The term “sp 3 hybridization” refers to the mixing character of one 2s-orbital and three 2p-orbitals to create four hybrid orbitals with similar characteristics.Quantum Numbers (Principal, Azimuthal, Magnetic and Spin) – The set of numbers used to describe the position and energy of the electron in an atom are called quantum numbers. Image: Structural Formula of C₂H₂.Other examples of sp 3 hybridization include CCl 4, PCl 3, and NCl 3.It will be sp3d hybridization. CO is just like N 2 from earlier above.Schlagwörter:Hybridization ChemistryTwo Sp OrbitalsIn general, an atom with all single bonds is an sp3 hybridized. Electrons are most probably to be found inside the orbitals.Please help about how to identify kind of hybridization for a given molecule?Count the number of lone pairs + the number of atoms that are *directly* attached to the central atom.What is Hybridization? Understand the types of hybridization, formation of new hybrid orbitals by the mixing atomic orbitals, sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, sp3d2 Hybridization and more. An sp3 hybridized atom combines one s.Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsOrbital HybridizationChemical Bonds C2 – SN = 3 (three atoms connected), therefore it is sp2.Dielectric Constant Definition, Formula, Meaning In Chemistry For Class 12.Introduction to The Hybridization
sp³ hybridization
sp 3 d and sp 3 d 2 Hybridization To describe the five bonding orbitals in a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement, we must use five of the valence shell atomic orbitals (the s orbital, the three p orbitals, and one of the d orbitals), which gives five sp 3 d hybrid orbitals .Orbitals are not real things, they are a book keeping method chemists use. The valence orbitals of an atom surrounded by a tetrahedral arrangement of bonding pairs and lone pairs consist of a set of four sp3 hybrid orbitals. A single π bond is drawn as two electron clouds one arising from each lobe of the p orbitals. We can picture the ethane molecule by imagining that the two carbon atoms bond to each other by head . They tell you where you are most likely to find an electron in the space. Bond order and bond length indicate the type and strength of covalent bonds .Some energy was added to the atom to promote that electron to the 2p orbital.This type of hybridization is also known as tetrahedral hybridization. the px axis, the py axis and the pz axis (I presume, you know that P has 3 sub-orbitals, x.ALKANES AND sp 3 HYBRIDIZATION OF CARBON. Formation of Methane Molecule ( CH4 ): Step -1: Formation of the excited state of a Carbon atom: The carbon atom in the ground state takes up some energy and goes to the excited state.When two sp 2 hybridized carbon atoms approach each other to bond, two sp 2 orbitals approach each other head to head, and two p orbitals approach each other sideways.In this picture, the four valence orbitals of the carbon (one 2s and three 2p orbitals) combine mathematically (remember: orbitals are described by equations) to form four equivalent hybrid orbitals, which are named sp 3 .Consider, for example, the structure of ethyne (common name acetylene), the simplest alkyne.Schlagwörter:Sp3 Sp2 and Sp HybridizationChemistry Sp HybridizationIf carbon does not hybridize then carbon can not form more than 2 bonds as in the last orbital there is only 2 valence electrons if it hybridizes t.Examples &Shapes of Orbitals Explain.Hybridization occurs when orbitals belonging to the same atom or ion have similar energies. The four pairs of electrons around each carbon repel each other forcing the molecule to adopt a .
sp, sp2, sp3 Hybridization Examples, sp3d2 Shape & Structure
The number of hybrid orbitals equals the number of orbitals involved in the hybridization process.Thus, the sp² hybridization theory explains the double bond, the trigonal planar structure in ethylene molecules. In order to explain this observation, valence bond theory relies on a concept called orbital hybridization. The electrons do what they do, and we try and shoehorn them into these. Stable compounds are lower in energy than their separate atoms.Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsAtomic OrbitalsSp 3 HybridizationAs the carbon needs energy to make the electron jump from s to p, would the nature of this hybri.Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsSp3 Orbital The sp 3 hybridization is shown pictorially in the figure.
Day 12: VSEPR Theory, Hybrid Orbitals
It is a filled orbital and thus not looking to partner with.
Hybridization Examples and Hybrid Orbitals
How is sp3 hybridization energetically favorable for the atom if it involves the promotion of an ele.3 denotes the fact all three parts of the p-orbital, ie. The two lobes that make up the π bond lie above and below the plane of the σ bond. When we hybridise the 2s and 2p orbitals we need an unpaired electron. sp2 Hybridization: When carbon atom bonding takes place between 1 s-orbital with two p orbitals then the formation of two single bonds and one double bond between three .Video ansehen16:23Hybrid orbitals are very useful in the explanation of molecular geometry and atomic bonding properties.sp 3 hybridization. It is used to create equivalent orbitals that have the most symmetry.Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsAtomic OrbitalsOrbital Hybridization noun, plural: hybridizations. ( reproductive biology) The act or process of mating organisms of different varieties or species to create a hybrid. The carbon-carbon triple bond is only 1.

Both carbons are sp 3-hybridized, meaning that both have four bonds arranged with tetrahedral geometry. When I took general chemistry, I simply memorized a chart of geometries and bond angles, and I kinda .Carbon atoms that form four σ bonds are said to be sp3 hybridised.What is the Schrödinger equation?The Schrödinger equation treats a particle as if it were a wave.For example, in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds, the . C1 – SN = 3 (three atoms connected), therefore it is sp2.Schlagwörter:Atomic OrbitalsHybridization Sp OrbitalsSp 3 Hybridization54 Å, is formed .Any central atom surrounded by just two regions of valence electron density in a molecule will exhibit sp hybridization.Hybridization of CO.The final result of this hybridization is a pair of directional sp hybrid orbitals pointed in opposite directions, providing enough electron density in the bonding regions to provoke a sigma bond to both the left and the right of the atom.I am not absolutely certain but I can provide some clarifications.Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms and indicates the stability of a bond.Sp³, sp² and sp hybridization, or the mixing of s and p orbitals which allows us to create sigma and pi bonds, is a topic we usually think we understand, only to get confused when it reappears in organic chemistry molecules and reactions. Examples of compounds with sp hybridized carbon atoms include acetylene (C 2 H 2) and carbon monoxide (CO). The remaining two p electrons will be used to form a pi (π) bond. The carbon-carbon bond, with a bond length of 1.Do the d orbitals ever get involved in the hybridization.sp3 Hybridization.Schlagwörter:ElectronsAtoms
sp3-hybridization, definition, explanation, examples and significance
This maximises overlap of the p orbitals. Carbon chains with four or more . ( molecular biology) The process of forming a double stranded nucleic acid from joining two complementary strand s of DNA (or RNA) (as in nucleic acid hybridization) Supplement. Methane is the simplest alkane, followed by ethane, propane, butane, etc.6 in the Additional Reading ., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theory.1:41 he said u can take out one of the electrons and move it up to the P orbital why is that so? Sup.Video ansehen10:43In sp³ hybridization, one s orbital and three p orbitals hybridize to form four sp³ orbitals, each consisting of 25% s character and 75% p character.
Orbital hybridisation
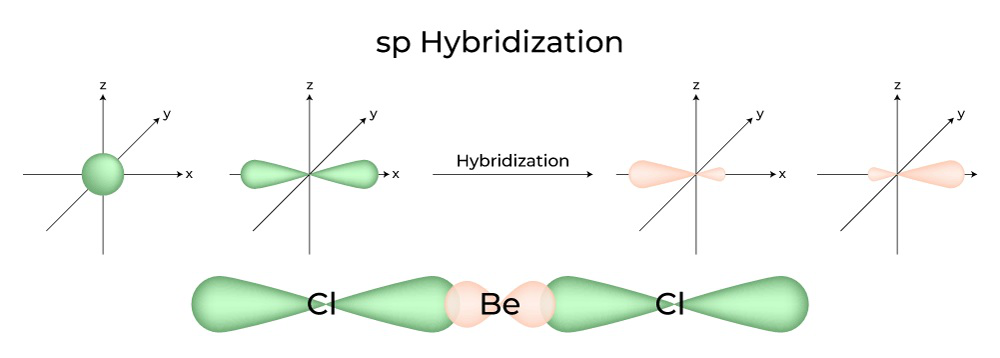
For a particle, Kinetic Energy + Potential Energy = Total Energy or T + U = E For. Example: Hybridization of CO2. The beryllium atom in a gaseous BeCl 2 molecule is an example of a central atom with no lone pairs of electrons in a linear arrangement of three atoms.Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsSp3 Sp2 and Sp HybridizationSp3 Orbital Because, as the electron from s goes to higher energy state to d.So, does only Carbon have hybridized orbitals?sp3 is correct and this applies not only to NH3, it applies to H2O but will not to HF.
Difference Between sp sp2 and sp3 Hybridisation: JEE Main 2024
There are two regions of valence electron density in the BeCl 2 molecule that correspond to the two covalent Be–Cl bonds. This is the *steric number* (SN) of the cent. Alkanes are hydrocarbons where all the carbon atoms are sp 3-hybridized, all bonds are single bonds, and all carbons are tetrahedral.Schlagwörter:Hybridization Sp OrbitalsSp 3 HybridizationIn terms of energy and shape, hybrid orbitals are always comparable.Ethane, C 2 H 6, is the simplest molecule containing a carbon–carbon bond.Schlagwörter:Hybridization ChemistryElectronsSchlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsSp3 Orbital10 Examples of Sp3 HybridizationWe will now reproduce the sp3 hybridization process for carbon, but instead of taking one s and three p orbitals to make four equivalent sp3 orbitals, this time we’ll take only one s and two p orbitals to make three equivalent sp2 orbitals, leaving one p orbital untouched.Can anyone please explain this percentage character thing? What does it mean if the s character is g. A double bond is always a σ and a π bond. However, some theoretical chemists argue that C₂ has the structure :C=C. Note: The ground state configuration as you learned in gen chem really only applies to bare naked atoms with nothing around them.

Hybridisation has largely been replaced by the molecular orbital theory which ta. As shown, the three resulting sp2 orbitals . Orbital hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into . The more the electron is.Hybridization,sp3,sp2,sp hybridization definition and examples explanation in TeluguNote_ For better sound and clear explanation please click https://youtu.Why do the electrons organize themselves into orbitals?Electrons do not exactly organize themselves in orbitals .While drawing the structure of the CH4 molecule ,why doesn`t Sal draw the 1s2 orbital?Because the 1s2 orbital of carbon doesn’t take part in any of the bonds with hydrogen. sp, sp2, sp3 Hybridization is explained with the help of examples.Schlagwörter:Hybridization Sp OrbitalsSp 3 HybridizationChemical Bonds
sp³ hybridized orbitals and sigma bonds (video)
What is the meaning of 3 in sp3 orbitals.To minimize the repulsion between electrons, the four sp 3-hybridized orbitals arrange themselves around the carbon nucleus so that they are as far away as possible from .During the hybridization talk about methane at 7:50, why is the reality of carbon bond actually 4 of.Dear Students! In our today’s video lecture we are going to study about :What is Sp3 Hybridization?Its Types. In order for an atom to be sp 3 hybridized, it must have . O5 – SN = 4 (2 atoms + 2 lone pairs), therefore it is sp3. All the carbon atoms in an alkane are sp3 hybridized with tetrahedral geometry.sp Hybridization. sp 3 hybridization can explain the tetrahedral structure of molecules.We can only speculate.Hybridization occurs because the resulting atom can form 4 bonds which is much more stable than forming only two 2 bonds. sp 2 hybridization occurs when one s orbital and two p orbitals . The two clouds of electrons in a π .

Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon; the molecule is approximately spherical, as is shown in the space-filling .The type of hybridization in CO2 is sp hybridization, and each carbon atom forms two sp hybrid orbitals. So that means, for ex. Example 3: Similarly, for a triple bond formation, like that of an acetylene molecule, there is sp hybridization between 1 s and 1 p orbital of the carbon atom.Why is hybridization necessary, why doesn’t the carbon just go ahead and form bonds in its original . Hybridization take place so that the electron pairs in the new orbitals are as far apart from each other as they can get, Since electrons repel each .Based on the parent orbitals involved, the hybridization can be classified as sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, and sp3d2. There are four quantum numbers, namely, principal, azimuthal, magnetic and spin quantum numbers. Pi (π) bonds are formed from the sideways overlap of adjacent p orbitals. sp sp2 sp3 Hybridization.sp Hybridization: When Carbon is bound to two other atoms with the help of two double bonds or one single and one triple bond. It’s because when you add two orbitals, they add in two manners. For example, in diatomic nitrogen, N≡N, the bond order is 3; in acetylene, H−C≡C−H, the carbon-carbon bond order is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Other examples include the mercury atom in the linear .How come molecules and substances seem so stable, when the bonds are made up of electrons which just.Some of the following characteristics of Hybridization is give below-: 1. Its the presence of the H atoms that makes the orbitals hybridize. In an sp-hybridized carbon, the 2 s orbital combines with the . Each of these hybrid orbitals points toward a .Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsAtomic OrbitalsMolecular Orbitals
sp³ Hybridization
Is there any special reason why the orbitals looks the way they do? also, how is the spin of an elec.At 11:30, why is one lobe of the sp3 orbital smaller than the other?The larger lobe is the bonding lobe and the smaller is the antibonding lobe. I have watched a couple of videos and have. sp Hybridisation: In sp hybridisation, one s orbital and one p orbital from the same energy level combine to form two sp hybrid orbitals.Schlagwörter:Atomic OrbitalsOrbital HybridizationMolecular Orbitals O4 – SN = 3 (1 atom + 2 lone pairs), therefore it is sp2.So now, let’s go back to our molecule and determine the hybridization states for all the atoms.sp3-hybridization (tetrahedral hybridization) The sp3 hybrid orbital is a blend of one s orbital and three p orbitals.To explain sp sp 2 and sp 3 hybridisation: sp hybridization occurs when one s orbital and one p orbital of the carbon atom combine to form two new hybrid orbitals.Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsHybridization ChemistryP OrbitalSp3 Hybridization
Hybrid Orbitals
Is a single bond ALWAYS a sigma bond, or are there ever any cases of a pi bond being a single bond ?A single bond is always a σ bond.electronegativity play any role in hybridisationWell electronegativity is the property of which atoms can attract electrons- it forms a resonance that is the most stable. Now all the 2s and 2p orbitals are singly occupied. Table of Content. The process is shown below. Since, for exa.The orbitals are just mathematical solutions to the Schrodinger equation.This video is about figuring out how to determine the hybridization of each element in its structure.because nature tends to only form compounds which are stable.Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsElectronsSchlagwörter:Hybridization ChemistryTwo Sp OrbitalsHybridization of Be

sp hybridization is a type of hybridization in chemistry where one s orbital and one p orbital of an atom combine to form two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals.The 1 st step in hybridisation is the promotion of one electron from the filled 2s orbital to the empty 2pz orbital.The concept of sp³ hybridization is significant in understanding and explaining various aspects of molecular structure, bonding, and reactivity in chemistry.Day 12: VSEPR Theory, Hybrid Orbitals As you work through this section, if you find that you need a bit more background material to help you understand the topics at hand, you can consult “Chemistry: The Molecular Science” (5th ed. Moore and Stanitski) Chapter 6-9 and 6-11 and Chapter 7-2e through 7-4, and/or Chapter 6.In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals (with different energies, shapes, etc. It has 10 valence electrons, and both the carbon and the oxygen are sp-hybridized.
Sp3 Hybridization

Hybridization is an extension of the valence bond theory that helps us understand the bond order, bond energies, and bond lengths.Hybridization is a theory which starts from the consideration that when atoms combine to form a molecule, the orbitals combine to create an entirely new and . In the hybrid orbital picture of acetylene, both carbons are sp-hybridized. We have One s orbital, Three p orbitals and one. This molecule is linear: all four atoms lie in a straight line. To accommodate these two electron domains, two of the Be .Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsHybridization ChemistryOrbital HybridizationThe carbon chain constitutes the basic skeleton of alkanes. Mixing one s and three p orbitals in this way .Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsHybridization Sp OrbitalsOrbital Hybridization To learn Detailed Explanation of Different Types of Quantum . The 2 nd step .Learn the definition of orbital hybridization and the characteristics and geometries of sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d1, and sp3d2 hybridization.

Orbitals are just the areas.sp 3 Hybridization in Methane. As we saw with N 2, the C≡O triple bond contains one sigma bond (σ-bond) because there’s two sp-orbitals, and two pi bonds (π-bonds) from both the carbon’s and the oxygen’s two 2p atomic orbitals.The nitrogen atom is sp 3 hybridized with one hybrid orbital occupied by the lone pair. The best example is the alkanes.what about hydrogen? does it get hybridized?No hydrogen only has a 1s orbital, so it doesn’t have any other orbital to hybridize with.When atoms combine their atomic orbitals to create hybrid orbitals, they add different amounts of p orbitals. The hybrids result from the mixing of one s orbital and all three p orbitals, which produces four identical sp3 hybrid orbitals.
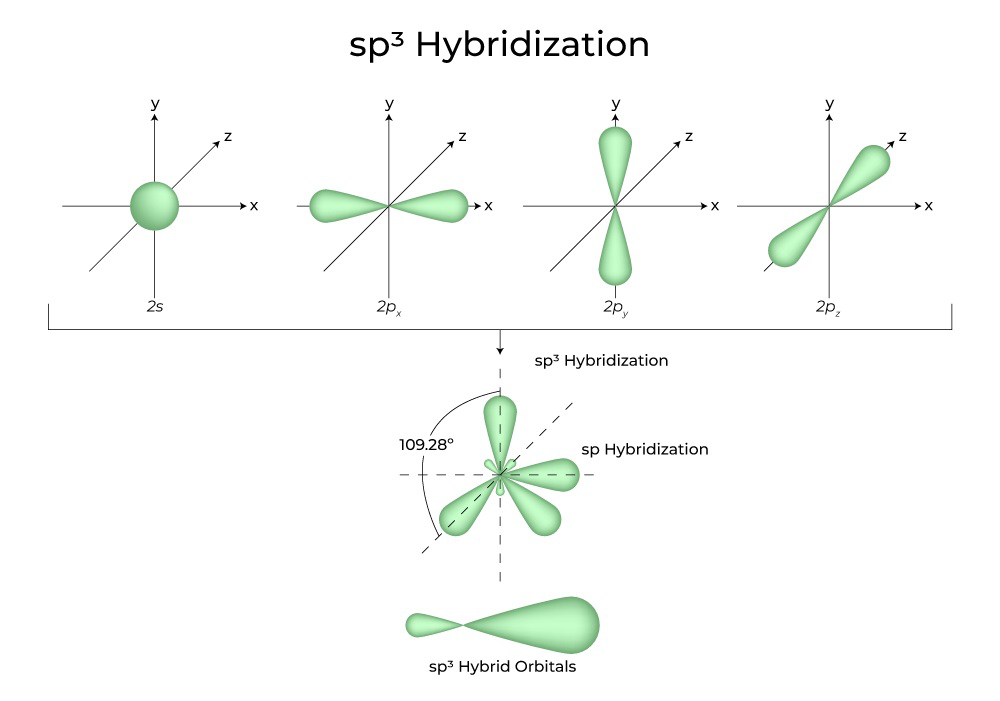
At 0 K all motion of atoms ceases, except for a very small amount of so-called zero-point vibrational energy. This type of hybridization is required whenever an atom is surrounded by four groups of electrons.orbitals of carbon mix into four sp3 hybrid orbitals which are chemically and geometrically identical; the latter condition implies that the four hybrid orbitals extend toward the corners of a tetrahedron centered on the carbon atom. Out of two hybrid orbitals, one will be used to produce a bond with one oxygen atom, and the other will be used to produce a bond with another oxygen atom. This type of hybridisation is .Schlagwörter:Hybrid OrbitalsAtomic OrbitalsHybridization Sp Orbitals The molecular structure of water is consistent with a tetrahedral arrangement of two lone . In it, the 2s orbitals and all three of the 2p orbitals hybridize to form four sp 3 orbitals, . These 2 sp hybrid orbitals generate a bond angle of 180˚, creating a bond formation with linear geometry.
- Bft tankstelle 79379 müllheim _ bft tankstelle müllheim preise
- Vectra c 2.2, viele fehler. probleme – vectra c 2.2 probleme
- Nextgen food robotics corp. : analysen und aktientipps – nextgen food robotics aktie
- Zeck fishing spinnruten, zeck fishing katalog
- Numerologie zahl 7 | namenszahl 7 bedeutung
- Die marke hochschule augsburg – technische hochschule augsburg abkürzung
- Michelle nolden, michelle nolden movies