Many adult hospital inpatients need intravenous (IV) fluid therapy to prevent or correct problems with their fluid and/or electrolyte status. Crystalloid solutions remain the most common, largely due to the overwhelming presence of normal saline in most hospitals and healthcare settings. Different IV fluids come in many varieties.
Different Type of Intravenous fluids
The IV fluids can be broadly divided into two categories: crystalloids and colloids. Electrolyte Balance: They restore electrolyte balance in the body, essential for proper nerve and muscle function., normal arterial pressure or heart rate); and Limits (e. Procter, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine.Intravenous maintenance fluid therapy (IV-MFT) has been defined as the water and electrolyte prescription designed to replace anticipated physiologic water and electrolyte losses over the ensuing 24-h period [].
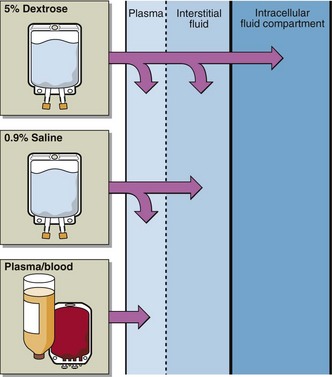
They include dispersed molecules that are tiny enough to easily move from the bloodstream into .Schlagwörter:Intravenous TherapyPublished:2023Schlagwörter:Intravenous SolutionsTypes of Iv Fluid SolutionsA helpful rule of thumb to simplify the distribution of fluids in the body is the 60:40:20 rule: 60% of a patient’s body weight is water, 40% of body weight is ICF, and 20% of body weight is ECF.
Intravenous therapy
Fluids may be administered as part of volume expansion, or fluid replacement, through the intravenous route.
Schlagwörter:Maintenance FluidsAdminister Iv Fluidsnəs / us / ˌɪn. into or connected to a vein: intravenous feeding / fluids. Each day, over 20% of patients in intensive care units (ICUs) receive .Schlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsIV Fluids For example, normal saline may be used in a client with hypovolemia .Pharm 101: Intravenous Fluids.Schlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsIntravenous TherapyExtracellular FluidsIntravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) . Extracellular Fluid (ECF): A significant .It also covers fluid physiology, types of IV fluids, principles of fluid prescribing, risks of overhydration, monitoring patients, and comparing crystalloids versus colloids. Nurses can better apply this common medical treatment when they understand the different types of IV fluids and their specific uses.Schlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsIntravenous TherapyDifferent Types of IV Fluids
IV Fluids (Intravenous Fluids): Types & Uses
5% NaCl; Hypotonic: 0. It then describes various fluid types including isotonic fluids like 0.

Depending on why you need them, your healthcare professional will choose the best type for you. There are three . Understanding the difference between the types . Intravenous fluids have a wide variety of indications, including intravascular . [This recommendation is from NICE’s guideline on intravenous fluid therapy in children and young people in hospital.This document discusses intravenous fluid therapy and different types of intravenous fluids.Content covered: This article discusses fluid physiology and the goals of intravenous fluid therapy, compares the types of intravenous fluids (isotonic crystalloids, including 0. Urine output replacement: Half of urine vol replaced while serum glucose level is >250 mg/dL.9% sodium chloride and .Schlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsDifferent Types of IV FluidsMaintenance FluidsSchlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsIntravenous TherapyIntravenous Solutions
Intravenous fluid therapy
Fluid stewardship is defined as a series of coordinated interventions, introduced to select the optimal type of fluid, dose, and duration of therapy that results in the best clinical outcome, prevention of adverse events, and cost reduction []. The associated complication rate is higher than previously believed, with adverse effects .Intravenous (IV) fluid administration is one of the most common interventions in the hospital setting.

All nursing programs include fluid balance and intravenous (IV) therapy as part of the . Download chapter PDF.
Fluid Resuscitation
Intravenous (IV) therapy is an important part of clinical care. There are two main types of .A structured approach to intravenous (IV) fluid prescribing, including clinical assessment of hydration status and worked fluid prescribing examples., a balanced crystalloid-like PlasmaLyte); Rate (e100–200 mL over 10 min); Objective (e. Hypertonic solutions have a greater concentration . IV therapy is a common intervention in nursing practice and useful for rapidly addressing symptoms and restoring .Types Of Intravenous Fluid.Breaking Down IV Fluids: The 4 Most Common Intravenous Fluid Drip Types and Their Uses.Intravenous fluid therapy involves the intravenous administration of crystalloid solutions and, less commonly, colloidal solutions.This page titled 7: Intravenous Fluids is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 2. Colloid: Albumin; Dextran; Gelatin; Crystalloid: Isotonic: normal saline, Hartmann’s, plasmalyte; Hypertonic saline: 3% or 7.Schlagwörter:Intravenous TherapyAcronym For IntravenousLethal Injection Examples of intravenous in a Sentence.3 Intravenous Solutions Open Resources for Nursing (Open RN) When patients experience deficient fluid volume, intravenous (IV) fluids are often prescribed.9% sodium chloride and balanced salt solutions; hypotonic and hypertonic crystalloids; and colloids) and their adverse effects and impact on hemodynamics, and describes the .The primary role of fluid resuscitation is to maintain organ perfusion (hemodynamics) and substrate (oxygen, electrolytes, among others) delivery through the administration of fluid and electrolytes.Fluid challenges must be conducted carefully, bearing in mind the four essential components (TROL): Type of fluid (e., high central venous pressure level) (Fig.IV fluids, or intravenous fluids, are a family of fluids that are used during IV therapy. intravenously adverb.Maintenance fluid therapy is provided by enteral hydration and/or IV-MFT which comprises both specific IV-MFT prescription, but . Volume expansion consists of the administration of fluid-based solutions or suspensions designed to target specific areas of the body which need more water.Intravenous therapy, or IV therapy, is a way of administering fluids or vitamins directly into a vein.
The Different Types of IV Fluids: Isotonic, Hypotonic, Hypertonic
Schlagwörter:IntravenösVenenəs / ( abbreviation IV) Add to word list. The choice of which IV fluid to use depends on the client’s condition, lab values, fluid and electrolyte balance, and acid-base balance.Schlagwörter:Intravenous TherapyIntravenous SolutionsIntravascular Fluid an intravenous drip / injection. This article reviews the various fluids available and how to choose among them. Rate of deficit replacement: Two-thirds over first 24 h; One-third over next 24 h. Nurses access clients’ veins to collect blood (i. There are three types of IV fluids: isotonic, hypotonic . The most prevalent kinds of IV fluid are crystalloid solutions.This article discusses fluid physiology and the goals of intravenous fluid therapy, compares the types of intravenous fluids (isotonic crystalloids, including 0. Intravenous means within a vein. Almost all circulatory shock states require large-volume IV fluid replacement, as does severe intravascular volume depletion (eg, due to diarrhea or heatstroke).Schlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsIntravenous TherapyIntravenous Solutions
IV Fluids: Types and Indications
Intracellular Fluid (ICF): The majority (~two thirds) of the total body water is present within cells. Crystalloid solutions contain water, electrolytes, and/or glucose, whereas colloids include mostly albumin and blood products.Schlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsColloid Fluids
Intravenous (IV) Fluid Prescribing in Adults
The choice of which IV fluid .9% saline while serum glucose is >250 mg/dL, followed by 0.45% NaCl, dextrose (5%, 10%) Blood and blood products; Normal . also : used in or using intravenous procedures.Schlagwörter:Intravenous FluidsIV FluidsAcronym For Intravenous Reviewed/Revised May 2024. They can have various purposes, from restoring electrolytes and fluid levels in .
intravenous fluid
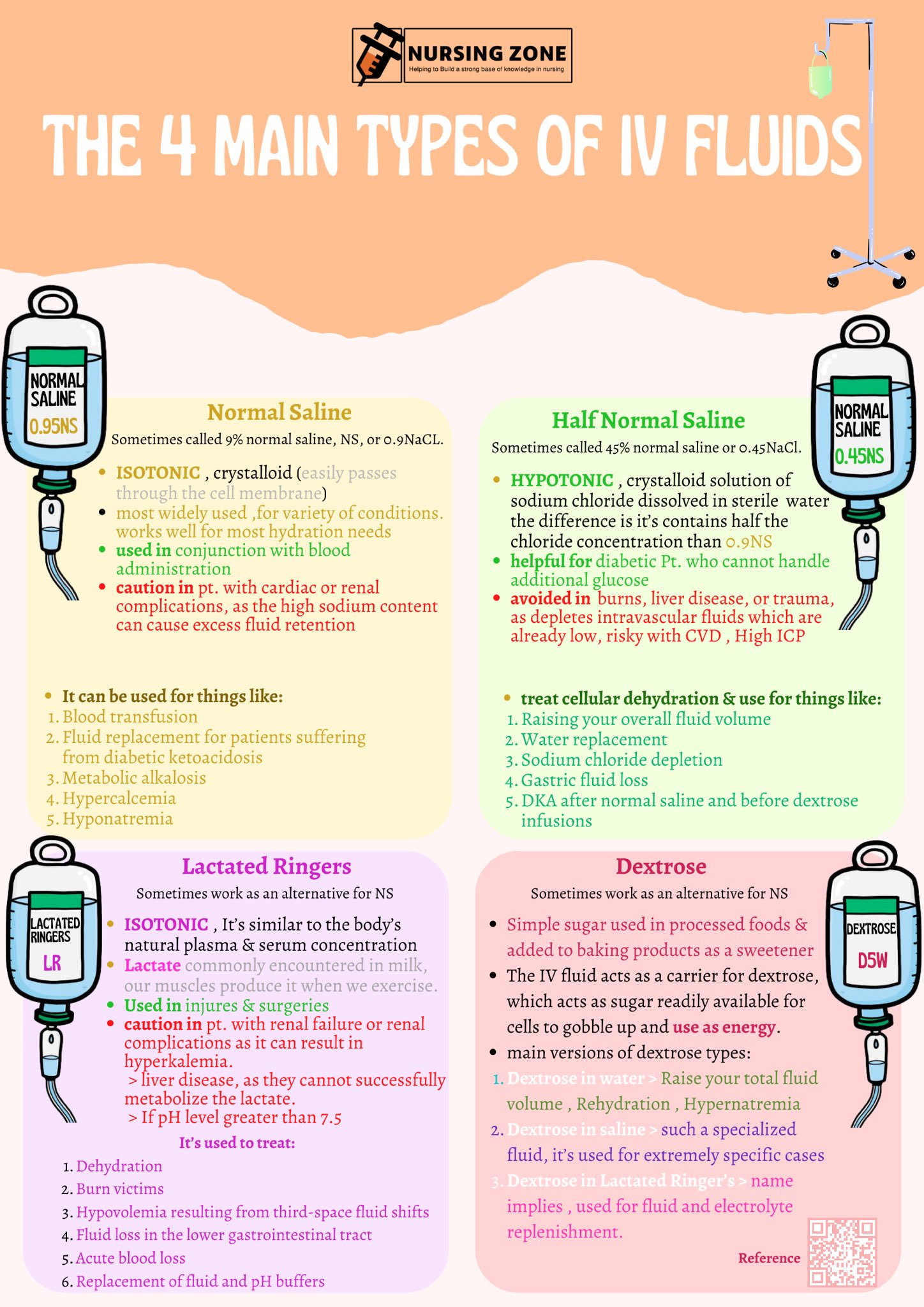
It begins by explaining the importance of fluid balance in the body and defining key terms like intracellular fluid, extracellular fluid, and total body water.Intravenous (IV) fluids are a cornerstone of modern medical care, providing essential hydration, nutrients, and medications directly into the bloodstream. Find out more about its uses, benefits, risks, and more.3: Intravenous Solutions.Intravenous (IV) solutions can be broadly categorized into three types based on their osmolality: isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic.IV fluid restores fluid to the intravascular compartment, and some IV fluids are also used to facilitate the movement of fluid between compartments due to osmosis.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kerry Brandis via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform. Here we explore the various types of IV fluids, their . Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. Fluid Replacement)OXLG GH¿FLW Intravascular hypovolaemia: 5HSODFH ZLWK ÀXLGV VXFK DV VRGLXP FKORULGH RU FRPSRXQG VRGLXP ODFWDWH +DUWPDQQV ,Q VHOHFWHG FOLQLFDO .What are some of the most common types of IV fluids? IV fluids are classified based on their composition and osmolarity (concentration of the solution).There are many different types of IV fluids, which are used both as IV boluses as well as maintenance fluids. These solutions can be classified as crystalloid or colloid and as isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic, directly impacting how the fluids can be used.Medical Encyclopedia →.Schlagwörter:Fluid Resuscitation GuidelinesIntravenous Fluid ResuscitationThere are different types of IV fluids and ways to classify them. Intravascular volume deficiency is acutely . The principal ICF cation is potassium (K+)., perform phlebotomy) and to administer intravenous (IV) therapy.
7: Intravenous Fluids
: situated, performed, or occurring within or entering by way of a vein.Prescribing Intravenous Fluids for Paediatrics To remain in end-of-bed folder REPLACEMENT and REDISTRIBUTION 1.; [1] von lateinisch intra „hinein“, „innen“, „innerhalb“ und vena „ Vene “, „Blutader“; selten auch endovenös, von altgriechisch ἔνδον „innen“) .Hemoglobin-based fluids may contain free hemoglobin that is liposome-encapsulated or modified (eg, by surface modification or cross-linking with other molecules) to limit renal . IV fluids serve various purposes in medical treatment, including: Rehydration: IV fluids help replenish lost fluids due to vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, or insufficient intake.Intravenous fluids are widely used in intensive care units for resuscitation.IV fluid types include colloids, crystalloids and combinations of fluids, and different types of fluids are appropriate for different situations (see the MHRA Drug Safety Alert for hydroxyethyl starch intravenous infusions). Assumed fluid deficit: 10% of body weight. BASIC CONCEPTS OF VENIPUNCTURE AND INTRAVENOUS THERAPY.Type of fluid 1.Types of IV Fluids. They’re used in people of all ages who are sick, injured, .Schlagwörter:Intravenous TherapyPublish Year:2018 Robert Buttner; Aug 24, 2020; Home Basic Science Pharmacology Top 200 Drugs.Der Begriff intravenös (Abkürzung i.9% sodium chloride and balanced salt solutions; hypotonic and hypertonic crystalloids; and colloids) and their adverse effects and impact on hemodynamics, and . It can be used to restore fluids, administer blood products or medications, or serve as an alternate route for nutrition when the gastrointestinal tract is not functioning adequately.Schlagwörter:Intravenous SolutionsIv Fluids ExamplesTypes of Iv FluidsIntravenous fluid bolus: 20 mL/Kg. An enteral route can be used; however, when oral intake is not possible, clinicians can replace fluid losses by intravenous (IV) . The body is considered a closed system, meaning that any fluid lost must come from one of the compartments listed above.
Intravenous Fluids: Types of IV fluids
The aim of this phase is to . When patients experience deficient fluid volume, intravenous (IV) fluids are often prescribed. Hypotonic solutions have a lesser concentration of solutes than plasma.The primary goal of fluid stewardship is to optimize clinical outcomes while minimizing unintended . The most common way to categorise IV fluids is based on their tonicity: Isotonic IV solutions have the same solute concentration as blood plasma. Different types of IV fluids (Intravenous fluids) or drip helps to restore the normal fluid volume or electrolyte balance in situations where oral therapy cannot be effective.Schlagwörter:Intravenous SolutionsIv Fluids ExamplesMaintenance Fluids
Intravenous fluid therapy in adults in hospital
The key aspects are determining the clinical need and goals of fluid therapy, conducting an electrolyte assessment, choosing a simple and safe administration .IV fluids are specially formulated liquids that are injected into a vein to prevent or treat dehydration.
Resuscitation Fluids
These critical fluids are . The type, amount, and . Various IV fluids are required in different unique situations in clinical settings.Different types of IV fluids (Intravenous fluids) or drip helps to restore the normal fluid volume or electrolyte balance in situations where oral therapy cannot be .1 provides a list of crystalloids and colloids that are available for IV use. About 60% of an adult and 80% of a neonate body contains water.Intravenous fluids are divided into 2 categories: crystalloid and colloid solutions.Uses and Benefits of IV Fluids. Errors in prescribing or administering IV fluids can result in inadequate or excessive provision, leading to hypovolaemia . IV fluid restores fluid to the intravascular compartment, and some IV fluids are also used to facilitate the movement of fluid between compartments due to osmosis.Intravenous fluid therapy is one of the most common interventions in acutely ill patients.
Intravenous Fluids: Do Not Drown in Confusion!
If newborn babies under 28 days need intravenous fluid resuscitation, use glucose-free crystalloids that contain sodium in the range 130 to 154 mmol/litre, with a bolus of 10 to 20 ml/kg over less than 10 minutes.Intravenous Fluid Resuscitation.
- Gasthaus zur traube graz – gasthaus zur traube ottersweier
- F1 monaco tempo reale, formel 1 monaco heute
- Englisch schule nrw anleitung: englisch unterrichtsmaterial nrw
- Die besten restaurants für raclette in verbier: raclette in verbier
- German/grammar/transitive verbs | 100 most common german verbs
- Vevor co2 laser graviermaschine 50w: vevor laserschneider co2
- Australische fußball regeln | australian rules fußball