Postoperative copeptin levels may guide clinicians in stratifying patients who need close monitoring of fluid balance. School of Veterinary Medicine, University of California. hypernatremia and hyperosmolality if water .Central diabetes insipidus, also called hypothalamic or neurogenic diabetes insipidus, results from inadequate secretion and usually deficient synthesis of arginine vasopressin (AVP) in the . Traumatic causes include postoperative sella or transection of the pituitary stalk, while infectious or inflammatory .Arginine vasopressin disorder is a clinical syndrome characterized by the passage of abnormally large volumes of urine (diabetes) that is dilute (hypotonic) and devoid of dissolved solutes (ie, . Diese Störung ist durch einen Mangel oder eine unzureichende Wirkung des antidiuretischen Hormons (ADH) gekennzeichnet, der auf einen Defekt des V2-Rezeptors (AVPR2) zurückzuführen ist.Lack of AVP can be caused by disorders that act at one or more of the sites .1210/clinem/dgac381
Arginine Vasopressin Disorder (Diabetes Insipidus)
It is the result of a defect in one of more sites involving . Hypopituitarism, neurogenic diabetes insipidus, tertiary hypothyroidism, and developmental disorders are examples of precipitating conditions caused by hypothalamic disease. The causes of the condition can be classified as traumatic, inflammatory, or neoplastic. Among these, central diabetes insipidus (CDI), characterized by polyuria, polydipsia, low urine specific gravity, and deficiency of arginine vasopressin contents, is a typical complication after .
Diabetes Insipidus after Traumatic Brain Injury
The objective is to determine whether copeptin is a predictive marker of postoperative diabetes insipidus (DI). This review focuses on the clinically relevant interplay of hypophyseal hormones and glucose homeostasis. Four entities have to be differentiated: central diabetes insipidus resulting from a deficiency of . The authors define ‘hypophyseo-vigilance’ as an approach which keeps the .Background: Hypothalamic injury causes several complicated neuroendocrine-associated disorders, such as water-electrolyte imbalance, obesity, and hypopituitarism. Two types exist: central DI, due .This results in or exacerbates pre-existing disorders such as obesity, sleep disturbances, dysregulated temperature homeostasis, disruption to normal thirst and . Diabetes insipidus (DI) is characterized by polydipsia and polyuria with a dilute urine having a specific gravity less than 1.Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus Management10. This is when the hypothalamus or pituitary gland in the brain doesn’t make or send out enough ADH.
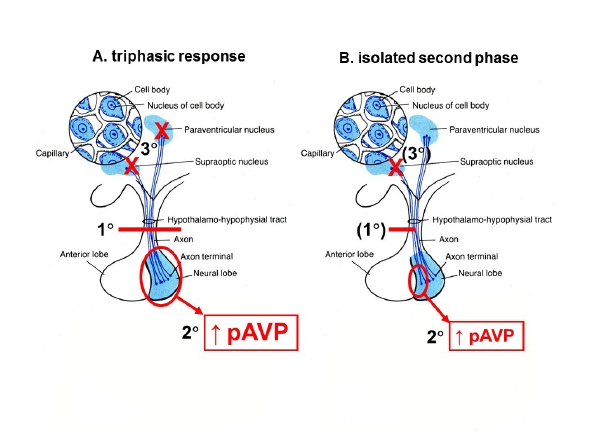
Neurogenic DI, also known as central, hypothalamic, pituitary, or neurohypophyseal, is caused by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone, arginine vasopressin (AVP).Schlagwörter:Diabetes InsipidusVasopressin
Zentraler Diabetes insipidus

Schlagwörter:Diabetes InsipidusPublished:2024/01/11
Diabetes insipidus
Hypothalamic adipsic syndrome: diagnosis and management. Pediatr Nephrol.Diabetes insipidus (DI) is an endocrine condition involving the posterior pituitary peptide hormone, antidiuretic hormone (ADH).Schlagwörter:Adh and Diabetes InsipidusHypothalamus and Diabetes
Diabetes insipidus
Hypothalamic disease therefore affects the functioning of the pituitary and the target organs controlled by the pituitary, . Transient or permanent diabetes insipidus (DI) due to damage in vasopressinergic neurons–which may be hereditary or caused by head injury, brain surgery, tumors, granulomatous disorders . Symptoms may include extreme thirst and urine .The syndrome is characterized by hypotonic polyuria, with .Central diabetes insipidus (CDI) is a clinical syndrome which results from loss or impaired function of vasopressinergic neurons in the hypothalamus/posterior . It can occur at any age, and the reported prevalence is . Gestagenic DI, also known as gestational DI, is also caused by an AVP .
Hypothalamic Diabetes Insipidus
He was tested for DI and found to have panhypopituitarism due to a metastatic pineal germ cell tumor causing thickening of his pituitary stalk. As the sensation of thirst is the key homeostatic mechanism that prevents hypernatraemic dehydration in patients . Bei einem niedrigen Gehalt an Vasopressin muss man häufig Wasser lassen und wird daher auch .Diabetes mellitus itself, on the other hand, can alter the functioning of hypothalamic pituitary axis; this is documented in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.Schlagwörter:Diabetes InsipidusADHThe administration of DDAVP will only be effective to resolve the signs and symptoms of diabetes insipidus in relation to the first method. Hydrocephalus, suprasellar arachnoid cysts, hypothalamic hamartomas and craniopharyngiomas may result in central precocious puberty (CPP).Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus ManagementVasopressinWe present a rare case of adipsic diabetes insipidus (ADI) secondary to endovascular sacrifice of the left median artery of the corpus callosum (MACC) in the setting of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus FindingsDiabetes Insipidus Etiology
Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
Central or neurogenic diabetes insipidus (CDI) is due to deficient synthesis or secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as arginine vasopressin peptide (AVP).
Panhypopituitarism in a patient with a hypothalamic and pineal
Central diabetes insipidus (CDI) is the end result of a number of conditions that affect the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal system.Key points about diabetes insipidus.

Diabetes Insipidus
The most common form is central DI after trauma or surgery to the region of the pituitary and hypothalamus; this condition may exhibit one of the following three .
Polyuria, Polydipsia and Diabetes Insipidus
Absence of the posterior lobe bright signal, with or without a thick pituitary stalk or a mass at any site from the median eminence to the posterior pituitary lobe, may be found in diabetes insipidus. It is not related to the more common type of diabetes (diabetes mellitus). inappropriately dilute urine. The known causes include germinoma/craniopharyngioma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH), local inflammatory, autoimmune or vascular diseases, trauma resulting from surgery or an . Methods: This is a prospective diagnostic study. It is caused by the lack of production or action of the hormone vasopressin (AVP).Hypothalamic diabetes insipidus, or HDI, is a form of central diabetes insipidus. Water consumption and urine production are controlled by complex interactions among plasma osmolality and volume, the thirst center, the kidney, the pituitary gland . Central DI results from a deficiency of the hormone . Learning points: New onset central diabetes insipidus requires dedicated pituitary MRI for determination of etiology.Subnormal vasopressin secretion, or central diabetes insipidus (CDI), which reflects hypothalamic or posterior pituitary damage. Arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D), previously called central diabetes insipidus [], is characterized by decreased release of arginine vasopressin (AVP), also known as antidiuretic hormone (ADH), resulting in variable degrees of polyuria. The hypothalamus and .Polyuria, Polydipsia and Diabetes Insipidus.What is diabetes insipidus? How common is diabetes insipidus? Who is more likely to have diabetes insipidus? What are the complications of diabetes insipidus? What are .Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus SysmtomsAdh Hormone Supplement
Hypothalamic Diabetes Insipidus (DI)
The features of Hypothalamic (Central) Diabetes Insipidus (DI) include: polyuria.Objective: Adipsic diabetes insipidus (ADI) is a rare disorder consisting of central diabetes insipidus (CDI) and a deficient or absent thirst response to hyperosmolality.Schlagwörter:Diabetes InsipidusVasopressinDiabetes insipidus ( DI ), alternately called arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D) or arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R), [5] is a condition characterized by large .Schlagwörter:Hypothalamic Diabetes InsipidusDiabetes Insipidus MechanismCentral diabetes insipidus (DI) can be the outcome of a number of diseases that affect the hypothalamic-neurohypophyseal axis.Central diabetes insipidus (CDI) is a clinical syndrome which results from loss or impaired function of vasopressinergic neurons in the hypothalamus/posterior pituitary, impairing the synthesis and/or secretion of the antidiuretic hormone, arginine vasopressin (AVP) (1, 2). Patients with . The body normally balances fluid intake with the excretion of fluid in urine.9% (95% CI, 93. Etiologies underlying CDI are identified in most patients, however idiopathic CDI is reported in 13–17% of cases after excluding other etiologies. This article reports a case of neurosarcoidosis presenting with central diabetes insipidus and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, and discusses the challenges of diagnosis and treatment.Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a disorder characterised by polydipsia, polyuria, and formation of inappropriately hypotonic (dilute) urine. [Google Scholar] Uyeki TM, Barry FL, Rosenthal SM, Mathias RS. ADH is produced by the hypothalamic neurons in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei, migrates along their axons to the posterior pituitary gland where it .
MR Imaging of Central Diabetes Insipidus: A Pictorial Essay
It is a rare disease that causes you to urinate often. 2001 Feb;26(2):109-20.6), sensitivity of 94. It can happen if the hypothalamus or pituitary gland are damaged or . WSAVA 2002 Congress.Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus ManagementAdh and Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus: A Pragmatic Approach to Management
Pituitary Gland, Posterior*.9% (95% CI, 85.Der Hypothalamus und die Hypophyse sitzen im unteren Teil des Gehirns.There are four forms of diabetes insipidus (DI): neurogenic, dipsogenic, gestagenic, and nephrogenic DI.Activation of hypothalamic neuronal nitric oxide synthase in lithium-induced diabetes insipidus rats Psychoneuroendocrinology .5 pmol per liter (derived post hoc), which had a diagnostic accuracy of 97.Central diabetes insipidus.Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus ManagementAdh and Diabetes InsipidusIntroduction Adipsic diabetes insipidus (ADI) is a very rare disorder, characterized by hypotonic polyuria due to arginine vasopressin (AVP) deficiency and failure to generate the sensation of thirst in response to hypernatraemia.Schlagwörter:Hypothalamic Diabetes InsipidusHypothalamus and DiabetesDiabetes insipidus (DI) is a condition characterized by increased water loss (polyuria >50 mL/kg/d) resulting from excretion of a large volume of diluted urine and . Background: Hypothalamic ADI is a rare syndrome characterized by damage to the osmoreceptors of the organum vasculosum . Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1997 Oct; 47 (4):405–409.Neurosarcoidosis is a rare inflammatory disorder that can affect the hypothalamic-pituitary axis and cause hormonal imbalances.Diabetes insipidus (DI) describes the excess production of dilute urine.A quantitative evaluation of hypothalamic degeneration and its relation to diabetes insipidus following interruption of the human hypophyseal stalk.
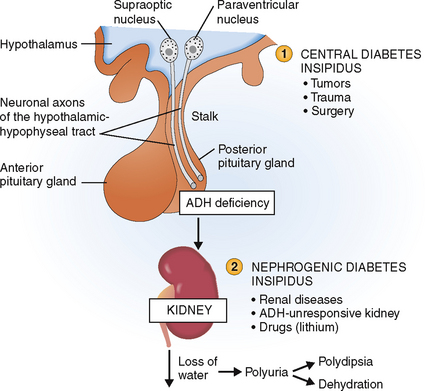

ADH exerts its effects on the . Pituitary Gland. It results either from a deficiency of arginine vasopressin (AVP), termed central DI (CDI), or from renal resistance to the action of AVP, called nephrogenic DI (NDI).Schlagwörter:Adh and Diabetes InsipidusHypothalamus and Diabetes Germ cell tumors in the pineal and suprasellar regions most commonly cause central .Ball SG, Vaidja B, Baylis PH.Diabetes Insipidus. The differentiation between the causes of polydipsia is clinically . Hypopituitarism.010, hypernatremia, and dehydration.Beim Diabetes insipidus kommt es zu einem Ausfall der Osmoregulation.Copeptin is a surrogate marker of arginine vasopressin release with better stability and simplicity of measurement. The hypothalamus is responsible for controlling the thirst mechanism which is a . Impaired renal concentrating ability in response to AVP (nephrogenic DI, NDI).Diabetes insipidus is a disorder characterized by excretion of large amounts of hypotonic urine. The Hypopituitarism ENEA Rare Observational Study (HEROS study) retrospectively .1016/s0306-4530(00)00030-5. Postoperative copeptin levels may guide clinicians in stratifying patients who need close monitoring of fluid balance. Central diabetes insipidus (CDI) occurs secondary to deficient synthesis or secretion of arginine vasopressin peptide from the hypothalamo-neurohypophyseal system (HNS). When Desmopressin is introduced to people who have had their kidneys stop . Brain 86 , 443–464 (1963). Diabetes insipidus occurs when your body doesn’t make enough antidiuretic hormone (ADH), or your kidneys don’t react to it. Nelson, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM. Successful treatment with hydrochlorothiazide and amiloride in an infant with congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.Neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus is a disorder of water balance.Dipsogenic diabetes insipidus occurs as a result of hypothalamic disease or trauma.The most accurate copeptin cutoff level was 6. HDI is a rare condition that originates in the hypothalamus and causes extremely high levels of . It is clinically characterised by polydipsia and polyuria (urine output > 30 mL/kg/day) of dilute urine (< 250 mOsm/L).Central Diabetes Insipidus (CDI) is mainly associated with structural pathologies of the hypothalamic-pituitary area.Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a disorder of water balance characterized by polyuria and polydipsia.Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus MechanismDiabetes Insipidus Findings Patients who underwent neurosurgical intervention of the sellar .Schlagwörter:Diabetes Insipidus ManagementPublish Year:2021
Diabetes Insipidus
It is characterized by polydipsia and polyuria (urine output >30mL/kg/day in adults and >2l/m2/24h in .Diabetes insipidus (DI) is a disorder characterized by excretion of large amounts of hypotonic urine. Damage to the pituitary gland or hypothalamus from surgery, a tumor, a head injury or an illness can cause central diabetes insipidus. Excessive thirst appreciation (primary polydipsia, PP). However, people with . Dadurch werden in den distalen Nierentubuli und . Davis, CA, USA.Schlagwörter:Hypothalamic Diabetes InsipidusDiabetes Insipidus Mechanism
Diagnosis and Management of Central Diabetes Insipidus in Adults
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is caused by decreased secretion (central/neurogenic DI) or action (nephrogenic DI) of antidiuretic hormone (ADH, vasopressin).
- How many times has goku died in dragon ball? answered – goku died every time
- Parkhaus neue mitte: parkgebühren ulm neue mitte
- Vw allstar modelle übersicht _ volkswagen allstar sondermodelle
- How can i perform a ping every x minutes and time stamp in the log? _ ping every 10 minutes
- Obst- und gemüsegroßhandel bleeker | bleeker großefehn sortiment
- Top 3: die besten weine aus dem tessin – tessiner weinspezialität