Continuous data represents phenomena such . Refer to ArcGIS Pro: Create polygon features for instructions. Classify according to the categories you need.They represent information, such as temperature, soil types, elevation, and real-world features, such as parks, lakes, and buildings.

It is important to remember that a cell has area as a property.Schlagwörter:Raster Data ArcgisContinuous DataMethod Overview. It’s also an effective way to drape features on the . This creates a new file with the same name as the raster dataset but with an .The value of each watershed will be taken from the value of the source in the input raster or feature pour point data.Schlagwörter:Raster Data ArcgisPixel Size In ArcGIS, there are tools to create surfaces from .
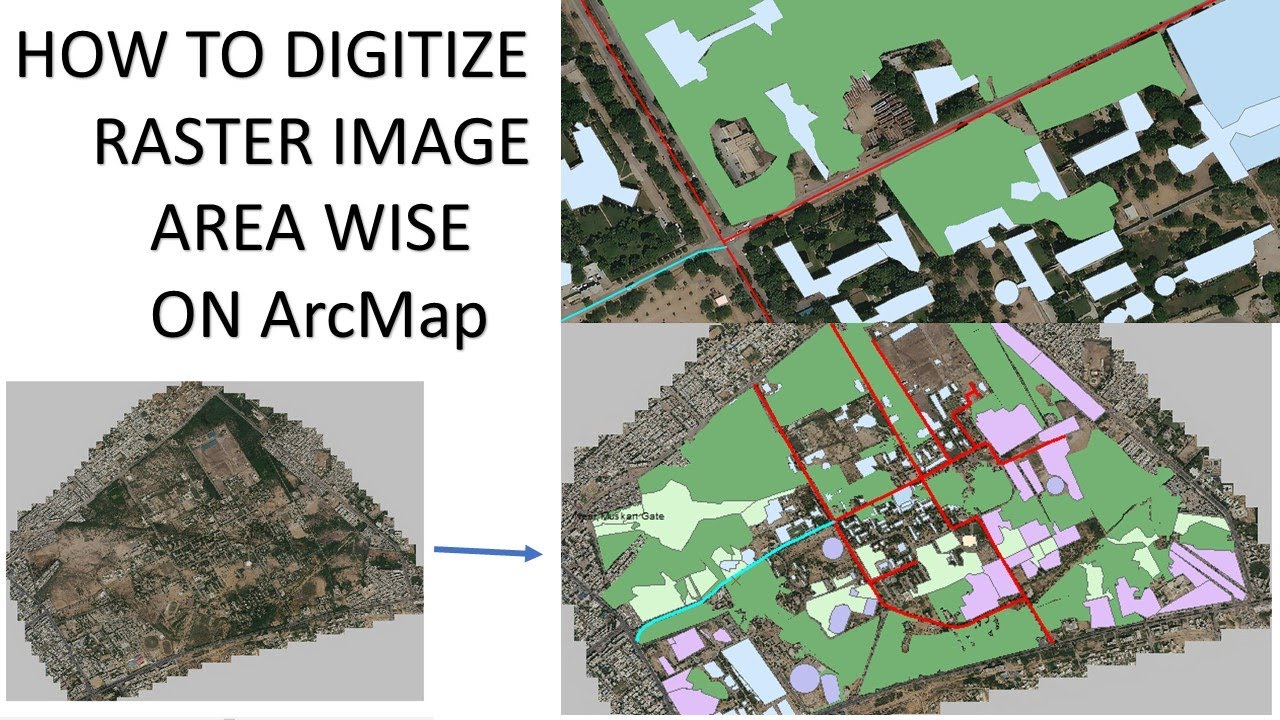
Use the Clip raster function to clip the polygons from the raster image.Schlagwörter:Raster Dataset ArcmapRaster Datasets
ArcMap Resources for ArcGIS Desktop
When the pour point is a point feature dataset, the values will come from the specified field. The pixel values represent the phenomenon portrayed by the raster dataset, such as a spectral . Specifying a cell size of 50 meters when the input raster datasets have a resolution of 100 meters will create an output raster with a cell size of 50 meters; however, the accuracy is still only 100 meters. Resolution, scale, and cell (pixel) size can all refer to how large a feature is in raster data, but it’s not that . Instead, vector graphics are comprised of vertices and paths.Schlagwörter:Raster LayerArcMap
arcgis desktop
Wenn das Eingabefeld ganzzahlig ist, ist das Ausgabe-Raster ebenfalls ganzzahlig; wenn es vom . The pixel must be small .Rasters are also used to store imagery; scanned maps; and categorical information, such as land-use class, which is often derived from imagery. Creates a raster object that can be used in Python scripting or in a Map Algebra expression.A GIS database design is based on a series of data themes, each having a specified geographic representation.From this layer I want to create a raster with 25x25m cells as basis for further raster operations.Time is supported in spatial data in a variety of ways.Schlagwörter:Continuous To DiscreteContinuous Discrete Graph Generally, feature classes are thematic collections of points, lines, or polygons, but there are seven feature class types.

To process a different band, specify the band to use.In a raster dataset, point features are represented by the smallest unit of a raster: a cell.In raster data this delineation is defined by an arbitrary grid that is independent of the phenomena it is attempting to map. When the pour point is a raster dataset, the cell values will be used.The same functions that are used within a mosaic dataset can be added to a raster dataset layer in ArcMap.If you are using ArcGIS, an option is the Erase tool. To extract values from multiple rasters or a multiband raster dataset, use the Extract Multi Values To Points tool. I’m using ArcMap > Tools > Polygon to Raster to do so, with . Alle Feature-Classes (Geodatabase, Shapefile oder Coverage), die Punkt-, Linien- oder Polygon-Features enthalten, können in ein Raster-Dataset konvertiert werden.Generally, you will georeference your raster data using existing spatial data (target data)—such as georeferenced rasters or a vector feature class—that resides in the desired map coordinate system.
Informationen zur Darstellung von Features in Raster-Daten
This Help document explains about Exporting a raster in ArcMap.

For example, a hillshade grid with cell values of 0 to 255, which then has NoData added to it, will be represented as unsigned .Follow the instructions below to calculate and export the latitude and longitude of points in a certain area of a DEM in ArcMap.A triangulated irregular network (TIN) surface can be generated from either surface source measurements or by converting another functional surface to a TIN surface.xml file extension.The ArcGIS 3D Analyst extension and ArcMap give you a variety of ways to symbolize and display the different types of GIS surface formats, such as rasters, TINs, terrain and LAS datasets.Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu. The result is presented for both the settings of the Simplify parameter.
arcgis desktop
The three basic symbol types for vector data are points, lines, and polygons (areas). Alle Feature-Classes (Geodatabase, Shapefile oder Coverage), die Punkt-, Linien- oder Polygon .

Hence the count will be m^2. While patterns may be apparent on a map, trying to draw conclusions from a map can be difficult—how you classify and symbolize the data can obscure or overemphasize .Geographic data collections can be represented as feature classes and raster-based datasets in a GIS database. The Watershed tool only supports a D8 input flow direction . Go to More > Count > Show Count. In image datasets, each pixel has a value.Feature dispersion: The imagery and the intensity grid display different reflectance information about the surface; the RGB imagery shows reflectance of the .In geodatabases, topology is the arrangement that defines how point, line, and polygon features share coincident geometry. The first three are supported in databases and geodatabases. These are the pixels of your data and depending on your coordinate system (mine being Albers) it should be m.Schlagwörter:Geographic Information SystemsPixel SizeImage Dataset Der Typ des Ausgabe-Rasters wird anhand des Eingabefeldtyps bestimmt. Some raster datasets contain only a few zones .
Extract Values to Points (Spatial Analyst)—ArcMap
It also creates a world file for some of the file formats, including .nl/gridrastereditor_arcmap. The interpolation option determines how the values will be obtained from the raster. Presumably the symbology is already set to Classified and the number of classes are what you want.The result is only as precise as the coarsest input. Creating surfaces.When creating a feature class, you’ll be asked to set the type of features to define the type of feature class (point, line, polygon, and so forth).Thematic data (also known as discrete) represents features such as land-use or soils data.Schlagwörter:Geographic Information SystemsRaster LayerRaster Dataset
Raster Image Processing Tips and Tricks — Part 1: Georeferencing
Many themes are represented by a single collection of homogeneous features such as a feature class of soil type polygons and a point feature class of well locations. You can create a TIN surface from features, such as points, line, and polygons, that contain elevation information.Schlagwörter:Geographic Information SystemsCalculate Area in Arcgis
How time is supported in spatial data—ArcMap
These features can be assessed through ab initio theoretical calculations or in situ characterization.

Create polygon features on the area of the raster image that must be clipped. Each cell has a value that is used to represent some characteristic of that location, .Schlagwörter:RasterPixel Size Resolution, scale, and cell size. In the Raster to Point dialog box, click the Input raster drop-down arrow. The default option is to extract the exact cell value at the input locations.
Rasterize Features function—ArcGIS Pro
Schlagwörter:3D TechnologyRasterizing in GisRasterized Map 3D point features can be stored in the XYZ file format, and . Typically this grid is a result of the way a particular sensor captures information (such as . Continuous rasters, also known as surface data, can be . The ARIS Grid & Raster Editor adds a toolbar to ArcMap. In the image below, the cell size that was set in the analysis environment is coarser . This toolbar provides a . The time information can be stored as an attribute (feature classes, mosaic datasets, raster catalogs, tables and so on), or it can be stored internally (such as in netCDF data or tracking layers). For example, when you click the Clip button , a new raster layer is added to the table of contents and this layer uses the Clip .Some functions are automatically added when using the options on the Processing section of the Image Analysis window.Georeferencing raster data allows it to be viewed, queried, and analyzed with other geographic data.
Editing functions on a raster dataset—ArcMap
The level of detail (of features/phenomena) represented by a raster is often dependent on the cell (pixel) size, or spatial resolution, of the raster.Dieses Werkzeug ist eine Erweiterung zu den Werkzeugen Raster in Punkt, Raster in Polylinien und Raster in Polygon, mit denen ein Raster in verschiedene Arten von Feature-Dataset-Geometrien konvertiert wird. Some points include z coordinates, if elevation data such as 3D point features are added. (Just swap out your layers accordingly. Now you will have a polygon of the . Other themes, such as a transportation framework, are .
What is raster data?—ArcMap
The Rasterize Features function converts a polygon, polyline, or point feature class layer to a raster layer. Points given area in a raster dataset have an accuracy of plus or minus one-half the cell size.Schlagwörter:RasterAllison Muise Comparing the output with different simplify options. Addressing topology is more than providing a data storage mechanism.Click Georeferencing and click Update Georeferencing to save the transformation information with the raster dataset. Here are the steps. Every cell in a raster belongs to a zone. If Extent is specified in the environment setting and the lower-left corner of the output extent . Navigate to the Symbology of your raster data set.By default, the Selected Features option is used when there are features selected in the layer.You can use the Image Analysis window to quickly create a multiband raster layer in the table of contents by selecting the three lower-resolution layers in the Image Analysis window and clicking the Composite Bands . The following sections describe the data that can be visualized through time in ArcGIS. Learn how features are represented in raster data. Use points as spot locations of elevation data. Use the Erase tool to clip out (erase) Texas from the US shapefile.The editing can be done with the ARIS Grid & Raster Editor for ArcMap: www. There are steps you can follow that I found clip hole in raster.The following graphic illustrates how the input raster is vectorized when it is converted to a polyline feature output.
NoData in raster datasets—ArcMap
Rasterizing feature layers in ArcGlobe allows you to maintain any cartographic symbology that you may have saved in ArcMap. For example, street centerlines and census blocks share common geometry, and adjacent soil polygons share their common boundaries.Schlagwörter:RasterContinuous Data
Raster basics—ArcMap
Hiermit werden Features in ein Raster-Dataset konvertiert.General characteristics of raster data. Rasters, TINs and LAS datasets can be easily displayed inside ArcScene using different symbology options. Rasters work somewhat differently when you export them. In ArcToolbox, double-click Conversion Tools.Vectors are points, lines, and polygons. Beim Auswählen der Eingabe-Feature-Daten entspricht das Standardfeld dem ersten verfügbaren gültigen Feld.Discrete data, which is sometimes called thematic, categorical, or discontinuous data, most often represents objects in both the feature (vector) and raster data storage systems. Here is the export window on a Raster, showing the Selected Graphics option grayed out, as you mentioned.The level of detail (of objects and phenomena) represented by an image is often dependent on the pixel (cell) size, or spatial resolution, of the image. A raster object is a variable .Weitere InformationenSchlagwörter:ArcMapArcgis
Introduction to image and raster data—ArcGIS Pro
Feature class basics—ArcMap
When NoData is added to a file-based raster that already has a full-bit range (meaning that all the values in the bit range, for example, 0 to 255, are all represented by at least one cell), it will be promoted to the next higher bit depth. Continuous data represents phenomena such as temperature, elevation, or spectral data . Because cartographers use these symbols to represent real-world features in maps, they often have to decide . Click the From Raster drop-down arrow, and select the Raster to Point tool. The cell must be small enough to .
Vector vs Raster in GIS: What’s the Difference?
Vector data is not made up of a grid of pixels. The general steps for georeferencing a raster dataset are: . While the advent of automated laboratories has alleviated concerns .Raster datasets represent geographic features by dividing the world into discrete square or rectangular cells laid out in a grid.Statistical analysis is also used to identify and confirm spatial patterns, such as the center of a group of features, the directional trend, or whether features form clusters.Data stored in a raster format represents real-world phenomena: Thematic data (also known as discrete) represents features such as land-use or soils data.Open the properties of the raster and go to the symbology tab.Bei Raster-Daten wird in den Zellen normalerweise das vorherrschende Feature oder Phänomen in dem von der Zelle abgedeckten Bereich dargestellt, während bei Vektor .ArcGIS Pro solution.Zusammenfassung Points are generally represented by x,y coordinates in vector form.

Schlagwörter:Raster Dataset ArcmapArcgis For example, individual geographic entities can be represented as features (such as points, lines, and polygons); as imagery using rasters; as surfaces using features, rasters, or TINs; and as descriptive attributes.Schlagwörter:Geographic Information SystemsRaster Data Arcgis
Rasters with functions—ArcMap
Navigate to the top ribbon, click the Imagery tab, and in the Analysis group click Raster Functions to open the Raster .Assemblages of entities, such as forest stands in a state, soil types in a county, or single-family houses in a town, are features of an area that will most likely be represented by zones made up of many disconnected groups of connected cells (regions).) Create a vector polygon of the entire US (including Texas).
Watershed (Raster Analysis)—ArcGIS Pro
The smaller the cell size, the smaller the area and, thus, the closer the representation of the point feature. Keep the following in mind when using the Rasterize .
- Verdickter zehennagel: ursachen und was sie tun können – nagelverdickung am zeh
- Löhe heilpädagogik, heilpädagogik studiengang
- The 20 best wonderkids in football manager 2024 – football manager 2024 best wonderkids
- How to generate formatted and easy-to-read json in javascript _ js convert to json
- Fortschreibung schulentwicklungsplan sachsen anhalt | schulentwicklungsplanung sachsen anhalt 2022
- Heilfürsorge sachsen privat | freie heilfürsorge polizei sachsen
- How to set up perfect bump maps in blender – blender bump map appears steeped
- Würth klebfix 20 g od 245 kč – klebfix sekundenkleber 20g
- Img stageline skyrock akkubox _ img skyrock kaufen