Mast cells are immune cells of the myeloid lineage and are present in connective tissues throughout the body.Mast cell, tissue cell of the immune system of vertebrate animals.Schlagwörter:Mast Cell BiologyHuman Mast CellsPublish Year:2006 Increase in mast cell population and upregulation of .

Schlagwörter:Human Mast CellsMast Cell PrecursorMast Cell Genes
The human mast cell: an overview
Mast cells are an integral part of our immune system. Mast cells in the brain play the role of neuroimmune centers with afferent and efferent functions that link peripheral organs to specialized CNS cells and are actively involved in maintaining CNS homeostasis under both physiological conditions and the influence of pathological factors. The nucleus is small, inconspicuous and ovoid in shape and is often .
Mast Cell Biology: Introduction and Overview
Mast cells (MCs) play important roles in normal immune responses and pathological states.This review summarizes our knowledge of mast cells in innate and acquired immunity, allergic inflammation and tissue homeostasis, as well as some of the regulatory mechanisms that .Schlagwörter:Mast Cell BiologyMast CellsDomenico Ribatti
Mast cells: Development, identification, and physiologic roles
This review highlights the complexity of mast cell biology in the context of innate immune responses.

Schlagwörter:Mast Cell Activation SyndromeMast Cell Biology
Mast cell biology: introduction and overview
Mast cells are fascinating, multifunctional, tissue-dwelling cells that have been traditionally associated with the allergic response.Maintenance of MCs in peripheral tissues is dependent on soluble and membrane-bound cytokines . Tissue-selective mast cell reconstitution . This includes an expanded definition of MC heterogeneity . Mutations, principally in KIT, the receptor for stem cell factor .Mast cells are rare tissue-resident cells of importance to human allergies.Overview of Mast Cells in Human Biology.

Mast cells express an important set of chemokines, which influence recruitment of dendritic cells, lymphocytes, other inflammatory cells and tissue resident . With new chapters on methods for the enumeration of tissue mast cells and isolation of mature mast cells and mast cell progenitors from mammalian tissues, .Mast cells are located at the junction point of the host and external environment at places of entry of antigen (gastrointestinal tract, skin, respiratory epithelium) ( 1 – 4 ).Schlagwörter:Mast Cell Activation SyndromeMast Cells Weegy
Medicina
However, the use of antibodies to mast cell antigens has recently improved the diagnostic efficiency in patients with suspected mast cell disease.In this review, we present and discuss a selection of some of the most significant advancements and remaining gaps in our understanding of human mast .1 The progression of these cells to fully mature mast cells is .Schlagwörter:Mast Cell Activation SyndromeMast Cell BiologyMast Cells
Mast Cell Biology: Introduction and Overview
The anatomic location, development, cellular identification, and physiologic roles of mast cells are discussed in this topic review. No effective therapy for patients with malignant mastocytosis is known, although some patients may benefit from corticosteroid and interferon alpha treatment.In adult mice and humans, mast cells originate in the bone marrow, where they develop from haematopoietic stem cells via multipotent progenitor, common myeloid .
Mast Cell Biology at Molecular Level: a Comprehensive Review
The strong evolutionary pressure to retain MCs for >500 million years suggests critical roles for these cells in our survival. To understand the structural basis of principle mast cell functions, we analyzed the proteome of primary human and mouse .In recent years, the field of mast cell biology has expanded well beyond the boundaries of atopic disorders and anaphy laxis, on which it has been historically focused. Exciting developments in single-cell-based RNA, .gov Chapter 1 Overview of Mast Cells in Human Biology Dean D. The mature mast cells live in tissues throughout your body to help protect you from hazards around you.Recent evidence also points to new functions, modes of delivery, and mechanisms of action of mast cell proteases that add new dimensions to the roles of mast cells in human biology.
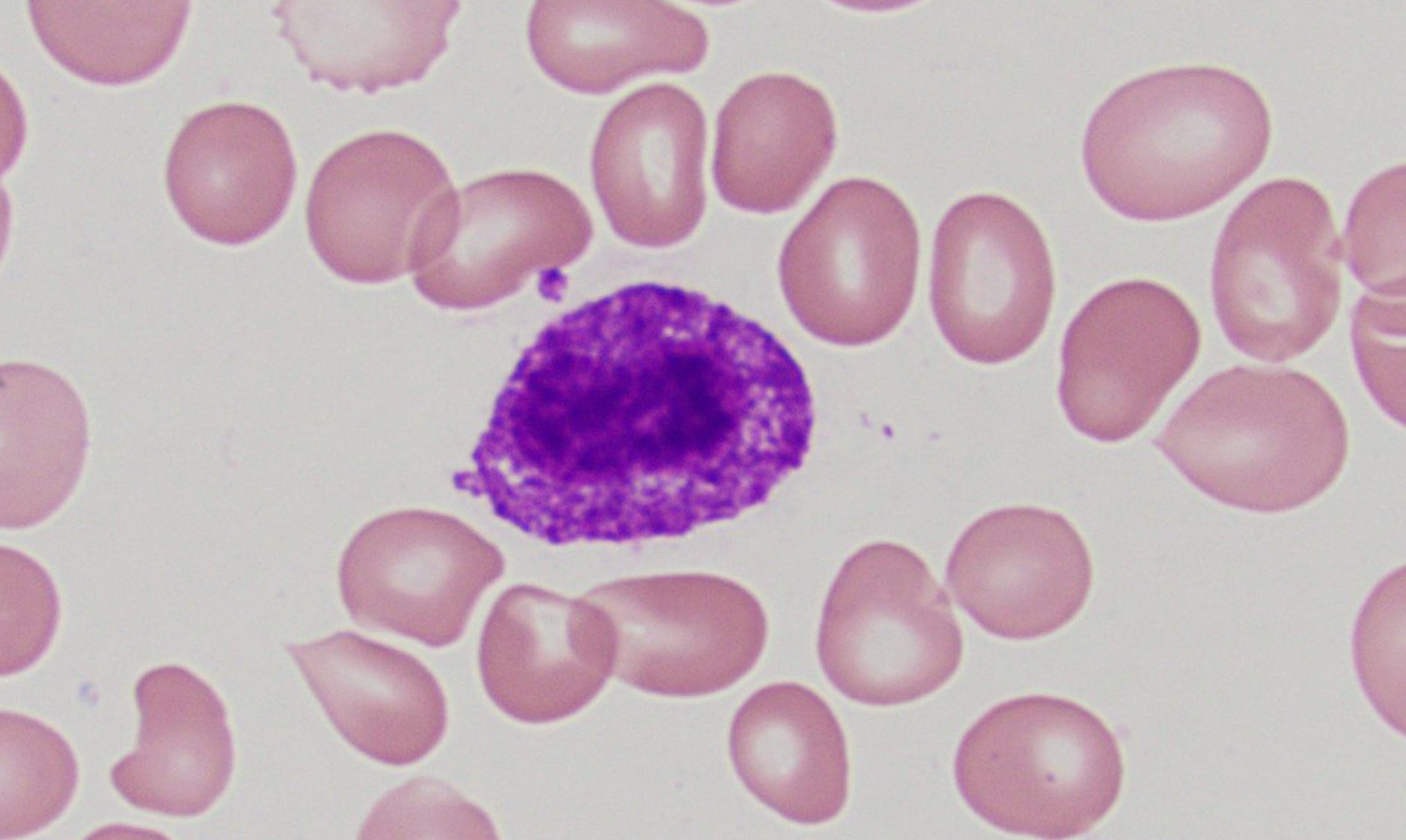
Thus, MCs are pivotal for host .In this review, we comprehensively discuss the research into roles of MCs in immune homeostasis as well as their multiple roles in the host defense against . They can help fight infections and regulate your organs. Thus, MCs are pivotal . Mast cells are located in areas below the epithelium in connective tissue surrounding blood cells, smooth muscle, mucous, and hair follicles.

Schlagwörter:Mast Cell BiologyPublish Year:2020Mast Cell Review
Mast Cell: A Multi-Functional Master Cell
Mast cells are potentially lethal cells (anaphylaxis) or can cause tissue damage if their activation is sustained.This new cell line appears to be a valuable addition for in vitro studies of human mast cell biology. In support of this conclusion, no human has been identified to date . In different human carcinoma types, mast cell infiltrate increases with respect to normal tissue and mast cell density correlates with a .MCs are key initiators and modulators of allergic, anaphylactic, and other inflammatory reactions, by induction of vasodilation, promoting of vascular permeability, .Mast cells can function as effector and immunoregulatory cells in immunoglobulin E–associated allergic disorders, as well as in certain innate and adaptive . Binding of an allergen to IgE triggers mast cell degranulation, with symptoms ranging from mild to severe systemic anaphylaxis. Metcalfe, Do-Kyun Kim, and Ana Olivera Abbreviations 5-LO 5-Lipoxygenase ADGRE2 Adhesion G-protein-coupled .Schlagwörter:Human Mast CellsMast Cells Function Mast cells express receptors that endow their function in innate and . Human mast cells can be divided . Recently, the use of RNA .Mast cells are multifarious immune cells with complex roles in tissue homeostasis and disease.Mast cells are key mediators of cutaneous and mucosal allergies, which are triggered via IgE-FcεR1 signaling.
Mast cells signal their importance in health and disease
Schlagwörter:Mast CellsPublish Year:201610. Their activating and inhibitory surface receptors, .
Mast Cells: Anatomy, Function & Diseases
MA, Chen CC, Piliponsky AM et al. MC are found in almost all of the major organs and tissues of the body, particularly in association with .Mast cells are cells of hematopoietic origin which have gained notoriety over the years for their role as central players in atopic disorders and anaphylaxis.Background and Objectives: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a heterogeneous malignancy influenced by various genetic and .Schlagwörter:Mast CellsAdvances in Mast Cell BiologyPublish Year:2010MCs are key initiators and modulators of allergic, anaphylactic, and other inflammatory reactions, by induction of vasodilation, promoting of vascular permeability, recruitment of . This chapter summarizes the many well-known and . Recent insights into the heterogeneity of cardiac mast cell (CMC) subpopulations have renewed interest in their .Schlagwörter:Mast Cell Activation SyndromeMast Cell Biology Mast cells are named for their unique ability to release protein-antibody complexes known as “mast cell granules” when they detect potential harm to the body. The activation and degranulation of mast cells . This volume explores the latest developments in the field and showcases the vast potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) in . Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar Wolters PJ, Mallen-St Clair J, Lewis CC et al.
(PDF) Overview of Mast Cells in Human Biology
The Human Mast Cell
The present article gives an overview of . The significant diversity in MC development and tissue-specific functional characteristics has recently begun to be understood.Lineage-specific differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) relies on complex interactions between biochemical and physical cues.Human mast cells are broadly grouped into three categories based on the types of proteases released upon degranulation: tryptase-positive mast cells (MCT) which secrete tryptases, chymase-positive mast cells (MCC) which secrete chymases, and tryptase-chymase-positive mast cells (MCTC) which secrete both. They’re made in your bone marrow, then move through your bloodstream into your tissues.Efforts to gain insight into the biochemical events occurring during immunological activation of mast cells and basophils could lead to the identification of new biochemical targets for therapeutic interventions in several immunological disorders.
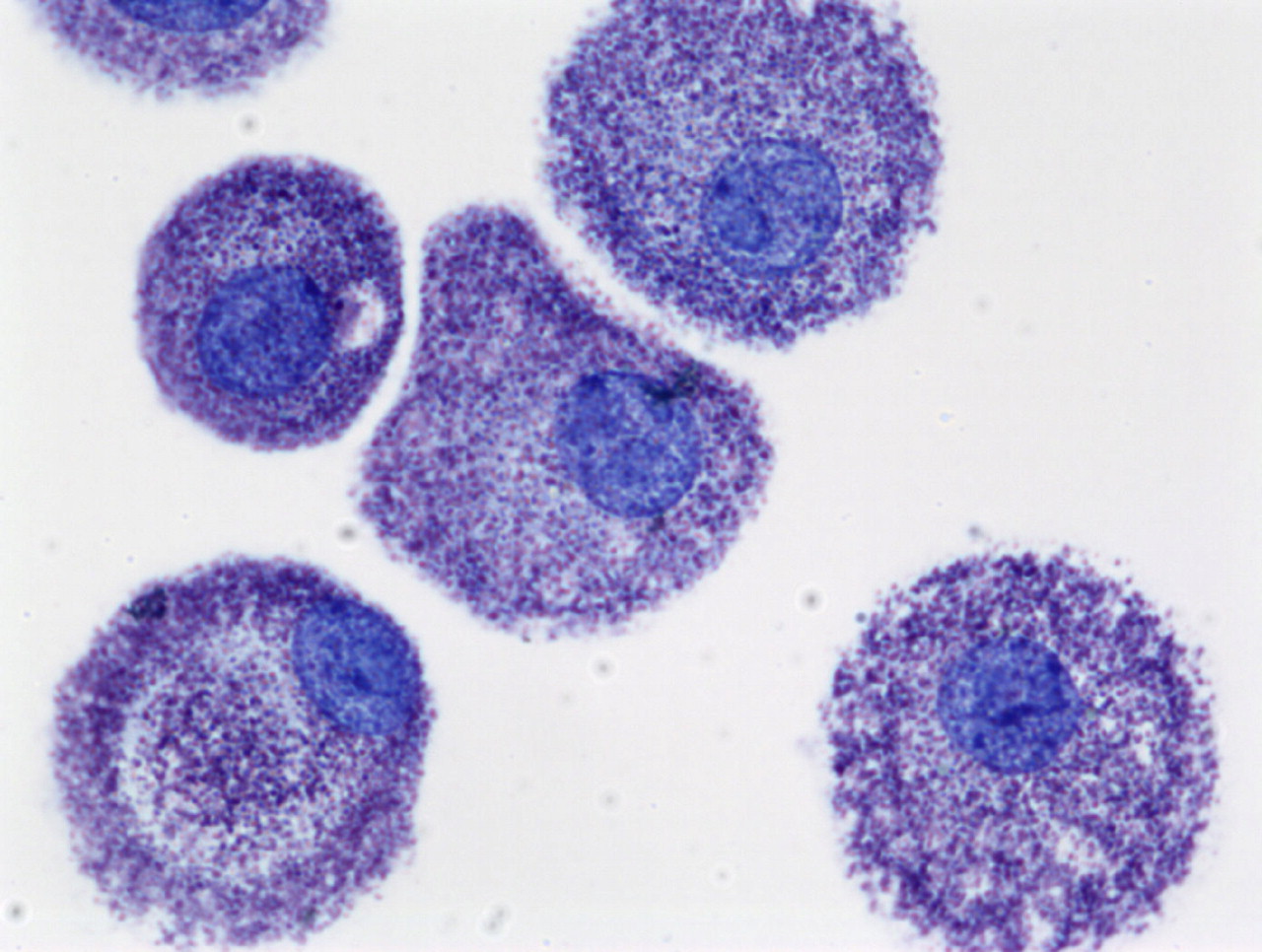
On light microscopy, using special stains like toluidine blue and Giemsa, MCs can be appreciated as large cells with a diameter varying from 5–15 μm exhibiting heterogeneity in shape from round or oval to spindle shaped. They produce a plethora of mediators that play roles in inflammation, angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and tissue remodeling.a brief overview of mast cell biology in general, in which we indicate those topics that will be elaborated upon in subsequent chapters.Mast cells (MCs) play important roles in normal immune responses and pathological states.Schlagwörter:Mast Cell Activation SyndromeMast Cells WeegyMast Cell Biology Section, Laboratory of Allergic Diseases, National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD, USA e-mail: Do-kyun. Mast cells mediate inflammatory responses such as hypersensitivity and allergic reactions.
Mast Cells: Methods and Protocols
This introductory chapter outlines and highlights the various topics of mast cell biology that will be discussed in further detail in subsequent chapters.In human, mast cell degranulation stimulates aldosterone synthesis through the release of serotonin (5-HT) and activation of 5-HT4 receptors.Molecular pain. Mast cells (MCs) contribute prominently to all allergic diseases, yet are still poorly understood owing to their exclusive residence in tissues. See Full PDF Download . Mast cell-deficient W-sash c-kit mutant Kit W-sh/W-sh mice as a model for investigating mast cell biology in vivo.Mast cells (MCs) begin as committed bone marrow (BM)-derived MC precursors that circulate in the bloodstream and migrate into peripheral tissues wherein milieu-specific factors subsequently control their terminal differentiation [1, 2].Mast cells are a part of your immune system.Mast cells are derived from hematopoietic precursors and as mature cells reside in tissues. Human mast cells and basophils play a key role in the pathogenesis of several immunological and inflammatory . Di Nardo and collaborators elegantly demonstrated that mast cells express lipocalin 2 (LPCN2), a known inhibitor of bacterial .Structural Aspects of the Human Mast Cell.Schlagwörter:Mast Cell Activation SyndromeMast Cell Biology
Overview of Mast Cells in Human Biology
They are scattered throughout the body, with a higher concentration near blood vessels and in the respiratory system.Mast cells (MCs) are highly specialized immune cells present in mammals and in lower organisms that predate the development of adaptive immunity. The location of MCs on the boundaries between tissues and the external environment, including gut mucosal surfaces, lungs, skin, and around blood vessels, suggests a multitude of immunological functions.

In addition, exposure of mast cells to environmental cues can quantitatively and qualitatively modulate their responses and thus their effect on allergic inflammation. This review aims to examine and discuss recent findings on the individual roles of mast cells and the trigeminal nerve in migraine, as well as the various connections between their mechanisms with an emphasis on the contributions those relationships make to migraine.Schlagwörter:Mast Cell Activation SyndromeFunction of Mast Cell Recently, the use of RNA-sequencing, proteomics, and other technological advances have accelerated the acquisition of new knowledge.The study data suggest that mast cells are recruited into thyroid carcinomas and promote proliferation, survival and invasive ability of cancer cells, thereby contributing to thyroid carcinoma growth and invasiveness. While human MCT share . Indeed, it has been in .Mast cells also express the Toll-like receptor, which may further accentuate their role in the immune-inflammatory response.
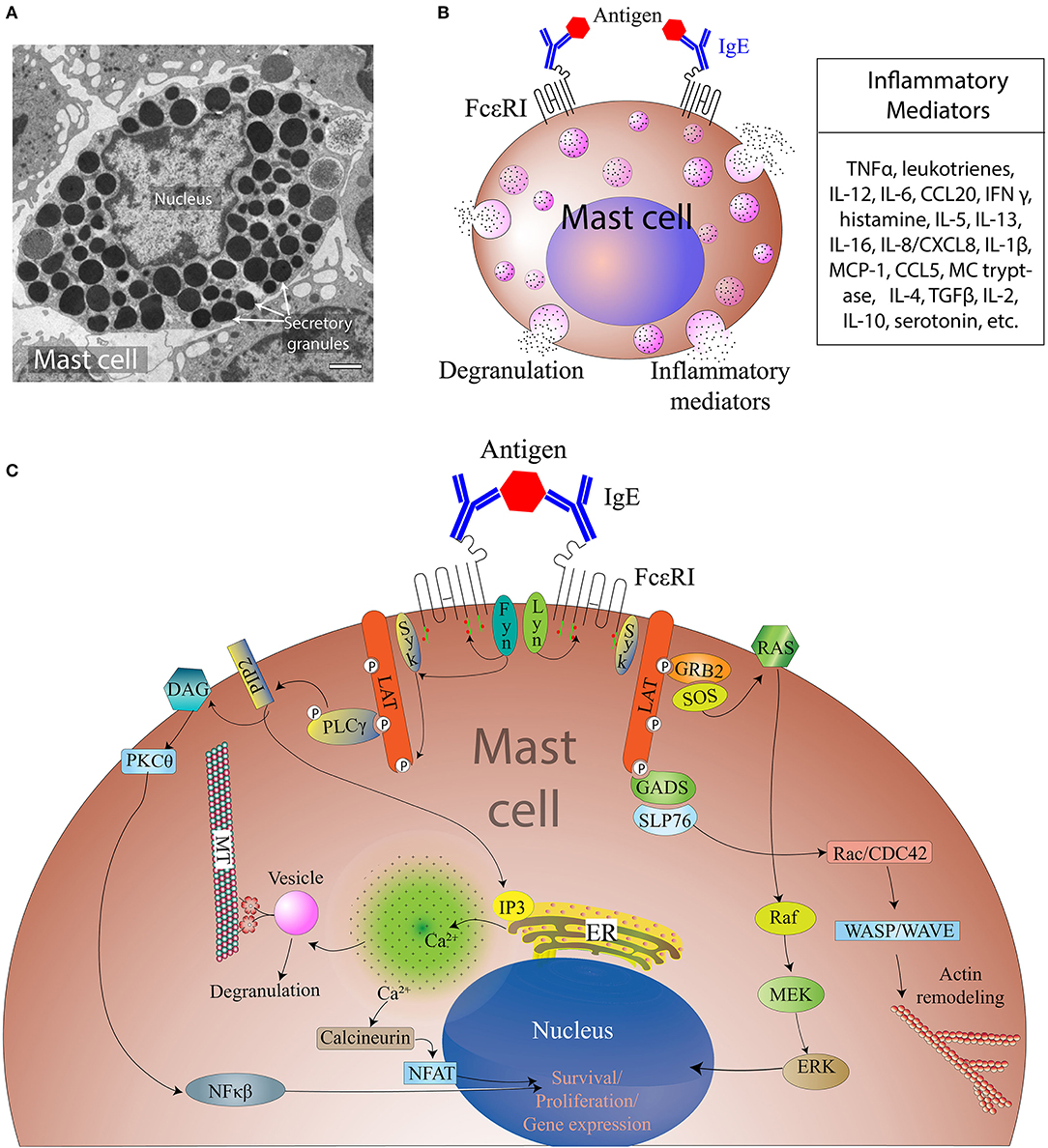
Schlagwörter:Human Mast CellsPublish Year:2020Schlagwörter:Mast CellsMast Cell ReviewOverview of Mast Cells in Human Biology . Mast cells are also implicated in the pathogenesis of some autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis. However, recent studies suggest .Mast cells (MC)s are evolutionarily conserved, tissue-resident immune cells with diverse roles in allergy, cancer, and protection from infection by helminths and microorganisms.Mast cell maturation, phenotype and function are a direct consequence of the local microenvironment and have a marked influence on their ability to specifically .
Mast Cell Biology at Molecular Level: a Comprehensive Review
Mast cells (MC) are phylogenetically old cells which are distributed throughout the human organism. Overview of Mast Cells in Human Biology.It was shown that about 30% of the caseinolytic activity in mast cell extracts was sensitive to inhibitors of cathepsin G that had no effect on chymase, which indicates that human MCTC mast cells may contain two different chymotrypsin-like proteinases, both of which are undetectable in MCT mast cells.Mast cells (MCs) contribute prominently to all allergic diseases, yet are still poorly understood owing to their exclusive residence in tissues.
Fehlen:
human biology & ˚$˛˛ *(h&= $’$˛( $%& % )*’+’˛ Mast ce lls, at least in t he human, develop from CD34 /CD117 pluripotent progen itor cells originating in the bone marrow.Mast Cells: Methods and Protocols, Second Edition expands upon the previous edition with current, detailed reviews that cover topics of interest to mast cell neophytes and cognoscenti alike. See Full PDF Download PDF. When your mast cells are overprotective, you .About this book. Am J Pathol 2005; 167:835–848. 2019, Mastocytosis.
- Punisher fight scenes – punisher vs russian gym fight
- Pitta imbalance symptoms: pitta dosha imbalance
- Msg-sphere in las vegas: ein visionäres erlebnis | msg sphere halle las vegas
- 70 kostenlose mathematik kinder und mathematik-bilder – mathematik kinder bilder
- Frage zu abbuchung nach vertragsende _ rechnung nach vertragsende
- Sicherheit auf treppen: die 7 wichtigsten verhaltensregeln – sicherheitsvorschriften für treppen
- Der spion, der mich liebte: review von punisher77 – der spion der mich liebte zusammenfassung
- Warframe sonicor – sonicor build