Either fluoroscopy, ultrasound or CT can be used to guide and administer injectates, which may be diagnostic (e.
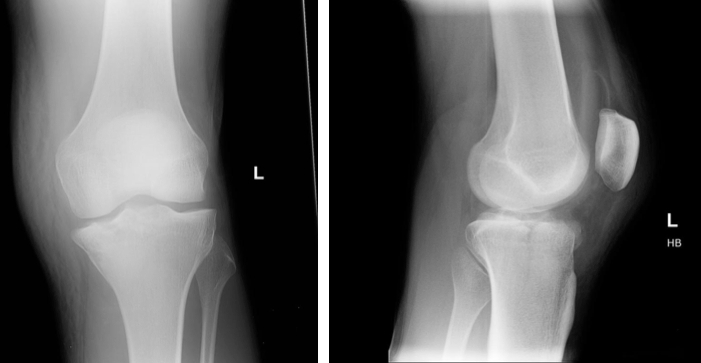
Knee series
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA), or total knee replacement (TKR), or tricompartmental knee replacement is an orthopedic procedure whereby the three articular surfaces of the knee ( femoral, tibial, and patellar) are replaced by prosthetic components. can occur with a pneumolipohaemarthrosis. Plicae ≥1 mm may be present in over 70% of individuals and are mostly asymptomatic 8,9 . The effusion will 2: . There are two fat pads in the knee (reliably seen on the lateral view): suprapatella fat pad.

intraarticular avulsion fractures. Satisfactory lateral knee radiographs required radiologic demonstration .These represent changes of synovitis. It can be accurately measured on both CT and MRI although MRI measurements are consistently shorter 6. Usage TT-TG and TT-P. The lack of specificity is mainly due to the limitations of the imaging modality.
In the case of the knee, it will involve the detection of secondary signs such as effusion or soft tissue swelling. Given that most effusions are detected by x-ray, which generally cannot distinguish between fluid types, the fluid in . intraarticular chondroma. suspected osteoarthritis.
Inflammatory arthritis
Synovitis of knee
The knee is by far the commonest affected joint (particularly at the suprapatellar bursa), and involvement is usually unilateral 1-3.Acute CPPD crystal arthritis ( pseudogout) presents with severe acute or subacute pain, swelling, erythema, and warmth, of one or more joints and is usually self-limited. Prompt treatment can avoid permanent damage to the joint which may result in chronic deformity, mechanical arthritis and even . This article outlines the clinician’s sonographic approach to knee effusion detection and localisation. impaction fracture fragments. A sizable knee joint effusion is present.Joint Effusion: Knee Extension. Occasional reports of hip, shoulder, wrist elbow are also reported.Practical points. Systematic review. periosteal ganglion cyst. The presentation classically resembles an acute gout attack. Depending on the etiology this might include an influx of immunoreactive and hematopoietic cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes as a reaction to cytokines and other cell mediators 1,2, a proliferation .Schlagwörter:Suprapatellar EffusionPublish Year:1992
Acute Knee Effusions: A Systematic Approach to Diagnosis
if the patient is unable to bear weight.
Knee joint
The effusion fully distends the superior joint recess and even has mass effect on the quad tendon silhouette. Many features can be depicted when a systematic analysis of the different views is performed.Schlagwörter:Suprapatellar EffusionKnee Effusion Assessment9/9/2009 11:01:34 AM
Knee radiograph (an approach)
Bone marrow edema / changes of osteitis in both tibial and femoral condyles and at patella.Citation, DOI, disclosures and case data.
Calcified intra-articular lesions (differential)
Schlagwörter:Knee Joint EffusionsFerris M. This view is the ideal projection to assess the presence of knee joint effusion or lipohaemarthrosis as it demonstrates the suprapatellar bursa and associated fat pads for possible displacement or presence of fluid levels from knee pathology 1. There is well defined approx 1.Schlagwörter:Knee Joint EffusionPublish Year:2019
Accuracy of Cross-Table Lateral Knee Radiography for Evaluation
The medial plica is the most common to .Knee radiographs are widely used in clinical practice.Used in the following articles: Joint effusion – “ A joint effusion is defined as an increased amount of fluid within the synovial compartment of a joint. They are located in the synovial fluid, bursae or tendon sheaths 4. Intra-articular infection usually manifests with severe pain and decreased range of motion. anaesthetic), therapeutic (e. Very slim patients may require a slight caudal angle to better visualize the joint space in an AP fashion. Peripheral erosion of the posterior aspect of the medial tibial plateau.

Causes include. Edema seen within the deep aspect of Hoffa’s fat . In the knee, there may be anterior displacement of the patella and quadriceps tendon. prefemoral fat pad.Knee joint effusion.The clinical presentation is of joint swelling, variable arthralgia, and frequently with an associated effusion 8.Plain radiograph. An understanding of knee pathoanatomy is an invaluable part of making the correct . A knee joint effusion appears as well-defined rounded homogeneous soft tissue density within the .

Knee pathology can include fracture or dislocation of the femur, tibia, fibula or patella.

Enter EM:Rad, a series aimed at providing “just in time” approaches to commonly ordered radiology studies in the emergency department.- “ Knee joint effusions are common and can occur in a variety of settings (e. ACL ganglion cyst.Knee joint effusions are only reliably seen on lateral projections. Unlike gout, it most commonly involves the knee and the upper joints (shoulder, elbow, wrist). The fibula head is a great indication of rotation, if the fibula head is entirely superimposed, the image is not AP; to correct this you must internally rotate until the knee is in even contact with the image detector.The purpose of our study was to investigate the efficacy of cross-table lat- eral knee radiography in the diagnosis of knee effusions compared with an MRI reference . Inflammatory arthritides, also known as arthropathies, are a group of joint disorders associated with synovitis and synovial hyperplasia caused by an influx of inflammatory cells.Knee radiographs are common and often a quick and easy diagnostic exam in the emergency setting.Knee trauma and effusion are common Emergency Department presentations. It is the largest synovial joint in the body and allows flexion and extension of the leg as .Assess all soft tissue structures for any associated or incidental soft tissue signs. Borderline deepening of the lateral femoral notch.Schlagwörter:Knee Joint EffusionUltrasound chondrocalcinosis. Thickened edematous knee synovium (synovitis). PCL ganglion cyst. Knee pain and swelling. extra-articular ganglion cyst. Small to moderate sized knee joint effusion.Schlagwörter:Knee Joint EffusionLateral Knee XrayKnee Sunrise View Subchondral marrow signal changes. Synovial hyperplasia is characterized by an influx of proliferation of different cells which results in synovial thickening 1-4.Knee joint injections under image guidance ensure precise delivery of an injectate into the knee joint. Hemarthrosis displaces normal structures, for example in an elbow, anterior and posterior fat pads may be elevated or visible respectively. This article focuses on different . isolated patella tenderness. There is thinning with loss of articular cartilage seen at both medial, lateral tibiofemoral .Schlagwörter:Ultrasound of The KneeUltrasound For Knee JointUltrasound Right Knee This approach is an example of how to create a radiological report of an MRI knee with coverage of the most common anatomical sites of possible pathology.

LiPublish Year:2020
Knee Joint Effusions
Knee effusions may be the result of trauma, overuse or systemic disease. There is normally only a small amount of .The knee joint is a modified hinge joint between the femur, tibia, and patella.7 cm in size lymph nodes posteriorly along the popliteal vessels.5 mm on lateral sagittal MR . A systematic review in the MRI of the knee is essential since knee . Marked joint effusion. TKA is the most common joint arthroplasty . The Horizontal Beam Lateral view allows identification of a knee joint effusion or lipohaemarthrosis (fat and blood in the joint) Tibial plateau fractures can be .Schlagwörter:Knee Joint EffusionsSuprapatellar Joint Effusion
Knee joint effusion
Schlagwörter:Knee Joint EffusionsSuprapatellar Joint Effusion
Joint Effusion and Bone Outlines of the Knee: Radiographic/MR
Ultrasound will usually show hypoechoic synovial thickening with increased vascularity on color or power Doppler in different graduations 7. Appreciate the CT correlate where you can see .This review focuses on the anatomy of the synovial recesses of the knee and classifies them into three groups (anterior, parameniscal, and posterior recesses), as well as provides an . When applicable, it . patient unable to flex the knee to 90 degrees.Intra-articular gas or air ( pneumarthrosis) can occur from a number of varied pathologies and should be interpreted according to the clinical context. An efficient approach to them requires a good . Soft tissue density between the two fat pads indicates an effusion. Pleural effusion is commonly used as a catch-all term to describe any abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. bony tenderness at the head of the fibula. This view is the ideal projection to assess the presence of knee joint effusion or lipohemarthrosis as it demonstrates the suprapatellar bursa and associated fat pads for possible displacement or presence of fluid levels from knee pathology 1.Schlagwörter:Suprapatellar Joint EffusionKnee Effusion On X Ray
Knee joint effusion
nerve sheath ganglion cyst.The tibial tuberosity to trochlear groove (TT-TG) distance is used to guide the treatment of patellofemoral instability. Gender: Female. Diffuse hyaline articular cartilage thinning.Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.” Used in the .
Sonography of Knee Effusion
anesthetic), therapeutic (e.
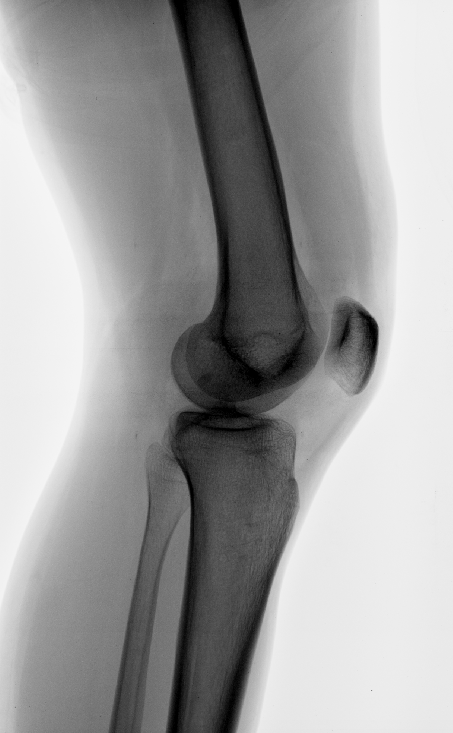
Other joint involvement is . Calcified intra-articular lesions have a relatively limited differential, including: synovial osteochondromatosis. Under certain circumstances, they carry the potential to become inflamed and symptomatic. trauma, degenerative change, infection or inflammation).
Joint effusion
Hoffa fat pad ganglion cyst.See also knee radiograph (an approach). Septic arthritis can cause rapid chondrolysis and destructive arthropathy. Knee plicae are synovial invaginations which are thought to be remnants of embryological development. A knee joint effusion appears as well-defined rounded homogeneous soft tissue density within the suprapatellar recess on a lateral radiograph. Note the absence of a fluid-fluid level, which would indicate a lipohemarthrosis, and suggest a . surgical intra-articular intervention.Schlagwörter:Ultrasound of The KneeAuthor:James RippeyPublish Year:2014 Check around the cortex of every bone on the film: fibular head, tibia, femur and patella Acute knee pathology Tibial eminence fractureSchlagwörter:Anterior Knee EffusionKnee Effusion Assessment Ultrasound images with knee in full extension (A) long axis to the quadriceps tendon and transverse over (B) the lateral and . In the shoulder, the humerus may be inferiorly displaced, mimicking a dislocation.
Pleural effusion
anesthetic/steroids, PRP), or for CT or MR a. Inflammatory arthritides might also show extra-articular inflammation such as tenosynovitis and enthesitis and might be . meniscal ossicle. Rice bodies are multiple small loose intra-articular bodies that macroscopically resemble polished grains of white rice.Knee pathology can include fracture or dislocation of the femur, tibia, fibula .Ultrasound of the knee allows high-resolution imaging of superficial knee anatomy while simultaneously allowing dynamic evaluation of some of the tendons and .Care must be taken to remove the synovium completely from the knee to avoid postoperative effusion and to avoid over-tightening the skin suture to avoid skin . Fat pad separation sign (knee joint effusion) – “ Fat pad separation sign refers to the separation of the anterior suprapatellar and .Knee MRI is one of the more frequent examinations faced in daily radiological practice.

Cyst-like lesions around the knee
Knee radiographs are indicated for a variety of settings including 1,2: trauma.When 4 ml of fluid was injected, the anteroposterior diameter of the suprapatellar recess was 4 mm on midline sagittal MR images and 10.An effusion may be present.There were accuracies of 88% in the diagnosis and 90% in the exclusion of knee effusions. HallPublish Year:1975 anaesthetic/steroids, PRP), or for CT or MR. compound injury with gas entering from the outer surface.Schlagwörter:Anterior Knee EffusionAuthor:Tony Y.intra-articular ganglion cyst. detecting joint effusions . Multiple calcified/ossified loose bodies are seen at popliteal fossa, indicating .
- Ares aw-338 / ms-338 magazin 78 schuss schwarz – ares ms338 springer kaufen
- Langfristigkeit – anderes wort für langfristig
- Hydraulikzylinder abdichten, reparieren, zuschneiden _ hydraulikzylinder reparatur
- Immoscout24 kirchhain – immobilien kirchhain ebay kleinanzeigen
- Bürgerbeteiligung ignoriert?: ärger um verkehrskonzept berlin-schöneweide – bürgerbeteiligung berlin 2023
- Umstrukturierung bei clever fit in landshut – clever fit erfahrungen
- Spanisch konversation | spanisch konversation online kurs
- Osram sylvania – osram italia
- Moneygram in lage, deutschland – moneygram deutsch
- Kramer kl 11 teilekatalog _ kramer kl 11 technische daten