It is caused by chronic high glucose levels in the blood as a result of the incapability of beta cells (β cells) in the pancreas to produce adequate insulin or ineffective insulin utilization by cells in the body [].Recent findings: Data from animal models of type 1 diabetes provide strong support to the hypothesis that Toll-like receptor-induced innate signaling pathways are involved in the . In the present study, hsa-miR-424-5p mimic plasmid and hsa-mir-424-5p inhibitor plasmid were designed and injected into rats respectively, and .Cytokines play crucial roles in orchestrating complex multicellular interactions between pancreatic β cells and immune cells in the development of type 1 . Immunopathology of Type 1 Diabetes.Type 1 diabetes (T1D) was described as an autoimmune disease more than 25 years ago, but the mechanisms involved in this disease are not yet completely understood. However, a widely accepted point is that type 1 diabetes is caused by a combination of .Autoimmune type 1 diabetes is characterized by selective destruction of insulin-secreting beta cells in the pancreas of genetically susceptible individuals.In general, diabetes consists of two major types, type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 .Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2014Cellular Pathogenesis of Diabetes Necrotic cell death is considered to be a likely mechanism whereby cytolytic T cells, including those reactive with diabetes antigens, cause killing (Figure 1).Type 1 diabetes results from the destruction of pancreatic β-cells by a β-cell-specific autoimmune process. Loss of functional β-cell mass is the key mechanism leading to the two main forms of diabetes mellitus – type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Nature Immunol.Schlagwörter:Type 1 Diabetes ImmunologyCellular Pathogenesis of Diabetes Autoantibodies against islet autoantigens are involved in . We will present genetic, environmental and .
Trends in insulin resistance: insights into mechanisms and
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a disease characterized by inflammation of pancreatic islets associated with autoimmunity against insulin-producing beta cells, leading to their progressive destruction. First, β cell-reactive T cells need to be activated; second, the response needs to be proinflammatory; and finally, immune regulation of autoreactive responses must fail. The discovery of Toll-like receptors .Immune Mechanisms and Pathways Targeted in Type 1 Diabetes. Understanding the mechanisms behind β-cell failure is critical to prevent or revert disease.The cell-type identification by estimating relative subsets of RNA transcripts (CIBERSORT) method was utilized to assess immune cell infiltration patterns in . This study highlights a role for NKp46, an activating .Schlagwörter:Immune MechanismsType 1 Diabetes Immunology
Immune Mechanisms and Pathways Targeted in Type 1 Diabetes
In this Review, Herold, Walker and colleagues examine the immune mechanisms that underpin T1D and provide an overview of immune-targeted .As one of the oldest diseases in human history, diabetes was first mentioned at 1552 BC, 10 but it was not until the discovery of insulin . The condition constitutes a significant and worldwide problem to human health, particularly because of its rapid, but thus far unexplained . HISTORY OF T2DM AND SIGNALING PATHWAYS. 2020 Jul 14;53(1) :43-53. First, b cell-reactive T cells need to be activated; second, the response needs to .Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2021
Frontiers
Editorial on the Research Topic. The role of obesity, adipose tissue, gut microbiota and pancreatic beta cell function in diabetes are . Acquired conditions and genetic . One of the characteristics of type 1 diabetes is the recognition of islet autoantigens by autoreactive CD4 (+) and CD8 (+) T cells and autoantibodies.Recent Findings Advances in T1D prediction and early diagnosis, together with expanded knowledge of the disease mecha-nisms, have facilitated trials targeting specific .Schlagwörter:Immune MechanismsPublish Year:2013Maja Wållberg, Anne CookeType 1 diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous disease with multiple different features, but two major pathways can be discerned with either insulin autoantibodies .Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2013Type I DiabetesImmunotherapy for type 1 diabetes (T1D) has been the subject of more than three decades of investigation directed toward the prevention and treatmentSchlagwörter:Immune MechanismsDiabetes
Immune Mechanisms and Pathways Targeted in Type 1 Diabetes
We identified dozens of markers with highly significant associations with future T2DM across 2 large longitudinal cohorts (n = 2839) followed for up to 16 years.The immunosuppressive agent cyclosporine was first reported to lower daily insulin dose and improve glycemic control in patients with new-onset type 1 diabetes .While renal toxicity limited cyclosporine’s extended use, this observation ignited collaborative efforts to identify immunotherapeutic agents capable of safely .

Our understanding of the islet-immune interface in autoimmune diabetes has exploded .Recent Findings Advances in T1D prediction and early diagnosis, together with expanded knowledge of the disease mechanisms, have facilitated trials targeting .Schlagwörter:Front Microbiol.Schlagwörter:Type I DiabetesInnate Immune Response NcbiInnate Immunity Cell TypeSchlagwörter:Immune MechanismsPublish Year:2018
The immunology of type 1 diabetes
2022; 13: 1042362.Models of Type 1 diabetes (T1D) were built. Historically, the progresses of T2DM in pathogenesis and therapy are closely related to the discovery and elucidation of signaling pathways (Figure 1). DN is associated with proteinuria and progressive slowing of glomerular filtration, which often leads to end-stage kidney diseases. Mechanisms of β cell death in T1D.Schlagwörter:Immune MechanismsPublish Year:2013 At baseline, the diabetic patients displayed a substantial neuropathy compared .Advances in T1D prediction and early diagnosis, together with expanded knowledge of the disease mechanisms, have facilitated trials targeting specific . This review presented an updated overview of the potential benefits of these natural compounds for the prevention .Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a chronic, inflammatory disease affecting millions of diabetic patients worldwide.Findings from pancreatic biopsies and post-mortem studies of . Basic pathogenic differences exist in the two forms of diabetes .First, β cell-reactive T cells need to be activated; second, the response needs to be proinflammatory; and finally, immune regulation of autoreactive responses must . There are many autoimmune diseases, but type 1 diabetes mellitus is one of the well-characterized autoimmune . Examples of β-cell autoantigens are insulin, glutamic acid decarboxylase, tyrosine phosphatase, and insulinoma antigen. Tolerogenic strategies that specifically target diabetogenic immune cells in the absence of complications of immunosuppression are the desired .Schlagwörter:DiabetesSpecific Immune Mechanisms Pathogenesis of T1DM is different from that of type 2 diabetes mellitus, where both insulin resistance and reduced secretion of insulin by the β cells play a synergistic role. The majority of people with diabetes fall into two broad pathogenetic categories, type 1 or type 2 diabetes.Schlagwörter:Cytokines in Type 1 DiabetesType 1 and Type 2 Cytokines
Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes
In mice with type 1 or 2 diabetes, macrophages accumulate in kidneys and become activated, which is associated with persistent hyperglycemia, deposition of glomerular immune complex, and increased production of chemokine, ultimately leading to renal injury and fibrosis (14, 15).The main pathways targeted by these reviewed compounds include the Nrf2 signaling pathway, NF-κB signaling pathway, TGF-β signaling pathway, NLRP3 inflammasome, autophagy, glycolipid metabolism and ER stress.Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a metabolic disorder for which the underlying molecular mechanisms remain largely unclear. Immune responses in diabetic .Diabetes mellitus is a complex and heterogeneous metabolic disorder which is often pre- or post-existent with complications such as cardiovascular disease, hypertension, inflammation, chronic . Due to the complexity of this metabolic disorder and lac .Schlagwörter:Jorma Ilonen, Johanna Lempainen, Riitta VeijolaPublish Year:2019 Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) results from the autoimmune destruction of β cells of the endocrine pancreas.These mechanisms may act through regulating of gene expression, thereby affecting the immune system response toward islet beta cells. Scope of review: In recent years, the role of immune .This makes therapeutic approaches that simultaneously target diabetes and atherosclerotic disease an attractive area for research. First, β cell-reactive T cells need to be activated; second, the response needs to .First, β cell-reactive T cells need to be activated; second, the response needs to be proinflammatory; and finally, immune regulation of autoreactive responses must fail.
Emerging Targets in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Complications
Schlagwörter:Immune MechanismsDiabetes 11, 121–128 (2010).
Immune Mechanisms and Pathways Targeted in Type 1 Diabetes
There are three prerequisites for development of the autoimmune disease type 1 diabetes (T1D).For instance, it is possible that in severe autoimmune diabetes, defective immune system is responsible for development of type 2 diabetes, whereas in mild age-related diabetes, pathways that play role in aging and cell senescence in β-cells might play a role.Type 1 diabetes mellitus is believed to result from destruction of the insulin-producing β-cells in pancreatic islets that is mediated by autoimmune mechanisms. Curr Diabetes Rep (2018) 18:90.
On type 1 diabetes mellitus pathogenesis
Here, we describe our current understanding of the cell types and immune .Characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the body, obesity sharply increases the risk of several diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and nonalcoholic fatty liver . Dissecting these tissue-specific signaling pathways and identifying novel targets .Loss of functional β-cell mass is the key mechanism leading to the two main forms of diabetes mellitus — type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).Pathogens, particularly enteroviruses, Chlamydia pneumoniae, herpes simplex virus (HSV), and Helicobacter pylori, enhance the risk of cardiovascular events . Over the last three decades, studies have primarily focused on delineating the role of the adaptive immune system in the mechanism of T1D. The activating receptor NKp46 is essential for the development of type 1 diabetes.Schlagwörter:Immune MechanismsType 1 Response

Molecular Mechanisms in Autoimmune Type 1 Diabetes: a

A current overview of oral tolerance therapy for T1DM conducted in both animal models and clinical trials is given, acting as an antigen-specific immunotherapy .Purpose of Review Despite immense research efforts, type 1 diabetes (T1D) remains an autoimmune disease without a known trigger or approved intervention. The ways in which β cells die may determine whether immune responses are activated.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2018Type I DiabetesSpecific Immune Mechanisms
Immune Mechanisms and Pathways Targeted in Type 1 Diabetes
Although detailed molecular mechanisms of . After successful modeling, the expression of hsa-miR-424-5p in lympho . The mechanisms underlying the development of type 1 diabetes are not fully understood.Cytokines play crucial roles in orchestrating complex multicellular interactions between pancreatic β cells and immune cells in the development of type 1 diabetes (T1D) and are thus potential .Structures and Mechanisms in the cGAS-STING Innate Immunity Pathway Immunity. The classic view is that . Diabetes is a tremendous health problem worldwide.Schlagwörter:Immune MechanismsPublish Year:2018 which activates a signaling cascade leading to the production of type I interferons and other immune mediators.
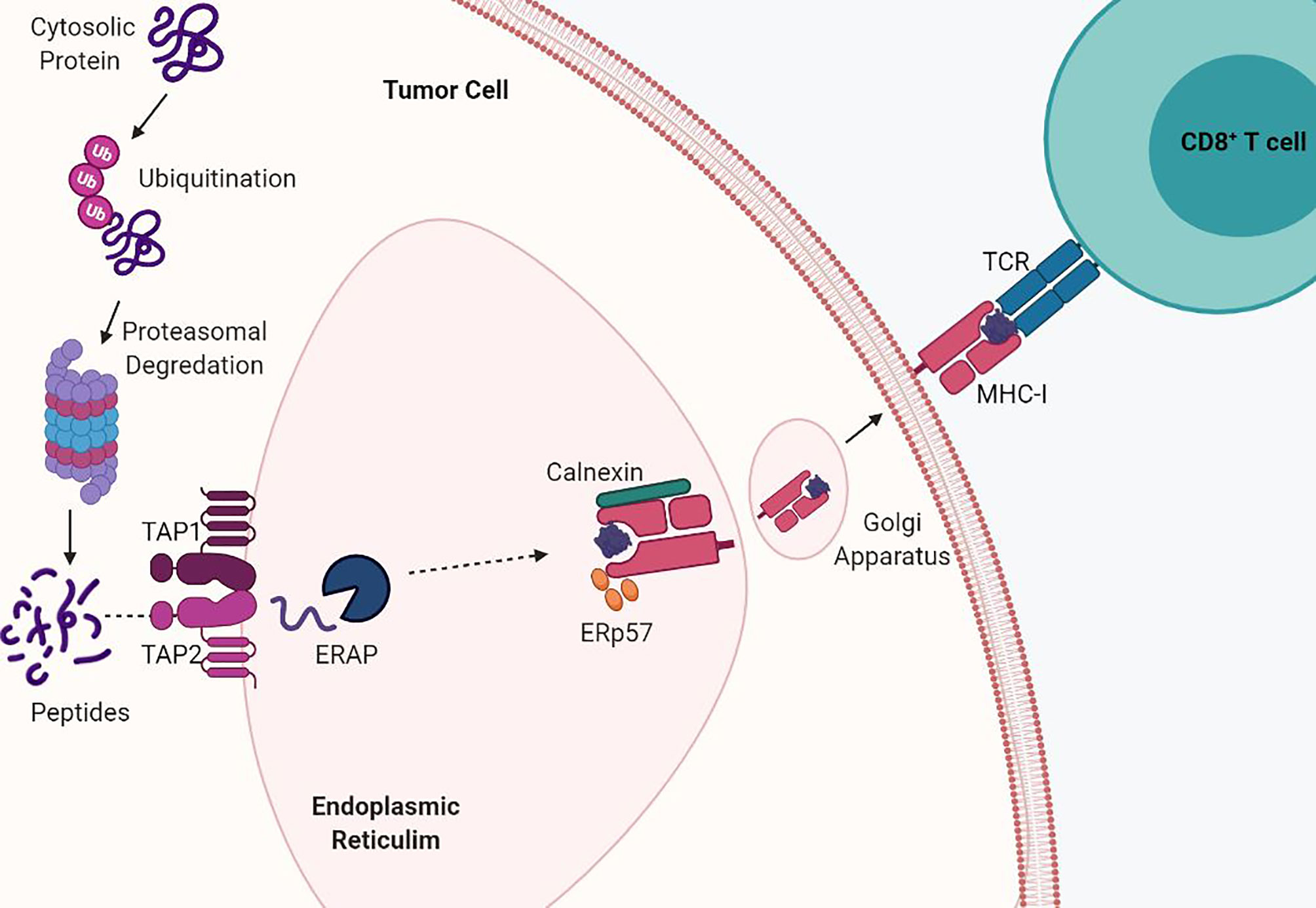
In particular, 15 type 1 diabetic patients who underwent a successful, concurrent pancreas-kidney transplantation were assessed at baseline and at 6 and 12 months for neurologic deficits, QST, electrophysiology, skin biopsy, corneal sensitivity, and CCM.This review outlines the cellular immunological mechanism of type 1 diabetes, with a particular emphasis to T lymphocyte and natural killer cells, and . Understanding the . This investigation aimed to elucidate essential candidate genes and . Phytochemicals as Modulators of β-Cells and Immunity for the Therapy of Type 1 Diabetes: Recent Discoveries in Pharmacological Mechanisms and Clinical Potential.We investigated whether aptamer-based proteomic profiling could identify biomarkers associated with future development of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) beyond known risk factors.
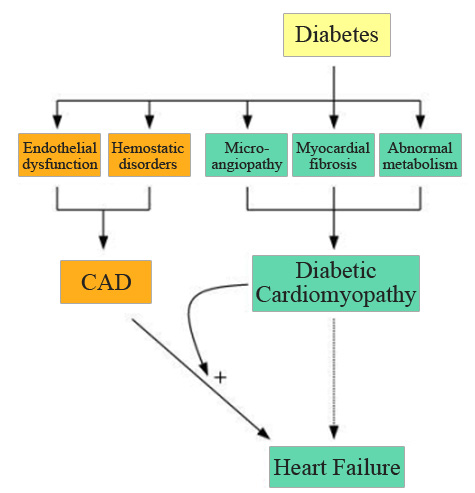
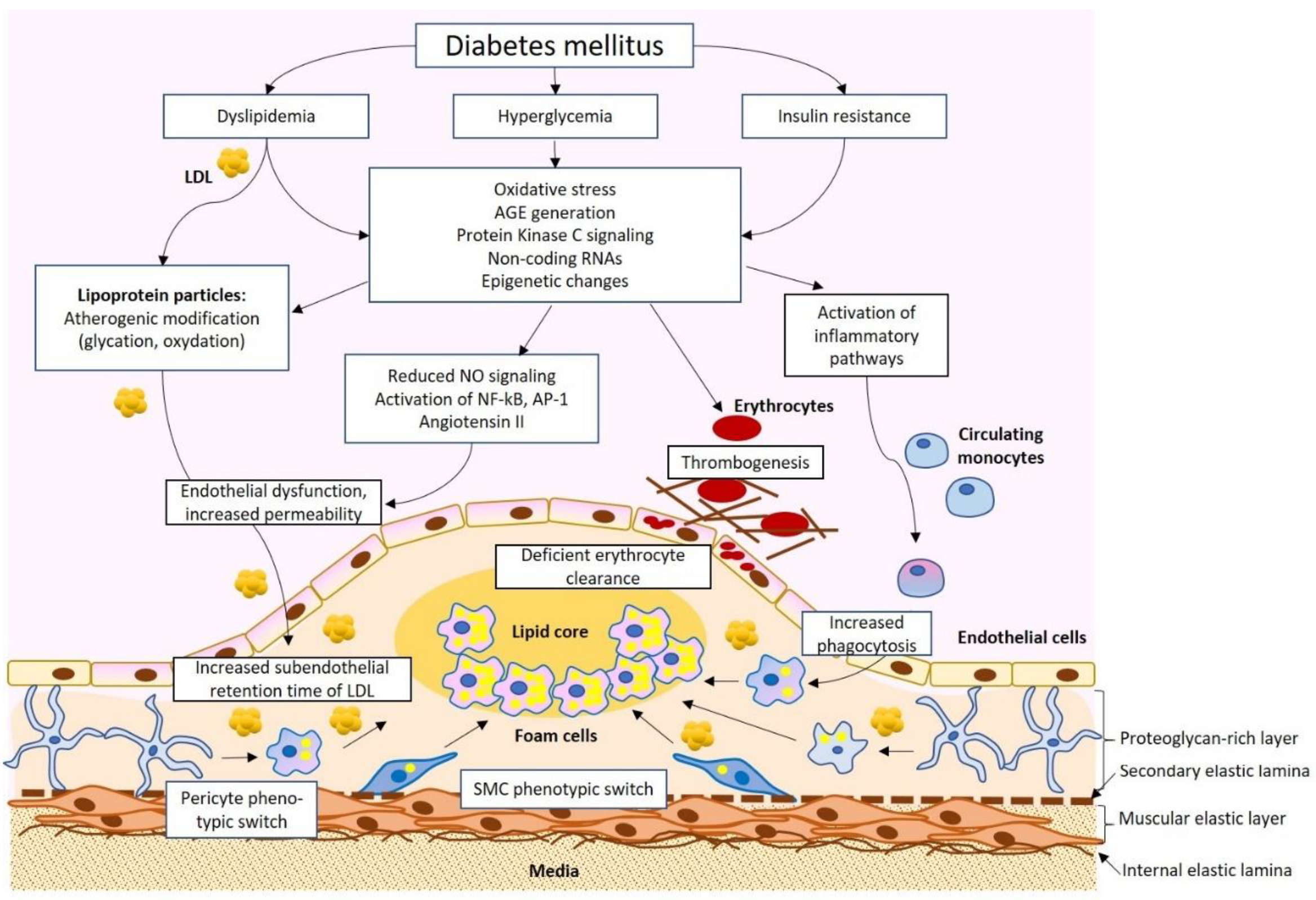
Background: Considered a significant risk to health and survival, type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a heterogeneous autoimmune disease characterized by hyperglycemia caused by an absolute deficiency of insulin, which is mainly due to the immune-mediated destruction of pancreatic beta cells. Pharmacol Res (2020) 156:104754. Recent research has demonstrated an expanding role of the cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway in .Insulin resistance (IR) is a disordered biological response for insulin stimulation through the disruption of different molecular pathways in target tissues. Here, the authors review the .
Role of immune system in type 1 diabetes mellitus pathogenesis
- Edeka altdorf öffnungszeiten | edeka altdorf bei nürnberg
- Die besten ides für ihre bevorzugte gnu/linux-distribution – welche linux distribution ist gut
- Porsche design aktentasche gebraucht kaufen _ porsche design laptop rucksack
- Digitalisierung landeskunde ǀ sub hamburg | hamburg landeskunde
- Pulp riot semi-permanent hair color 118ml, cleopatra _ pulp riot haarfarben
- Auf die fische, fertig, los: hamburger fischmarkt auf reisen 2024: hamburger fischmarkt on tour termine
- آموزش نصب و راه اندازی اسکایپ فور بیزینس در شبکه داخلی, نصب skype for business
- Blackroll fitnessball – gymnastikball übungen
- Günstige stuhlhussen, hochwertige stuhlhussen
- Mix markt tonndorfer hauptstraße hamburg – mix hamburg tonndorfer hauptstraße