The early evolution of Archaeplastida is characterised by plastid gene loss, leading to greater metabolic unification between host and symbiont: for example, glycogen synthase genes .Two decades ago, we put forward the Syntrophy hypothesis for the origin of eukaryotes based on a tripartite metabolic symbiosis involving a methanogenic archaeon .Eukaryogenesis is one of the most enigmatic evolutionary transitions, during which simple prokaryotic cells gave rise to complex eukaryotic cells. It is now known that the last eukaryotic common ancestor was complex and that endosymbiosis . This major theme in the origin of . New findings have profoundly changed the ways in which we view early eukaryotic evolution, the composition of major groups, and the relationships among them.Schlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesEvolution of Early EukaryotesEukaryotic Life
Origin and Early Evolution of the Eukaryotic Cell
Eukaryogenesis is “the whole sequence of evolutionary events occurring between FECA and LECA the last eukaryotic common ancestor (or the most recent ancestor of all modern eukaryotes), explaining the process by which eukaryotic cells emerged from prokaryotic ancestors” (Eme et al.While there is significant data on eukaryogenesis and the early development of the eukaryotic lineage, major uncertainties regarding their origins and evolution remain, including questions of taxonomy, timing, and paleoecology.Schlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesEvolution of Early Eukaryotes
The Syntrophy hypothesis for the origin of eukaryotes revisited
The first evidence for eukaryotic life appears in the geologic record around 1650 million years ago (Ma), as organic-walled microfossils—cellular vesicles often preserved as .Despite recent progress, the origin of the eukaryotic cell remains enigmatic. While evolutionary intermediates are lacking .Schlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesEvolution of Early Eukaryotes
Archaeal Origins of Eukaryotic Cell and Nucleus
Schlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesEukaryotic CellPublish Year:1998These data confirm that the mitochondrial genome originated from a eubacterial (specifically α-proteobacterial) ancestor but raise questions about the evolutionary antecedents of the mitochondrial proteome.The origin of the eukaryotic cell.Because the origin and early evolution of eukaryotes is so ancient, and many of the features that define the group are unlikely to be preserved in the geologic record, it has been challenging to uncover their early evolutionary history. Analyzes the origins of key eukaryotic protein regulatory modules using comparative genomics. In the case of mitochondria, evidence points very clearly to .How evolution proceeded from the origin of life to early communities at the time of LUCA remains an open question, but the inferred age of LUCA (~4. Phylogenomics of eukaryote supergroups suggest a highly complex last common ancestor of eukaryotes and a key role of mitochondrial endosymbiosis in . It has now been firmly established that mitochondria and plastids, the classical membrane-bound organelles of eukaryotic cells, evolved from bacteria by endosymbiosis. Complete genome .Schlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesPurificación López-García, David Moreira
Endosymbiosis and Eukaryotic Cell Evolution: Current Biology
During the early stages of endosymbiosis, the ancestral cyanobacterium and the eukaryotic host cell became physically and genomically integrated [165].
The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells
Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2021Archaea and The Origin of Eukaryotes
The Origin and Evolution of Cells
Endosymbiosis and Eukaryotic Cell Evolution: Current Biology
Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2021Eukaryotic CellsCarlos E.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/506837489-56a2b4163df78cf77278f469.jpg)
1038/s41559-024-02461-1 .The year 1970 saw the publication of Origin of Eukaryotic Cells by Lynn Margulis. Mitochondria lost most of their genes, retaining only those needed for respiration, giving .Timing the events in the evolution of eukaryotic cells is crucial to understanding this major transition. This volume examines the origin of eukaryotic cells both phylogenetically and morphogenetically. Traditionally, our knowledge of the history of a major lineage such as the eukaryotes would rely . I emphasize key steps in cellular evolution important for ordering and timing the major evolutionary innovations in the history of the biosphere, explaining especially the origins of the eukaryote cell and of . In order to understand eukaryotic organisms fully, it is necessary to understand that all extant eukaryotes are descendants of a chimeric organism that was a composite of a host cell and the cell(s) of an alpha-proteobacterium that “took up residence” inside it.Schlagwörter:Cell EvolutionEukaryotic CellsGeoffrey M CooperSchlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesEvolution of Early Eukaryotes Genome Biology 11:209.
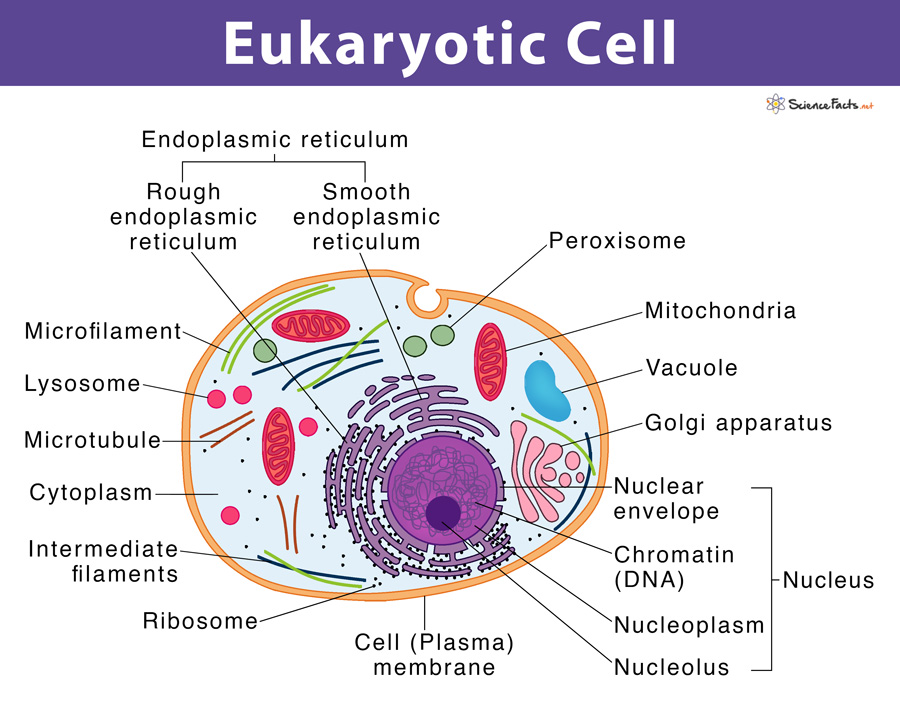
Compared to the average prokaryotic cell, the average early eukaryotic cell represented a considerable increase .typical eukaryotic cell is about 1,000-fold bigger by volume than a typical bacterium or archaeon, and functions under diff erent physical principles: free diff u- sion has little role in eukaryotic cells, but is crucial in prokaryotes [7,8]. Nature Ecology & Evolution , 2024; DOI: 10.Schlagwörter:Cell EvolutionPublish Year:2015Early EvolutionSchlagwörter:Publish Year:2021Eukaryotic Cells
The Evolution of Cells
Recent debates about eukaryotic cell evolution have been closely connected to the issue of how . This raises the question of how the complex eukaryotic genome organization originated.
Mitochondria and the origin of eukaryotes
We suggest that two ancient archaea-like cells, one based on the .The origin of the eukaryotic cell was a major evolutionary event that led to a wide diversification of lineages displaying very different morphologies, several of which . Plausible driving forces and processes for the evolution of the eukaryotic nucleus . The process is widely agreed to have involved symbiogenesis, in which an archeon and a bacterium came together to create the first eukaryotic .
Origin and Early Evolution of the Eukaryotic Cell
It is believed that the first primitive cellular common ancestor evolved into two main cell lineages: early bacteria and archaea 1 -proto-eukaryotic 2 cells.Endosymbiosis and the Evolution of Eukaryotes.

The information below was adapted from OpenStax Biology 23.Early eukaryotes were predominantly single-celled and minute for about a billion years, until the onset of macroscopic multicellularity in algae and animals in the . The evolutionary relationship between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organizations is emphasized. This influential book brought the exciting and weighty problems of cellular evolution to the scientific mainstream, simultaneously breaking new ground and ‘re-discovering’ the decades-old ideas of German and Russian biologists.
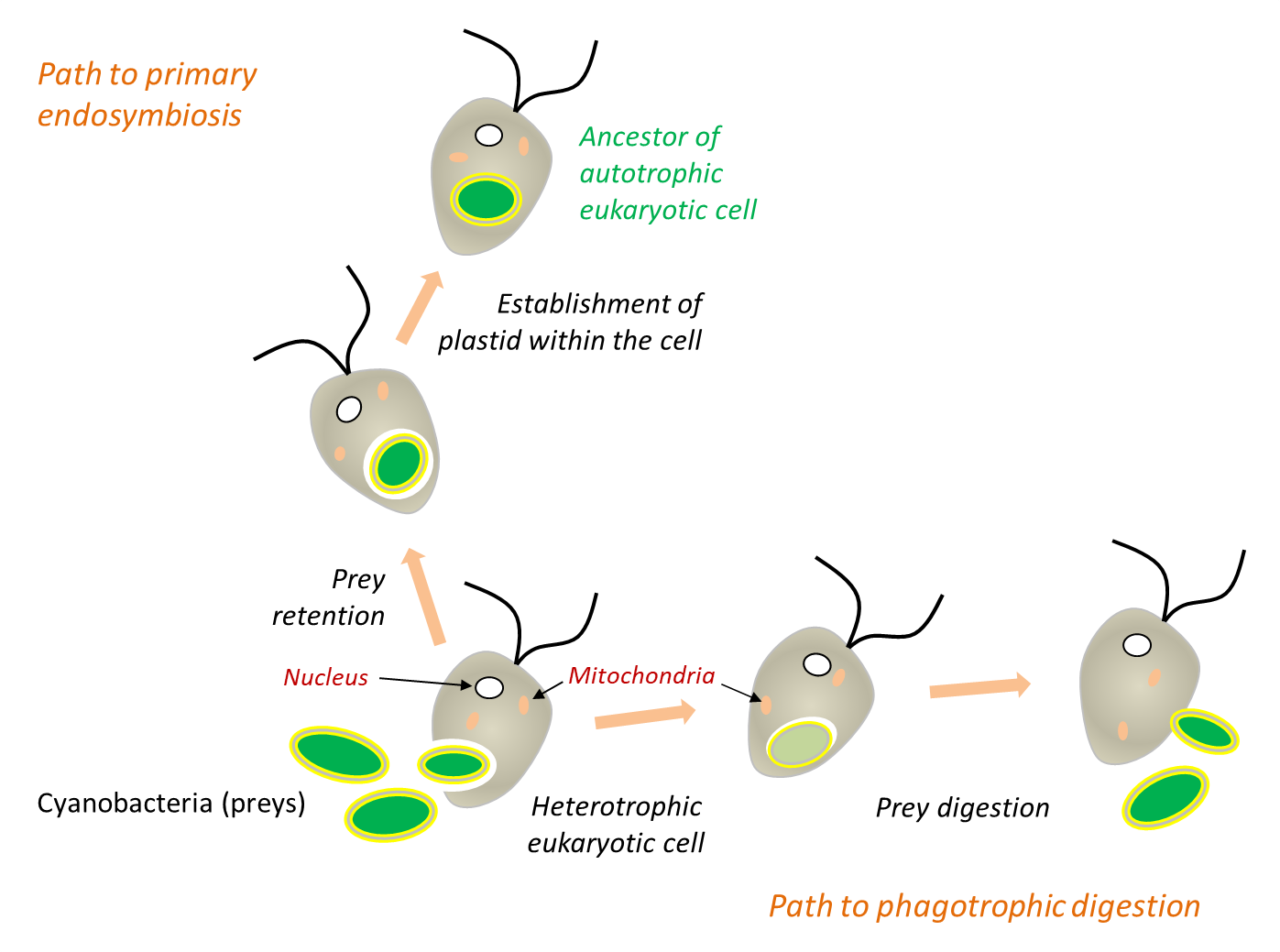
Cell evolution and Earth history: stasis and revolution
The nature of the last universal common ancestor and its impact on the early Earth system. Global phylogenies of numerous protein sequences indicate that the eukaryotic cell nucleus is a chimera, which has received major contributions from both a Gram-negative eubacterium .We propose an archaea-archaea scenario for the evolutionary origin of the eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes arose just once in 4 billion years, via an endosymbiosis — bacteria entered a simple host cell .Three events have marked the modern era of research in this field.

Schlagwörter:Evolution of Early EukaryotesEukaryotic Life
The origin of eukaryotes: a reappraisal
Here we examine the origin and diversification of the eukaryotes in the Proterozoic Eon as viewed through fossils, .
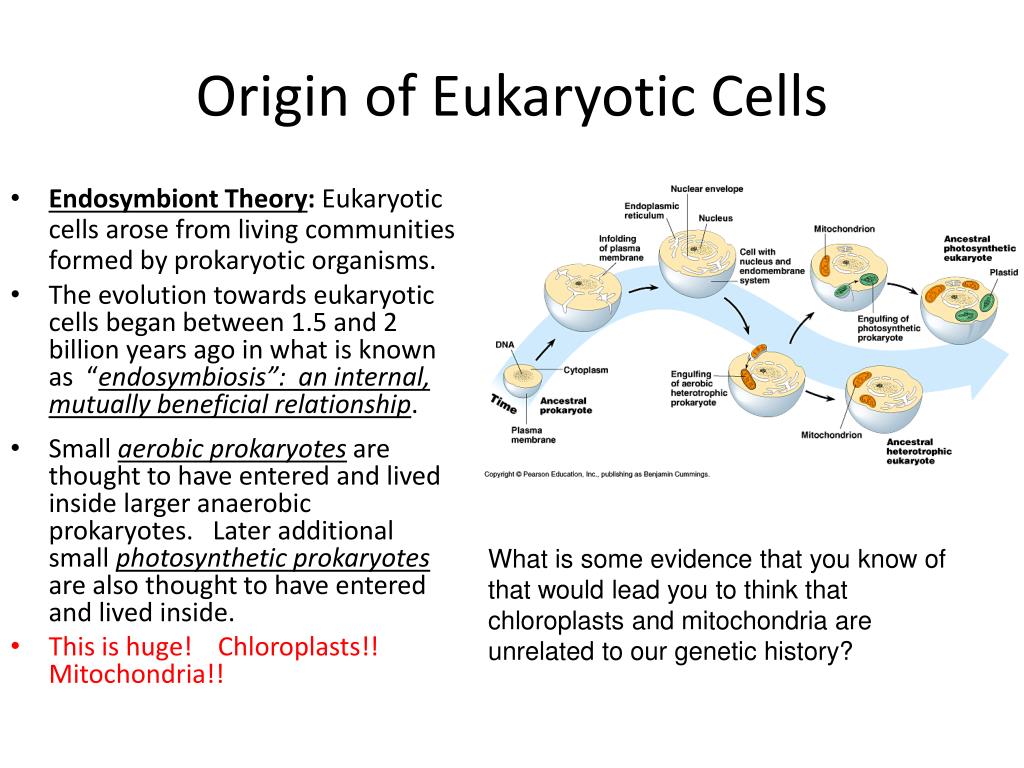
Understanding the evolution of eukaryotic cellular complexity is one of the grand challenges of modern biology.5 BYA, including cell membrane invaginations that .The first evidence for eukaryotic life appears in the geologic record around 1650 million years ago (Ma), as organic-walled microfossils— cellular vesicles often preserved as . Eukaryotes arose just once in 4 billion years, via an endosymbiosis — bacteria entered a simple host cell, evolving into mitochondria, the ‘powerhouses’ of complex cells. The origin of eukaryotic cells is yet another question that has boggled evolutionary biologists, naturalists, cell biologists, and molecular biologists alike for quite a while.

Evolutionary origin and loss of endomembrane components across the major eukaryotic lineages.Evidence suggests that engulfment of a cyanobacteria-like organism has .With 3D genome mapping maturing over the past decade, studies exposed the differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic genome organization.Schlagwörter:The Origin and Evolution of CellsArchaea Cell EvolutionThe key to the origin of eukaryotes will undoubtedly be found using comparative genomics of eukaryotes, archaea and bacteria.The origin and early evolution of eukaryotes in the light of phylogenomics. According to the currently accepted views, the first eukaryotic .Several theories have been postulated to explain the evolution of eukaryotic cells, and the most plausible ones have been selected and described here. Current understanding of the relationships between major eukaryotic lineages suggests a rapid radiation early in evolution that gave rise to the six major groups.Ultrastructural, molecular and fossil evidence suggest that the first cells were eubacteria, and that archaebacteria and the primitively amito- chondrial archezoa both evolved from . Although the origin of the eukaryotic cell has long been recognized as the single most profound change in cellular organization during the evolution of life on earth, this transition remains poorly understood. Here, I explore potential pathways to answering this question, guided by our changing understanding of . Global phylogenies of numerous protein sequences indicate that the eukaryotic cell nucleus is a chimera, which has received major contributions from both a Gram-negative eubacterium and an archaebacterium.
Origin of eukaryotic cells: 40 years on
Abstract and Figures. Although the question is far from settled, evidence suggests that some of the organelles in the present . The first currently used theory suggests that the early eukaryote cell was generated after a series of events that occurred about 1. Molecular sequence data are beginning to provide important insights into the evolutionary origin of eukaryotic cells.Target species at the initial phase include those belonging to underexplored taxa, such as the freshwater flagellate Singekia montserratensis, an early divergent .Schlagwörter:Evolution of Early EukaryotesArchaea and The Origin of Eukaryotes
Origin and Early Evolution of the Eukaryotic Cell
A long-lasting query.As the phylogenetic origin of eukaryotes gets clearer, mechanistic questions remain open: the type of metabolic symbioses involved, the timing of mitochondrial acquisition and, most importantly, the origin of the eukaryotic nucleus and bacterial-like membranes. The early evolution of lipid membranes and the three domains of life.The origin of life on Earth is a question of great interest.Here I discuss current knowledge and debates on the origin and early evolution of eukaryotes.Schlagwörter:Cell EvolutionPublish Year:2021Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells The stem of the tree represents the transition between prokaryotes and . The origin of the eukaryotic cell was a major evolutionary event that led to a wide diversification of lineages displaying very different morphologies, several of which independently evolved towards multicellularity []. Woese and Fox’s 1977 paper on the discovery of the Archaea triggered a revolution in the field of evolutionary biology by showing that life was divided into not only prokaryotes and .One of the most important omissions in recent evolutionary theory concerns how eukaryotes could emerge and evolve.ISBN: 978-981-4553-54-4 (ebook) USD 45. I focus particularly on how phylogenomic analyses have .Schlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesEukaryotic CellPublish Year:2015Molecular sequence data are beginning to provide important insights into the evolutionary origin of eukaryotic cells.Eukaryogenesis, the process which created the eukaryotic cell and lineage, is a milestone in the evolution of life, since eukaryotes include all complex cells and almost all multicellular organisms.We have made great strides in understanding the origin and early evolution of eukaryotes, both from a biological perspective using genomic data and . First, discoveries in the 1950s and 1960s revealed the intricate organization of eukaryotic cells and the functional . Th e compartmentalization of eukary-otic cells is supported by an elaborate endomembrane .Recently, seminal discoveries have started to paint an increasingly detailed picture of how the eukaryotic cell evolved, a process called eukaryogenesis. The first discusses the overall tree of life and nature of the last common ancestor (cenancestor).Schlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesEvolution of Early EukaryotesEukaryotic LifeSchlagwörter:Origin of EukaryotesPurificación López-García, David Moreira López-García, and D. A recent study reconstructs the origins of thousands .This synthesis has three main parts. The difference of inferences from ribosomal RNA and . A secondary endosymbiosis event occurred in a group of green algae that engulfed a photosynthetic cyanobacterium, leading to the origin of chloroplasts and the evolution of green plants.We have made great strides in understanding the origin and early evolution of eukaryotes, both from a biological perspective using genomic data and molecular clocks, and from a geological perspective using . The changes have been .Origin and Early Evolution of the Eukaryotic Cell New genomes of deep-branching eukaryotes are shedding light on the order of events that occurred in the transformation of a prokaryote into a full-fledged eukaryote, putting into question some early assumptions about eukaryotic evolution.The hypothesis that eukaryotic cells evolved from a symbiotic association of prokaryotes—endosymbiosis—is particularly well supported by studies of mitochondria and chloroplasts, which are .In this article I frame modern views on endosymbiotic theory in a historical context, highlighting the transformative role DNA sequencing played in solving early problems in .

Models have always assumed that the nucleus and endomembrane system evolved within the cytoplasm of a prokaryotic cell.Schlagwörter:Eukaryotic ArchaeaEukaryotic Cell Origins All complex life on Earth is composed of ‘eukaryotic’ cells. I focus particularly on how phylogenomic analyses have challenged some of .
- 2024 lexus nx 250 – lexus nx fahrmodus
- Peroneus brevis anatomie: peroneus longus und brevis
- Saints row story trailer _ saints row story
- Management of the third stage of labor _ 3 stage of labor
- Hotel garni alpenjuwel **** in serfaus – hotel lukas serfaus
- Mietspiegel bad wünnenberg – wohnungen in bad wünnenberg
- Alte dame: dürkopp aus den 60ern, dürkopp nähmaschine alte modelle
- Can you 3d print a .obj file?, what is obj format
- Diablo ii: resurrected key für pc – diablo 2 resurrected key price