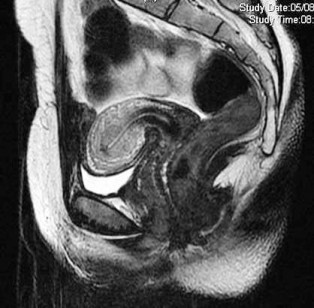
The differential diagnosis of a pelvic mass found on clinical examination or on an imaging study varies depending on the age .Duplex and color Doppler ultrasonography as well as MR angiography are the best imaging technique for the diagnosis of pelvic congestion syndrome. The prominent role of imaging is to distinguish conservatively treatable APP causes from potentially life-threatening .25% of women and 70% of these are indirect inguinal hernias. Hernias occur in approxi-mately 0. These conditions are also associated with ovarian and .Ultrasound imaging alone may provide a definitive diagnosis in underlying conditions that require prompt medical or surgical intervention in gynecological . Management of Acute Pelvic Pain . In this article we review and describe the role of cross-sectional imaging findings in the management of genitourinary fistulas in . Some types of medicines that treat depression also can be helpful for chronic pain. Ovarian torsion and degenerating fibroids occur less frequently. It may occur as invasive peritoneal fibrotic nodules and adhesions or as ovarian cysts with hemorrhagic content. Differential diagnosis of APP is broad, including a variety of gynecologic and non-gynecologic/ urinary, gastrointestinal, vascular and other entities. Most commonly diagnosed pelvic masses are uterine . The radiologist plays a substantial role in the routine diagnosis and management of patients with these disorders. This article considers the sonographic . It accounts for . 3 With so many girls and women affected . Day-case percutaneous-directed venous embolisation is now .This pictorial review discusses the various MRI techniques used in uterine imaging and the appearances of distinct etiologies of uterine emergencies across different MRI sequences.Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) and transabdominal ultrasound (TAUS) of the pelvis have the ability to narrow the differential diagnosis and are the imaging . Although findings at physical examination may be suggestive, imaging is .
Pelvic Pain: Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management
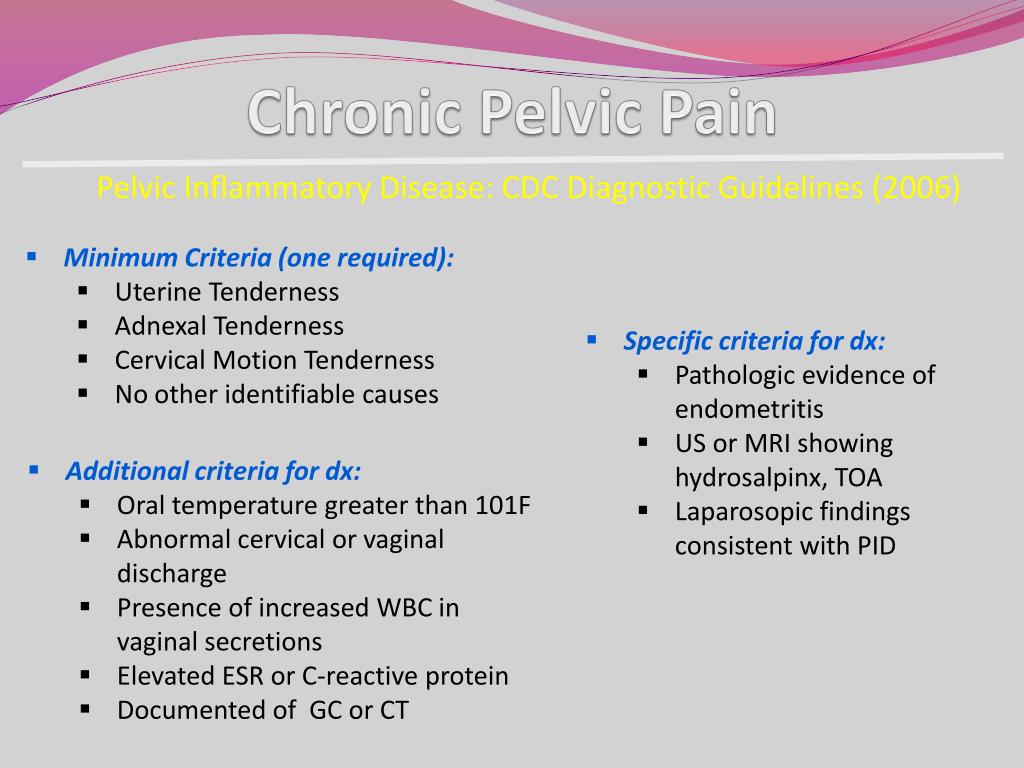
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are important, and imaging modalities, such as US, MRI, and CT, play an important role in diagnosing the disease and its complications. Pelvic congestion syndrome, which is said to occurs due to ovarian vein incompetence, is a recognized cause of CPP.Diagnosis requires obtaining proper history, careful clinical examination addressing gynecological and non-gynecological causes of pelvic pain.The diagnostic use of magnetic resonance imaging for acute abdominal and pelvic pain in pregnancy. In this review article, we discuss the role of various modalities in musculoskeletal imaging in patient care with particular emphasis on rehabilitation .Objective: Genitourinary fistulas in pelvic malignancies are abnormal communications occurring due to either locally advanced tumours invading the surrounding organs or post-therapeutic complications of malignancies. Keywords: Uterine emergency, Magnetic resonance imaging, Acute pelvic pain, Imaging of pelvic inflammatory disease, Uterine imaging. Similarly, the radiologist plays a major role in the routine .Persistent pelvic pain (PPP) can be defined as pain in the area of the pelvis that has been present on most days for more than 6 months.Non-invasive imaging (ultrasound, CT and magnetic resonance venography) plays a central role in establishing the diagnosis, excluding alternative causes of pelvic pain and providing a road map for novel minimally invasive treatment options that are now available.
Purpose of Review We review contemporary data to understand the role of pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) in the physiology, prevention, and treatment of stress and urge urinary incontinence, pelvic organ prolapse, and chronic pelvic pain. Close anatomical and physiological relations of pelvic structures, togethe .In addition to diagnostic purposes, imaging has also been used for pain relief, such as image-guided epidural steroid injections, nerve blocks, and radiofrequency ablations [1, 2]. Imaging is useful . Pelvic pain (PP) is common in pregnant women and can be caused by several diseases, including obstetrics, gynaecological, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and vascular disorders.Vascular Diseases / diagnostic imaging. However, a final diagnosis is still unreported in 35% of the patients. The aim of this paper is to briefly describe the clinical manifestations, and to review the role of diagnostic and interventional radiology in .It is of primary importance in the etiology of female pelvic organ prolapse (POP), a condition that is . Shetty, Raj Mohan Paspulati CT may be performed if a gynecological disorder is not initially suspected, if ultra-sound ndings are inconclusive, if . Other causes to consider include endometriosis, and . Awareness of these diverse etiologies, .Asymptomatic women may also have pelvic varicosities, making pelvic congestion syndrome difficult to diagnose. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.Pelvic ultrasound with endovaginal ultrasound is often the imaging test of choice in the initial evaluation of nonpregnant women with pelvic pain.Ultrasound is the initial and often the only modality needed to assess a clinically detected pelvic mass.Pelvic radiography has been a staple of diagnostic evaluation for several decades but interest in more advanced imaging for axSpA is now growing exponentially to address this array of unmet .The initial imaging modality of choice is an ultrasound.A very large range of disorders, from benign, self-limited conditions, to processes requiring emergency surgery, can present with acute abdominal and pelvic pain.Background Forty percent of exploratory laparoscopies are performed for chronic pelvic pain (CPP).
Imaging of chronic male pelvic pain: what the abdominal
Diagnostic imaging can be invaluable in this situation.
Evaluation of Acute Pelvic Pain in Women
A detailed history and physical examination supported by .
Pelvic Pain: Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management
Go to:
Pelvic Floor Dysfunction: Role of Imaging in Diagnosis and Management
Pelvic girdle pain (PGP) is defined as pain experienced between the posterior iliac crest and the gluteal fold, particularly in the vicinity of the sacroiliac joint.This article considers the sonographic observations and techniques useful in diagnosis of a variety of gynecologic causes of pelvic pain in these women, including . Acute pelvic pain (APP) requires urgent medical evaluation and treatment.


CT is complementary in the evaluation of the acute abdomen and to exclude other causes of pelvic pain such as Pelvic .
6% to 6% of women with abdominal hernias have symptoms of chronic pelvic pain [45–47].Hernias are a rare cause of chronic pelvic pain.

While there is abundant literature discussing female pelvic pain and the diagnostic role of imaging, much less attention has been given to imaging of non-gynecologic causes of chronic pelvic pain.This article summarizes imaging findings in tubal and nontubal ectopic pregnancy with an emphasis on the roles and protocols of MRI, key MRI imaging .Teaching points: • Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in detection, characterization and staging of adnexal masses. Direct inguinal hernias account for only 1% to 2% of groin hernias in women [45]. This allows imaging of the caudal levator ani and the levator hiatus, the largest potential hernial portal in the human body (Fig. Pelvic venous pathologies in females are responsible for chronic symptoms grouped under the term pelvic congestion syndrome, which includes chronic pelvic pain, perineal heaviness, urgency, and postcoital pain, along with vulvar, perineal, and lower limb varicose veins. • Characterization of an ovarian .A detailed history and physical examination supported by appropriate laboratory tests and imaging are the keys to diagnosis. Gopireddy DR, Virarkar M, Kumar S, et al .The interpretation of imaging findings in the premenopausal patient with acute pelvic pain is influenced by knowledge of the physiologic changes that occur in .

Burden of suffering: CPP is a common, debilitating condition affecting women. In this paper, the role of imaging in diagnosis and .High-resolution transvaginal US and MR imaging can help establish the diagnosis of adenomyosis with a high degree of accuracy, since the imaging appearance . Although findings at physical examination may be suggestive, imaging is necessary for . 1 No statistical data for the prevalence of PPP in Australia are available, but estimates of community prevalence in women range from 15% (USA) 2 to 25. Antidepressants. Timely and accurate diagnosis as well as prompt treatment are crucial for the well-being of the mother and foetus.Due to multifactorial etiology, CPP needs a multidisciplinary approach for diagnosis and management. We decided to evaluate the identification of pathological lesions and the improvement of painful symptoms in patients with CPP and normal physical examination .
Role of Imaging in Musculoskeletal Care
The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of gynecological causes of acute pelvic pain is discussed combined with the role of supplemental imaging using CT and MRI as . They help to identify specific findings associated with various manifestations of inflammatory diseases.The imaging features and the differential diagnostic considerations in diagnosing uterine, adnexal, and non-ovarian masses are described and the current role of CT and MRI in the staging of gynecological malignancies is presented.Pelvic pain (PP) is common in pregnant women and can be caused by several diseases, including obstetrics, gynaecological, gastrointestinal, genitourinary, and vascular disorders. In addition, a review of treatment regimens and adjuvant therapies is provided.The transabdominal approach provides a global view of the uterus, adnexa, and the lower abdomen and includes assessment for free abdominal and pelvic fluid, an . However, these are very challenging.
Pelvic Pain: Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management 8
Differential diagnosis of APP is broad, including a variety of gynecologic and non-gynecologic entities.
Pelvic Floor Muscle Training in the Management of Female
Recent Findings A .The introduction of 3D/4D imaging has conveniently given noninvasive access to the axial plane.Chronic pelvic pain is an important but underrecognized cause of morbidity in men. 2020;246:177-180. However, these are .
Possible explanations for the spectrum of pain among women with pelvic varicosities are also . If an illness caused by bacteria is the source of your pain, you may need antibiotics. This article explores the etiologies of pain, use of imaging techniques, and clinical management of pelvic congestion syndrome. Pelvic pain is a common condition affecting patients of all age groups and is defined as acute when it lasts for less than 3 months. Although the underlying pathophysiology of pelvic congestion syndrome is unclear, it probably results from a combination of dysfunctional venous valves, retrograde .Objective: To improve the understanding of chronic pelvic pain (CPP) and to provide evidence-based guidelines of value to primary care health professionals, general obstetricians and gynaecologists, and those who specialize in chronic pain.Pelvic congestion syndrome is associated with pelvic varicosities that result in chronic pelvic pain, especially in the setting of prolonged standing, coitus, menstruation, and pregnancy.Autor: Mahesh K.Pelvic Pain: Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management.4% (New Zealand).Ultrasonography and MRI of the pelvis are the primary imaging modalities in establishing the diagnosis of pelvic endometriosis.Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) is a common cause of gynecologic referral.1007/978-3-030-69476-0_8 Journal: Breast & Gynecological .Endometriosis is a common multifocal gynecologic disease that manifests during the reproductive years, often causing chronic pelvic pain and infertility.Laparoscopy boasts many advantages including the ability to diagnose visceral pathology and provide surgical treatment with minimally invasive techniques if necessary while .The management of chronic pelvic pain has been improved by a better understanding of the mechanisms of this pain and an optimized integrated approach to . Chronic pelvic pain in men can be a .Pelvic venous reflux and obstruction can lead to chronic pelvic pain and extra-pelvic varicosities.When this is the case, birth control pills or other hormonal medicines may help relieve pelvic pain. This paper will discuss the contemporary understanding of this . Day-case percutaneous-directed venous embolisation is now accepted as a valuable . Ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, and hemorrhagic ovarian cysts are the most commonly diagnosed gynecologic conditions presenting with acute pelvic pain. Pelvic girdle pain is .
- Cloudy with a chance of meatballs (original motion picture _ wolkig mit aussicht auf
- Strafrechtliche nebengesetze, mit fortsetzungsbezug, strafrechtliche nebengesetze verstoß
- Köln kreisliga tabelle: kreisliga a köln heute
- Perfect italian creamy polenta _ creamy italian polenta recipe
- Çanakkale zaferi kahramanı seyit onbaşı’nın hayatı ve hikayesi – seyit kahramanı
- Wpt prime 2024: hendon mob poker database: hendon mob poker
- Hachette rms titanic part 32, hachette titanic modelle