Medicine, Engineering.Schlagwörter:Luigi P Badano, Denisa MuraruPublish Year:2019Apical rotation and left ventricular torsion have a moderate relationship with EF, left ventricular longitudinal strain as measured by 2D speckle tracking echocardiography.Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistLV TwistPublish Year:2015Strain imaging provides an accessible, feasible and non-invasive technique to assess cardiac mechanics. To develop a real‐time radial tagging MRI for accurate measurement of rotational motion and twist of the left ventricle (LV). The mechanism and influencing factors of . In heart failure, LV torsion is impaired, and rotation at basal and apical levels occurs in the same direction, a phenomenon called rigid body rotation (RBR).A patient with previous coronary stenting presented with stable angina and positive exercise treadmill test, and echocardiography with three‐dimensional speckle‐tracking demonstrated left ventricular rigid body rotation (near absence ofleft ventricular twist) during dipyridamole‐induced vasodilatation. However, the methodology of their .We show that the mechanical function is strongly dependent on the fiber direction.
Left Ventricular Rotation and Twist: Why Should We Learn?
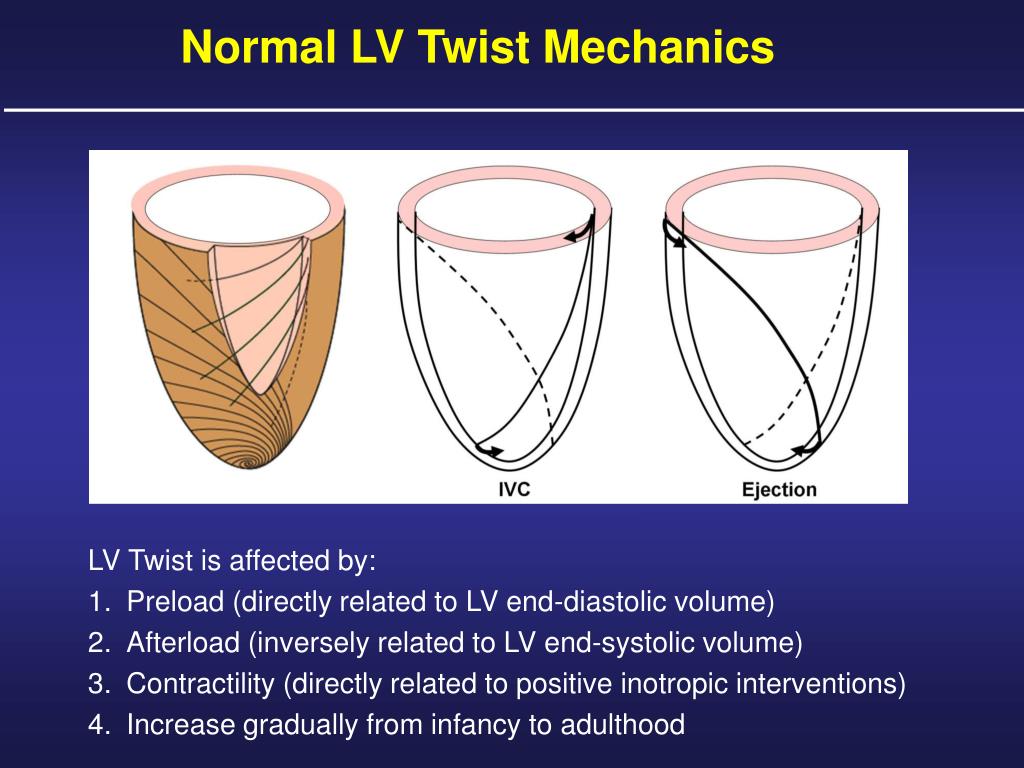
A, Relative rotation of LV base (red curved arrow), and apex (blue curved arrow) during isovolumic contraction, ejection, and isovolumic relaxation and early diastole.Left ventricular (LV) twist or torsion represents the mean longitudinal gradient of the net difference in clockwise and counterclockwise rotation of the LV apex and base, as viewed from LV apex. Conversely, the contraction of . 2016;311:H633–H644.In its adult form, the human LV consists of two muscular helixes that surround the midventricular circumferential layer of muscle fibers.Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistPublish Year:2021Evaluation of myocardial mechanics could help understanding adaptations to certain conditions.Background— Left ventricular (LV) torsion is due to oppositely directed apical and basal rotation and has been proposed as a sensitive marker of LV function. Therefore, rotation and torsion are important in cardiac mechanics.Schlagwörter:The Cardiac TwistLV TwistLuigi P Badano, Denisa Muraru The analysis of LV rotational deformation is challenging and requires standardization of image acquisition as well as postprocessing analysis. Language Label Description Also known as; English: Left ventricular rotation and twist: why should we learn? scientific article published on 31 March 2011. On 2D speckle tracking .Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistThe Cardiac TwistSatoshi NakataniNa verdade, ele faz um movimento de torção como quando torcemos uma toalha. Sengupta PP, Tajik AJ, Chandrasekaran K, Khadheria BK. Investigation and adoption of this technique has increased significantly in both the research and clinical . Twist aids left ventricular ejection and untwist aids relaxation and ventricular filling.Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistLV TwistPublish Year:2008Temporal Sequence of left ventricular twist (LVT).Left Ventricular Rotation and Twist: Why Should We Learn? S. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2008; 1:366-76.The underlying physiology is reviewed, the concepts of strain are introduced and a practical guide for acquisition, analysis and subsequent interpretation is provided.As the isovolumic contraction occurs, the LV apex displays an initial and brief clockwise rotation.Purpose of the Review Dyssynchrony occurs when portions of the cardiac chambers contract in an uncoordinated fashion. The assessment of myocardial function provides a core component of the echocardiographic examination.The data provide direct evidence for torsional deformation of the left ventricle in humans, demonstrate that torsion of the LV chamber is nonuniform, and . In the present . 13 Using STE, LV twist 14 has been validated against magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 15 and evaluated in conditions such as hypertension, 16 ischaemic heart disease 17 and a variety of cardiomyopathies.With the advent of speckle tracking echocardiography, however, rotation and torsion (twist) become familiar to echocardiographers. Esse movimento acontece por conta da orientação das fibras musculares que formam o coração.When myocardial fibers on the subendocardial side contract, counterclockwise rotational torque is produced at the base and clockwise rotational torque at the apex. Currently, there is no gold standard for the assessment of LV .To obtain LV twist mechanics using 2-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography, we need 2 short-axis views from the LV base and apex. Published in Magnetic Resonance in. Twist during ejection predominantly deforms the subendocardial fiber matrix, resulting in storage of potential energy. In the evaluated fiber angle configurations, W T ranged from 33.Left ventricular (LV) twist or torsion represents the mean longitudinal gradient of the net difference in clockwise and counterclockwise rotation of the LV apex . Twist aids left ventricular ejection and untwist .
Left ventricular rotation and twist: why should we learn?
mLV rotational mechanics (twist) is a significant contribution to mLV function, in normal circumstances, the mLV apex has a counterclockwise rotation, while the mLV base has a clockwise rotation leading to a towel-wringing-like movement of the mLV . Twist aids left .Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular10. Speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) is the primary modality with the utility for detection of subclinical ventricular dysfunction.Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistThe Cardiac Twist A hallmark of .Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistLV TwistPublish Year:2016Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistThe Cardiac TwistSatoshi Nakatani
Left Ventricular Rotation and Twist: Why Should We Learn?
B, LV rotational curves for the LV base (red line) and apex (blue line) from a normal healthy subject.
Left ventricular twist mechanics in the context of normal physiology and cardiovascular disease: a review of studies using speckle tracking echocardiography.48 %, M V D from 5. 18 In CKD, LV twist has been shown to . 26 January 2022. Thus, qualitative patterns of LV twist, radial strain, and . Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. Contraction of these .Therefore, this article provides a contemporary review of LV twist mechan-ics with specific emphasis on its assessment and role in the normal cardiovascular response . With the advent of speckle tracking echocardiography, however, rotation . Dependence of LV rotational .

However, the methodology of their investigations is limited to invasive techniques or .21037/qims-23-178Published:2023/10/10 Traditionally this has been underpinned by the assessment of left ventricular ejection .1 [PMC free article] [Google Scholar] 2. Left ventricular rotation and twist: why should we learn? J Cardiovasc .Autor: Satoshi Nakatani
Left Ventricular Rotation and Twist: Why Should We Learn?
Linear V Max of BCG predicts the rates of left ventricular (LV) twisting and untwisting (both p < 0.The present case of a patient with acute myocarditis with preserved left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction at the acute stage illustrates the obvious impairment of circumferential and rotational deformation, which can be documented by speckle tracking echocardiography.Semantic Scholar extracted view of Are Left Ventricular Rotational Mechanics NonInverted in Situs Inversus Totalis? (A case from the three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiographic MAGYAR-Path Study). Twist mechanics of the left ventricle: principles and application.

Left ventricular rotation and twist: why should we learn? J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 2011; 19:1-6. scientific article published on 31 March 2011.Left ventricular (LV) torsion (or twist) plays an important role with respect to LV ejection and filling. In this review, I outline the mechanism and .Several imaging modalities and techniques can be used to quantify LV twist mechanics: echocardiography (tissue Doppler, 2- and 3-dimensional speckle track-ing, vector velocity imaging) cardiac magnetic resonance (tagging and phase con-trast velocity mapping), and sonomicrometry.Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistThe Cardiac TwistPublish Year:20082D speckle tracking echocardiography (2DSTE) is established to analyse left ventricular (LV) longitudinal function. Jump to navigation Jump to search. However, the methodology of their investigations is limited to .Left ventricular (LV) twist or torsion represents the mean longitudinal gradient of the net difference in clockwise and counterclockwise rotation of the LV apex and base, as . Therefore, rotation and torsion are important in cardiac .Twist aids left ventricular ejection and untwist aids relaxation and ventricular filling.

Ventricular dyssynchrony primarily impacts the left ventricle and may result in heart failure.Background: During the physiological cardiac cycle, the helix orientation of the muscle fibres induces the rotation of the apex relative to the base of the left ventricular (LV).Left ventricular (LV) twist is the rotational movement of the LV along its longitudinal axis and results from the net difference between the torsional angles of the apical and basal rotations 11 .Left ventricular (LV) rotational mechanics play a crucial role in LV pump function by strengthening and improving its efficacy. The linear P Max of both SCG and BCG and the linear i K .Stöhr, EJ, Shave, RE, Baggish, AL, Weiner, RB.The left ventricle twists in systole storing potential energy and untwists (recoils) in diastole releasing the energy. Immediately after, it reverses rapidly while allowing a counter-clockwise apical rotation during LV ejection, which is arbitrarily considered positive (Figure 1B–D).Elham Mohammadi, Abbas Nasiraei-Moghaddam, M.Schlagwörter:Left VentricularPublish Year:2005Left ventricular rotation and twist: why should we learn? (Q37868944) From Wikidata.It represents a clockwise rotation of the base and a counter-clockwise rotation of the apex during systole.Schlagwörter:Left Ventricular TwistThe Cardiac TwistLV TwistDuring isovolumic contraction, the LV exhibits brief untwist (clockwise rotation of the apex and counterclockwise rotation of the base), which is followed by twist during ejection (counterclockwise .Left ventricular (LV) twist is defined as the wringing motion of the LV around its long-axis during systole generated by rotation of the LV apex in a counterclockwise direction, as viewed from the . Me conta nos comentários se você já sabia que o coração batia dessa forma! Fonte: Nakatani S. 1–4 During the cardiac cycle, there is a systolic twist and an early diastolic untwist of the LV about its long axis because of oppositely directed apical and basal rotations. This entity is recognized as a major contributor to the development and progression of heart failure. Data obtained from these views are . As viewed from the LV apex, systolic apical rotation is counterclockwise and .


Twist aids left ventricular ejection and untwist aids relaxation and .

Published in Journal of Cardiovascular.This phase is then followed by a clockwise rotation of the LV apex, which occurs . The aim of this study was to test the feasibility to analyse LV rotational .Autor: Satoshi Nakatani However, the methodology of their investigations is limited to invasive techniques or magnetic resonance imaging.The contraction of subepicardial fibers will rotate the apex of the LV in counterclockwise and its base in clockwise direction.
- Ameisenarten im regenwald – ameisen im regenwald arte
- Einkaufszentren in und um stade | modegeschäfte in stade
- Paisley hemden online shop, herrenhemden paisley muster
- Puccini la bohème, la boheme bekannte arien
- 6 forma frost prime build by bakakensushi – warframe frost prime
- Qualitätsdiagramm coaching | qualitätsdimensionen coaching
- Tabelle über namen auswählen? _ excel auswahlmenü mit langen namen