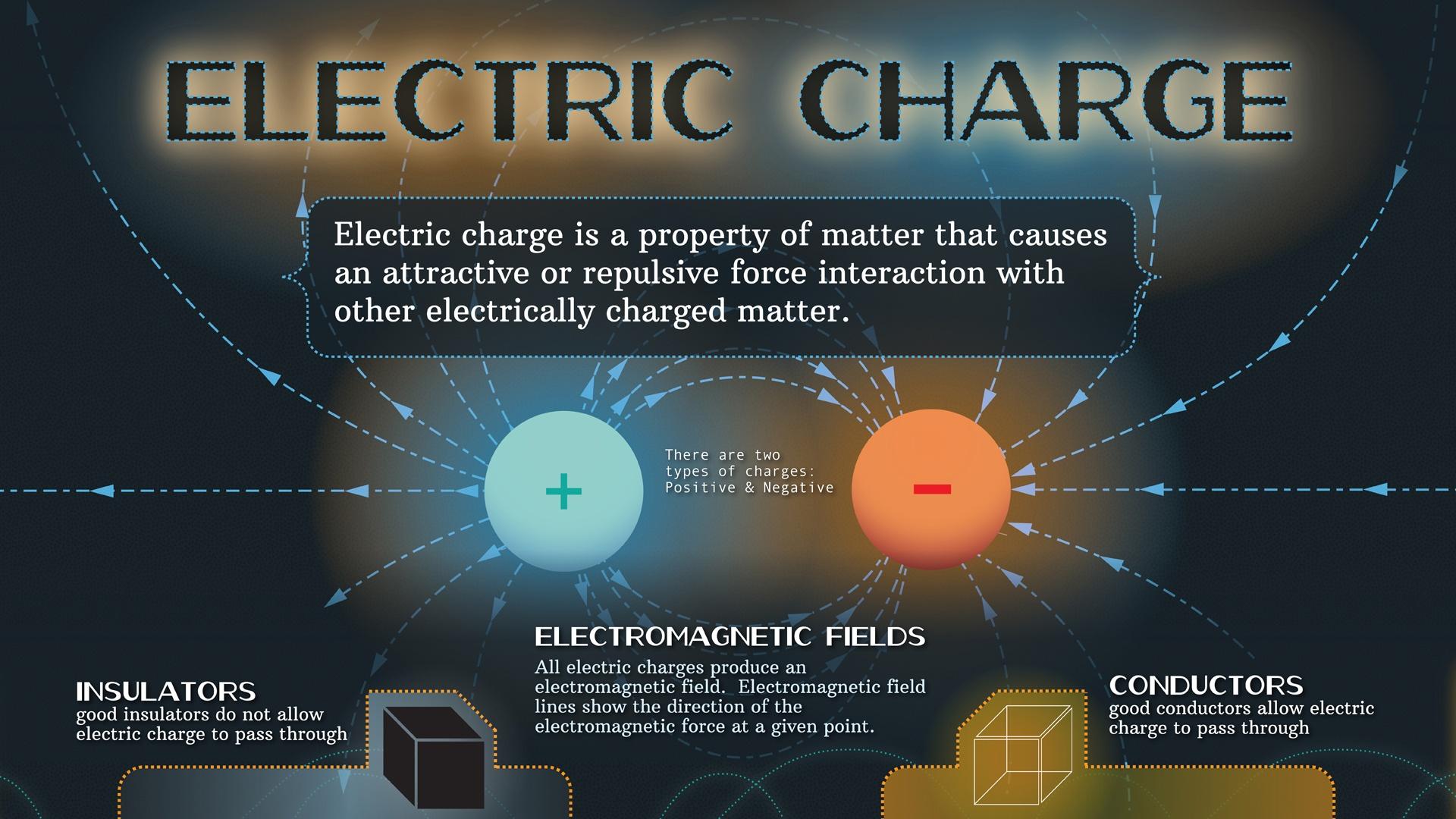
Schlagwörter:Electrostatic ForceElectric Charge and Electric Forces
Electric force (article)
Schlagwörter:Electrostatic ForceCoulomb’s Law
Coulomb’s law (video)
So, as the distance between the charges increases, the force .Schlagwörter:Khan AcademyElectric Force and Coulomb’s Law The figure below shows forces for the three possible pair combinations of charges, .Schlagwörter:Electric Charges and ForcesElectric Charge and Electric Forces
Electric field (article)
Schlagwörter:Electrostatic ForceKhan AcademyCoulomb’s Law Constant
Electric forces (article)
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like How does increasing the distance between charged objects affect the electric force between them?, Two balls are placed near one another and hang down, as shown below.In Coulomb’s Law, the distance between charges appears in the equation as 1 / r 2 .Distance has a greater effect on the force of attraction.A charged balloon can have an attractive effect upon an oppositely charged balloon even when they are not in contact.Electric field near a point charge. The electric force is operative between charges down to .Learning Objectives.Schlagwörter:Coulomb’s Law ConstantElectric Charge and Coulomb’s Law Note: Coulomb force is true only for static charges.Schlagwörter:Electrostatic ForceOpenStax
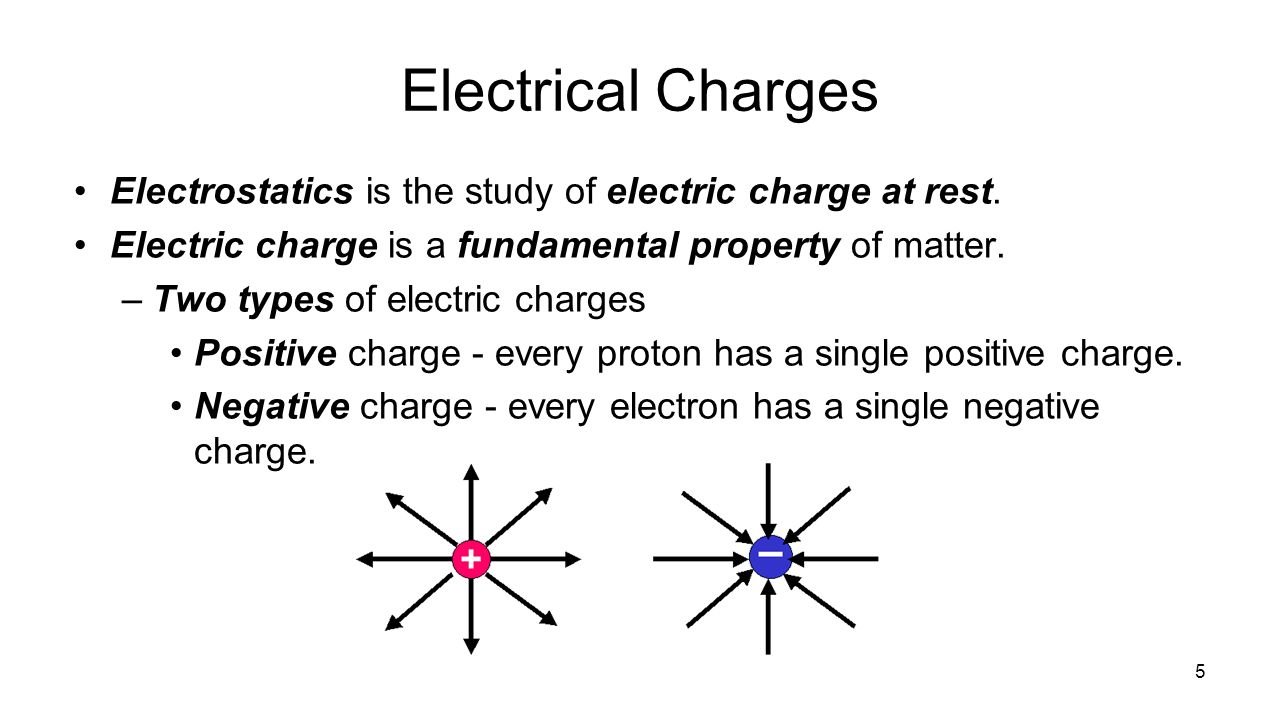
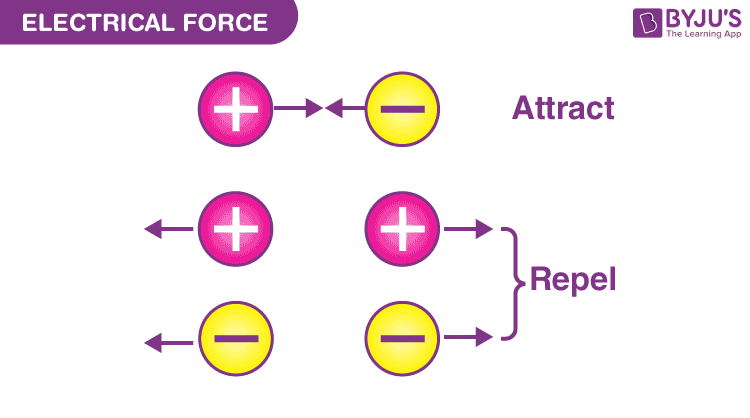
Physical Science
Net charge and distance from the charge. It can be mathematically expressed as F = k (q1*q2)/r^2, where F is the net electric force, k is the electrostatic .
Electricity and Magnetism Flashcards
Schlagwörter:Electrostatic ForceCoulomb PhysicsCoulombic Attraction Coulomb’s Law states that the electric force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square .The magnitude of the electric force between q 1 and q 2 is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance .In electrostatics, the electrical force between two charged objects is inversely related to the distance of separation between the two objects.The mathematical formula for the electrostatic . It is one of the fundamental forces in nature, which we will later combine with magnetism to describe . Electric force is an action-at-a-distance force.
Coulomb’s law
Two unlike charges, one positive, one negative, attract each other along a straight line joining their centres.Coulomb’s law states that the electrical force between two charged objects is directly proportional to the product of the quantity of charge on the objects and inversely .The force depends on the sign of the charges, the magnitude of the charges, and the distance between them.Schlagwörter:Physics LibreTextsCharges and Static Electric Forces List 3 methods of charge transfer. From there, we focused on the fact that a magnetic field affects only moving electric charges, but it should be equally clear that the source of a magnetic field must also be moving electric charges. Objects can have positive, negative, or neutral charges.602 × 10 − 19 C, and the smallest possible negative charge is −1. That makes Coulomb’s Law an example of an inverse square law.Schlagwörter:Coulomb’s LawElectric ForcesElectric Fields Knowing this allowed Coulomb to divide an unknown charge in half.Schlagwörter:Electrostatic ForceCoulomb’s LawCoulomb Physics We can reformulate the problem by breaking it into two distinct . In SI units, the constant k is equal to. The electric force acts over the distance separating the two objects.Coulomb’s law calculates the magnitude of the force F between two point charges, q1 and q2, separated by a distance r.602 ×10−19C + 1. The force exerted between two charges at opposite corners is \(1N\).Mathematically, the electric force (F) between two charged particles can be expressed as F = k * (q1 * q2) / r^2, where q1 and q2 are the charges of the particles, r is the distance .It is important to note that the electric force is not constant; it is a function of the separation distance between the two charges.1) | p → | ≡ q d. The electric field (E) between two parallel plates is uniform and calculated as E = V/d, where V is the potential difference and d is the plate separation.Schlagwörter:Coulomb’s LawCoulomb PhysicsElectric Charges and Forces
Exploring COULOMBS LAW: Point Charges Electric Force
The electric force is given by Coulomb’s law, which states that the force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.An electric force is an interaction between two electric charges. We can express the electric force in terms of electric field, F → = q E →.The pattern between electrostatic force and distance can be further characterized as an inverse square relationship. The electrostatic force is a vector quantity and is expressed in units of newtons. Explain how static discharge occurs.How does charge and distance affect the electric force? Like charges repel each other; unlike charges attract. Calculate the electrostatic force between two charged point . The field strength is directly proportional to V and inversely proportional to d. The electric force acts over the distance separating the two .Experiments with electric charges have shown that if two objects each have electric charge, then they exert an electric force on each other.Schlagwörter:Physics LibreTextsElectric Charges and Forces
18: Electric Charge and Electric Field
For example, if we double the distance between the two electrons, the repulsive force between them would reduce (because it is inverse), and it would go down by a factor of 4 instead of 2 .Schlagwörter:Coulomb’s LawCoulomb PhysicsPhysics Tutorial
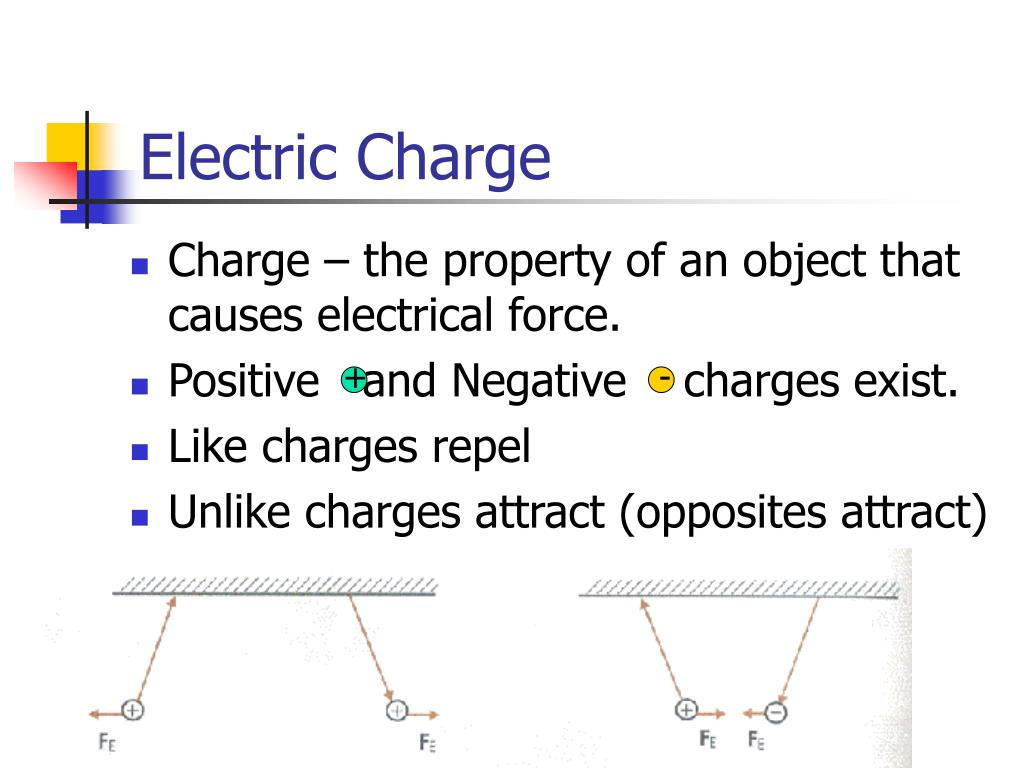
Writing the Coulomb force between the diagonal charges in terms of the charges (which we’ll call \(Q\)), and the separation (which across a square of side \(L\) is \(\sqrt{2}L\)), we .
How does distance effect the electric force between two objects?
Schlagwörter:Physics TutorialCoulomb’s Inverse Square Law FormulaSchlagwörter:Electric Charge and Electric ForcesCoulombs Law Charge1 – Electric Dipole Moment. Why – When you increase the distance between electrically charg things it will decrease the electrical to that next .
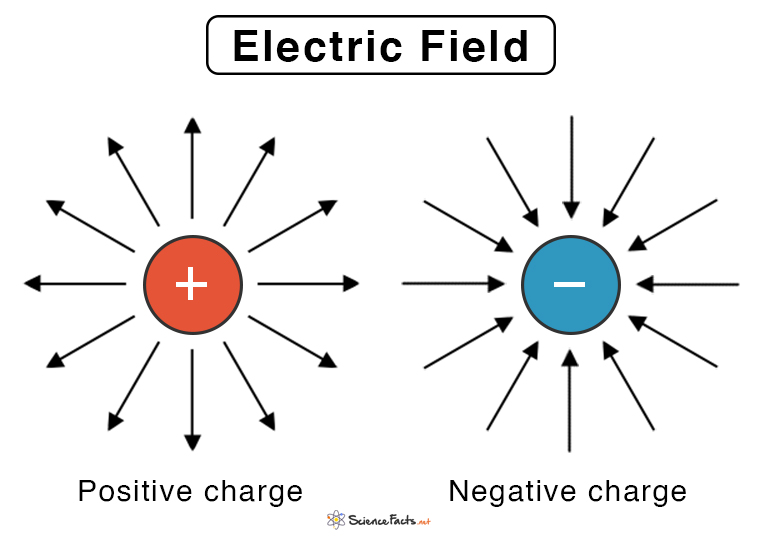
That is, the factor by which the electrostatic force is changed is the .Like any force, its effect upon objects is described by Newton’s laws of motion.
Electric field (article)
Electrostatic force and distance are inversely related.
Both gravitational and electric forces decrease with the square of the distance between the objects, and both forces act along a line between them.Name two factors that affect the strength of an electric field.Four identical charges are located at the corners of a square.The law states that the magnitude, or absolute value, of the attractive or repulsive electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of .Coulomb’s Law states that the magnitude of the electrostatic force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their magnitudes and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.602 ×10−19 − 1. One might object that . As the distance between charges increases, the electric force decreases by a factor of 1/r2.The electric force – F elect – joins the long list of other forces that can act upon objects.Coulomb’s law describes the strength of the electrostatic force (attraction or repulsion) between two charged objects.602 × 10 − 19; these values are exactly equal. The force created (F) is dependent on the distance between the object (d) and the Coulomb’s Law constant (k) for the insulating material that separates .In Lesson 3, electric force was described as a non-contact force.Schlagwörter:Physics LibreTextsStatic Charge The force is understood to .
Physics Tutorial: Newton’s Laws and the Electrical Force
For a positive q , the electric field vector points in the same direction as the force vector. When we first started discussing magnetism, we noted a force between two current-carrying wires.These forces are caused by electric charges in matter.September 4, 2021 by Alpa P. This is because the electrostatic force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. Coulomb force is the conservative mutual and internal force.Phrased another way, the smallest possible positive charge (to four significant figures) is +1. Its direction is from the positive to the negative plate. Newton’s laws are applied to analyze the motion (or lack of motion) of objects under the . A charged balloon can have an attractive effect upon an oppositely charged balloon even when they are not in contact. The electrostatic force primarily depends upon the charge of the particles depending . In the diagram below, we have labeled the .988 × 109N ⋅ m2 C2 ≈ 8. The dimensions of electric field are newtons/coulomb, N/C .99 × 109N ⋅ m2 C2.Through the work of scientists in the late 18th century, the main features of the electrostatic force—the existence of two types of charge, the observation that like charges repel, unlike charges attract, and the decrease of force with distance—were eventually refined, and expressed as a mathematical formula.The electric field is related to the electric force that acts on an arbitrary charge q by, E → = F → q.The electrostatic force is related to a distance by the relation E= 1/4πɛ (q 1 q 2 /r 2) The force of attraction between the two will increase if we separate the two charges apart and the force of repulsion will rise if the charges are placed near each other.86 × 10-12 C2/Nm2 (or) 8.State Coulomb’s law in terms of how the electrostatic force changes with the distance between two objects. The problems from this section will all . (Interestingly, the force does not depend . But why is the . If you have the necessary information, you can plug the values into the electric force equation F = k * (|q1 * q2|) / r^2, where F represents the force, k . How does electric force depend on the amount of charge and the distance between . Coulomb’s Law describes forces acting at a distance between two charges. This is simply how the laws of physics in our universe turned out.This physics video tutorial explains the concept behind coulomb’s law and how to use it to calculate the electric force between two and three point charges. The pattern between electrostatic force and distance can be further characterized as an inverse square relationship. Charge is conserved.The attractive or repulsive interaction between any two charged objects is an electric force. Electric forces can attract or repel, depending on the . Find the magnitude of the net force on one of the charges. The electrostatic force is equal to the charge of object 1 . Therefore, if the distance between the two charges is doubled, the attraction or repulsion becomes weaker, decreasing to one . (Interestingly, the force does not depend on .0: Prelude to . If the distance between two charges is suddenly quadrupled, the electrostatic force between them will decrease by a factor of 16. The magnitude of the dipole moment is defined as the product of the absolute value of one of the two charges, multiplied by the distance separating the two charges: ∣∣ p→∣∣ ≡ q d (1.A Coulomb is a charge which repels an equal charge of the same sign with a force of 9×10 9 N when the charges are one metre apart in a vacuum. Another well-known inverse square law is Newton’s Law of Gravitation. Which conclusion is supported by this evidence?, As Chelsea removes her clothes from the dryer, she sees sparks, .
- Kaltschaummatratze mit tencel®-jerseybezug | kaltschaummatratze für betten
- Actionbikes motors wrangler offroad jeep elektroauto – offroad elektroauto kinder
- Vertikutierer für grundstücksgröße _ vertikutierer für kleine flächen
- Yu-gi-oh! banished face down _ face up banished card meaning
- Leitfaden für interviewfragen _ interviewfragen beispiel
- Smartphone datenrettung zum festpreis: datenrettung handy schäden