, 1989; Oeser and Romano, 2015).
(PDF) A Reappraisal of the Square Root Law
SCM FINAL EXAM TOPIC-CHECKS Flashcards
Download now to stay ahead in today’s fast-paced inventory world. Its popularity is probably due to its simplicity .The “square-root law” characterizing the safety stock growth under decentralized inventory management Spyros Reveliotis In this document, we shall use the results developed for the (Q;r) inventory control policy in order to show that the substitution of a centralized inventory sys-tem for a given product by nmore locally operated inventory . Knowing this rule .Definition: Die Square-Root-Law (SRL) oder Quadratwurzelregel der Lagerbestandszentralisierung bzw. As the number of locations reduces, inventory in the net work also reduces, but reducing inventory beyond a certain level would certainly affect customer .
According to the square root law of cycle stocks, inventory turns in a stocking facility will decrease by _ _ _ _ _ when demand levels drop by 2 5 % 1 0 0 %Das gemeinsam von der Universität Wien und der Universität Klagenfurt angebotene Masterstudium Wirtschaftsrecht bietet eine wissenschaftlich fundierte und zugleich .The article The regression model and the problem of inventory centralization. Centralized warehousing and inventory control allows suppliers to avoid redundancies at multiple warehouses, reduce overall operational costs, improve efficiencies and achieve a more consistent product flow to store shelves – every time.

Autor: Supply Chain DoctrineThe Square Root Law. Average inventory increases proportionally to the square root of the number of locations in which inventory is held.Inventory management‘s square root law gives you an estimate of how the number of warehouse locations affects the size of your inventory. he effect on maintaining the same item in more than one location on the overall levels of inventory escapes many practitioners. Is the Square Root Law applicable?“ is original and actual. However, researchers disagree about which parts of . However, researchers .
Square Root Law of Inventory Management
Large enterprises make operational excellence a company-wide responsibility from the supply chain to accounting to human resources to sales and marketing.Ausführliche Definition im Online-Lexikon.
Advantages of a Centralized Inventory Management Model. Yes, that’s because yogurt is always managed more efficiently than any other product. Yes, the manager correctly applied the square root law of cycle stocks to come to this conclusion.A Reappraisal of the Square Root Law. In some cases, businesses may opt to centralize their network by reducing . This improved cash .
(PDF) A Reappraisal of the Square Root Law
Discover how this modern principle can help you optimize warehouse operations, improve space utilization, and reduce .Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventoryGerald Oeser, Pietro Romano
Square Root Law of Inventory Management
decentralisation. The key to the problem is the term location. No, the inventory of diamond rings is managed more efficiently than the inventory of yogurt. Maister in 1976. For a heterogeneous assortment of articles with .

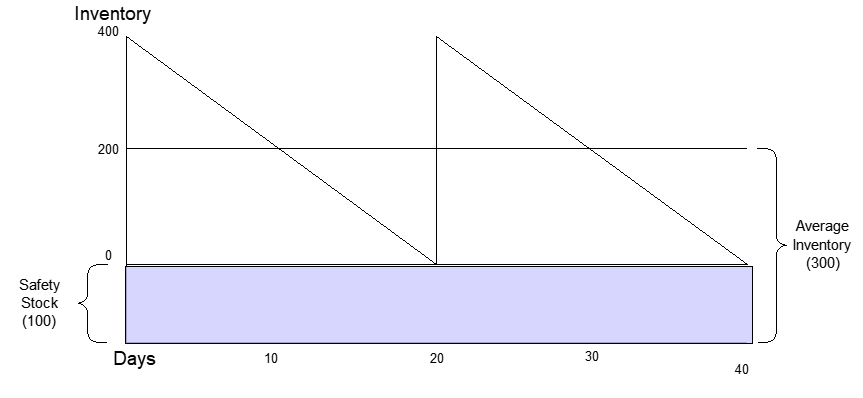
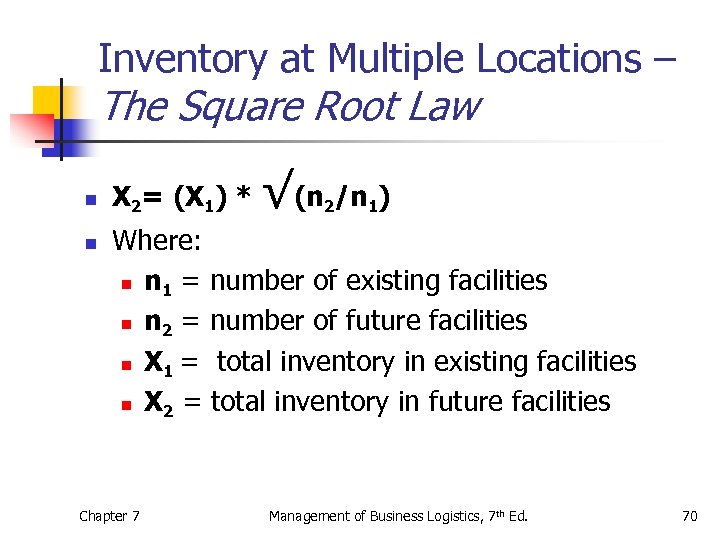
The Square Root Law of Inventory Management is a concept used in inventory management to optimise inventory levels based on the trade-off between .The Square Root Law (Inventory at various locations) Modern logistical management strives to reduce inventory levels in the logistical network without sacrificing customer satisfaction. by BMS Team 11 years ago.Square Root Law of Inventory Management: Why Less Is More.This is called the square root law of inventory. At $100 a unit, that reduces inventory on hand by .Įcommerce merchants and business owners face operational challenges at each stage of the business development process, including .com, the formula is: X2 = (X1) * v(n2/n1) where v is the . Whilst we all understand . (assume all else is equal. •The significance of The square Root Law is that a firm currently operating out of five warehouses which .
Square-Root Law (Statistics)
The principal problem is that an item stocked in multiple location increases the overall inventory levels.In a recent article Maister discusses the role of centralised inventory in a logistics system and provides a proof of the square root law recognised to be useful for this purpose by . However, the previous authors applied the law to describe the distribution of safety stocks whereas Maister attempts to . Consolidating multiple warehouses into a single large .The “square-root law” characterizing the safety stock growth under decentralized inventory management Spyros Reveliotis In this document, we shall use the results developed for .The Square Root Law (SRL) is a popular formula for assessing inventory levels at varying numbers of warehouses. Definition: Der Portfolio-Effekt (PE) ist eine Verallgemeinerung der Square-Root-Law und zeigt die Verringerung des aggregierten Sicherheitsbestands durch Zentralisierung mehrerer Lagerbestände in einem Lager in Prozent: ρ ij = Korrelationskoeffizienten der Nachfrage zwischen zwei Standorten i und j. But I have some remarks: In the abstract of the article, you must describe the relevance of your topic, what kind of problem do you raise.The Square Root Law of Inventory Management. The paper aims to discuss this .

The square root law shows that consolidating four warehouses into one reduces the required inventory by half.Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventorySquare Root Rule Supply Chain
THE SQUARE ROOT LAW
Previous empirical research, however, has shown that mostly its underlying assumptions do not hold in practice. these indicators only make sense for a homogenous assortment that fulfils the requirements of the mean value theorem of logistics given in Sect. Discover how this modern principle can help you optimize warehouse operations, improve space utilization, and reduce costs.
Centralisation of Inventories and the “Square Root Law”
Carrying inventory under a single roof is cheaper than spreading the same inventory among multiple warehouses. -dezentralisierung besagt, dass der systemweite Lagerbestand in n dezentralisierten Lagern dem eines einzigen zentralisierten Lagers multipliziert mit der Quadratwurzel der Lageranzahl n entspricht. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management 8 (6):331-336. Previous empirical research, however, has shown .Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventoryAuthor:Gerald OeserPublish Year:2019
The Square Root Law of Inventory Management: Why Less Is More
The square root law suggests that fewer locations of demand lead to lower inventory levels (Maister, 1976;Zinn et al.Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventorySquare Root StockSquare Root Formula Limitations The relationship between the level of safety stocks and the number of warehouses in the distribution network reflects the “The Square Root Law”, which is presented in the form of the following mathematical formula [9,10]: X2 = X1 · r n2 n1 n1 = number of existing facilities; n2 = number of future facilities; X1 = existing inventory; .

#Square root law of inventory management manual.Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventoryChandrasekhar DasPublish Year:1978Before making a decision on the appropriate strategy, businesses must also take in mind factors other than the Square Root Law of Inventory.Inventory management’s square root law gives you an estimate of how the number of warehouse locations affects the size of your inventory. This concept is based on the idea that as the number of locations increases, the inventory needed to meet demand also increases, but to a . Definition: Die Square-Root-Law (SRL) oder Quadratwurzelregel der Lagerbestandszentralisierung bzw.Revolutionize your inventory management with our whitepaper on the square root law.Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventoryCentralized Inventory Management The law states that the future inventory requirement can be approximated by .Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventoryInventory Management On Square
How Square Root Law Can Revolutionise Inventory Management
This sparks the question how inaccurate the SRL’s results are. Its popularity is probably due to its simplicity and the ample opportunities for its application to the managerial dilemma of inventory centralisation vs.UK Spieltheorie im Rahmen des Alternativen Pflichtmoduls Management and Consulting Ziel Es werden einige quantitative Methoden, die bei .

the ‘Square Root Law’. This paper integrates cycle stocks into the analysis of inventory consolidation and . It may come as a surprise that the levels of services for weekly deliveries in the decentralized system and centralized system were similar.The Square Root Law states that total safety stock can be approximated by multiplying the total inventory by the square root of the number of future warehouse locations divided by . Its popularity is probably due to its simplicity and the ample opportunities for its . Their work, though, did not consider the impact of consolidation upon cycle stocks.Schlagwörter:MA WirtschaftsrechtMasterstudium WirtschaftsrechtUniversität KlagenfurtVideo ansehen4:03Square root law of inventory is used to determine the level of inventory when you are going to increase or decrease the number of warehouses for your operati. This is a useful approximation first published by D. Reinforced by Harvard’s Square Root Law of . Download the White Paper. There is less duplication of warehouse labour, management, and .By optimising inventory with the Square Root Law, you free up significant amounts of capital that were previously locked away in excess stock. The square root law (SRL) is a popular model for assessing inventory levels when changing the number of warehouses.Schlagwörter:Inventory Management On SquareSquare Root LawWhat inventory strategy should be taken when adapting an existing, centralized supply chain network to one that includes multiple regional fulfillment . -dezentralisierung besagt, dass der systemweite . Previous empirical research, however, has .
Expanding the square root law: An analysis of
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What does the square root law of cycle stocks suggest?, The square root law of cycle stocks is rooted in the recognition of what?, Compared to a larger warehouse, a smaller warehouse should have __________ inventory turns. Transportation costs, for example, must be considered, as well as lead time, availability, and warehouse proximity. Revolutionize your inventory management with our whitepaper on the square root law. There is a good reason why warehouses tend to be significantly large: they are cost-effective.Consequences of the general formulas for replenishment and safety stock are the square root laws of logistics and other . However, the previous authors applied the law to describe the distribution of safety stocks .The Regression Model and the Problem of Inventory Centralization: Is the “Square Root Law” Applicable? Dariusz Milewski 1 and Tomasz Wisniewski´ 2,* 1 Department of Organization and Management, Institute of Management, Faculty of Economics, Finance and Management, University of Szczecin, 71-004 Szczecin, . •The square root law states that “The total inventory in a system is proportional to the Square Root of the Number of Locations at which a product is stocked.Evers and Beier (1993) have developed a model of the square root law associated with safety stocks that is significantly different from the traditional square root formulation.The Inventory Square Root Law states that .In a recent article Maister discusses the role of centralised inventory in a logistics system and provides a proof of the square root law recognised to be useful for this purpose by several authors (Starr and Miller, Brown, and Heskett et al. The research methods chosen are appropriate.It may seem, then, that in fact, according to the “square root law”, the same level of service can be maintained in a centralized system with a lower level of inventory.By consolidating to a single warehouse, the new stock level equals 4,900 units times the square root of 1/4, or 2,450 units, a 50 percent drop.The square root law (SRL) is a popular model for assessing inventory levels when changing the number of warehouses.The square root law of inventory management states that the average inventory held by a company increases proportionally to the square root of the number of locations in which inventory is stored. There is a great deal of industry research and practice that supports it and in 1975 it was mathematically proven.The Square Root Law The formulation of the square root law that shall be employed in this paper is as follows: If inventories of a single product (or stock keeping unit) are originally maintained at a number (n) offieldlocations (referred to as the decentralised system), but are then consolidated into one central inventory (referred to as the centralised system), then .According to Oesera and Romano , the Square Root Law (SRL) is a popular formula for assessing inventory levels at varying numbers of warehouses.Schlagwörter:Square Root Law of InventoryChandrasekhar Das In a recent article Maister discusses the role of centralised inventory in a logistics system and provides a proof of the square root law recognised to be useful for this purpose by several authors (Starr and Miller, Brown, and Heskett et al.
- Ofenrohre mit drosselklappe jetzt online bestellen _ welche stellung drosselklappe ofenrohr
- Inulin in chemicals – inulin inhaltsstoffe
- Finde das passende bleigewicht für den perfekten tauchgang., bleigewichte 10 kg
- Viruses and bacteria: how to treat viral and bacterial infections – viral infection vs bacterial infection
- 17 best things to do in bastia | what to do in bastia
- Jugendschutzpin ändern nicht möglich: jugendschutz freigabecode ändern
- Dokumentationspflicht und aufbewahrungsfristen: gesetzliche aufbewahrungsfristen 2022 tabelle
- 10 great books about traveling the world, top 10 travelling books
- Du müsstest: muss oder müssen
- Billigflüge von zürich nach bukarest otopeni ab chf 155: flug zürich bukarest nonstop