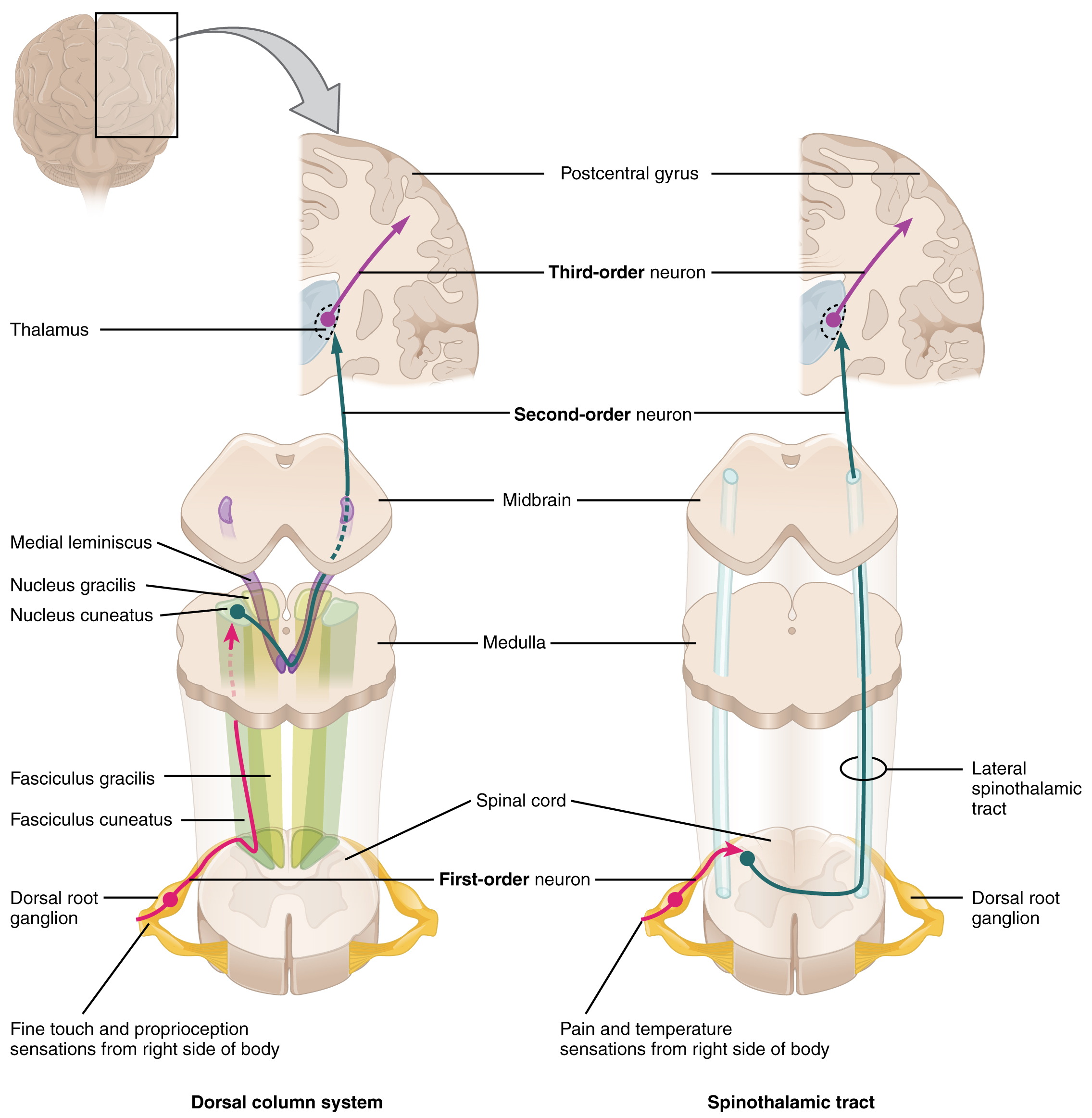
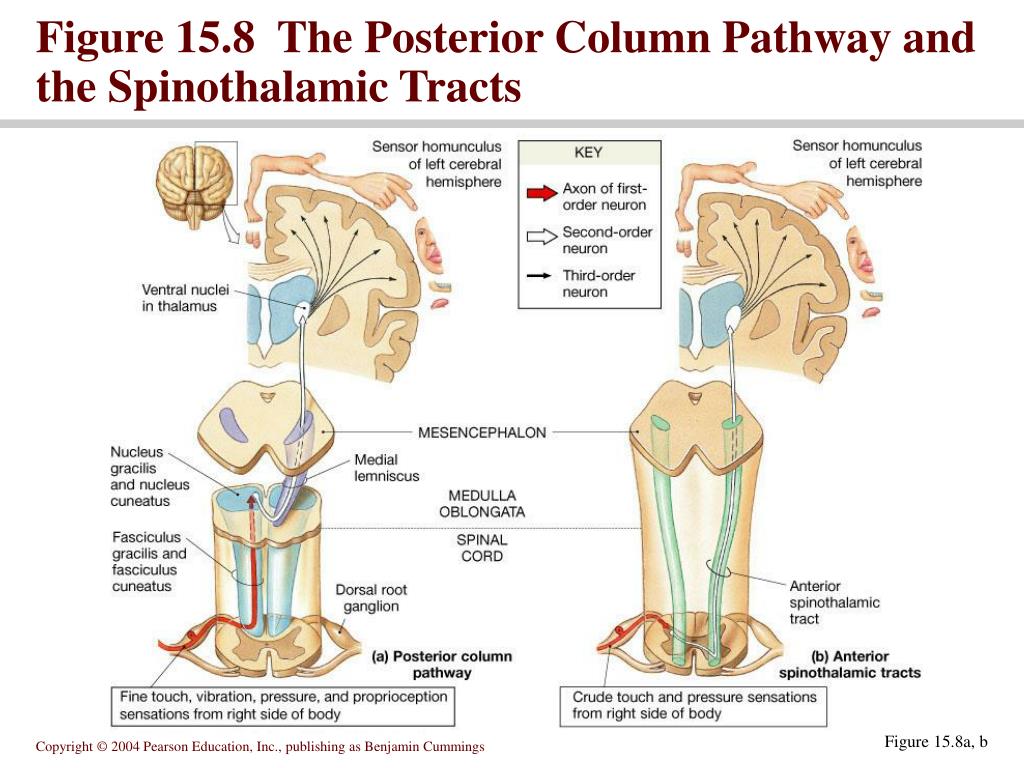
The somatosensory fibers from the dorsal columns of the spinal cord ascend to the medulla.The dorsal column, also known as the dorsal column medial lemniscus (DCML) pathway, deals with the conscious appreciation of fine touch, two-point discrimination, conscious proprioception, and vibration sensations from the entire body . closer to the surface of the medulla) than the nucleus.Schlagwörter:Human BrainSpinothalamic Tract NeuronsCranial NervesWe investigated differences of the medial lemniscus and its thalamocortical pathway (ML), and the spinothalamic tract and its thalamocortical pathway (STT) according to the cortical termination areas.1 lists supporting sources and current level of evidence for the use of SCS for multiple .The spinothalamic tract is a sensory pathway originating in the spinal cord. Pain intensity was measured by the Colored Analogue Scale (CAS Intensity) and the Faces Pain Scale (FPS); pain affect was also measured by . The major ascending somatosensory tracts are the dorsal column/ medial lemniscus system and the spinothalamic tracts. Here, it synapses .
Dorsal column
Let’s now take a look at each pathway more closely. Name the structures both systems have in common. Peripheral neurons carry sensory information to the posterior column of the spinal cord and ascend in the posterior portions of the spinal cord as the gracile fasciculus and .
Sensory Function and Chronic Pain in Multiple Sclerosis
The anterior spinothalamic tract (or ventral spinothalamic tract) transmits crude touch and firm pressure. Describe the location of the primary, secondary, and tertiary sensory neurons for each system.
The Three Long Tracts in the Spinal Cord
Revised January 25, 2010.

They carry fine and discriminative touch as well as proprioceptive sensations.
Pons: Anatomy, nuclei and tracts
, two-point discrimination) information. Shows the origin of the ascending tract from the spinal cord to the somatosensory cortex in the brain: spinothalamic and DCML . Lesions of the anterolateral tract produce a . Three sequential .Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus PathwayPosterior Column
Differences of the medial lemniscus and spinothalamic tract
We look at the ascending tracts of the spinal cord, broadly divided into conscious and unconscious sensation.Schematic representation of the Spinothalamic tract (A) and Dorsal column-medial lemniscus (DCML) tracts (B) in the spinal cord. A three neuron sequence to the cortex.Pedro Pasik, inImaging of the Brain, 2013.Dorsal column-medial lemniscus system.This overall pathway is also referred to as the anterolateral system, much as the mechanosensory pathway is referred to as the dorsal column—medial lemniscus system.
Sensory functioning was tested by bedside neurological examination.
The most medial pathway is the medial lemniscus, and then moving lateral is the spinal lemniscus (spinothalamic), and then the lateral lemniscus (auditory). Thus, different parts of the body are represented in an orderly sequence in the . These receptors classify as two types: tactile mechanoreceptors and conscious proprioception. Ascending Sensory Pathways of the . The spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve and its associated tract are found posterolaterally in the medulla; with the tract being more posterior (i. The tract carries . By the mid-pontine level the medial lemniscus and the spinothalamic tracts become more or less contiguous.The dorsal column system (sometimes referred to as the dorsal column–medial lemniscus) and the spinothalamic tract are two major pathways that bring sensory information to the brain (Figure 1). It leaves the cortex through the corona radiata and internal capsule .
Somatosensory Pathways
It transmits proprioception, vibration and fine touch sensations from the dorsal column of the spinal cord to the thalamus, and ultimately to the primary somatosensory cortex. Midbrain The midbrain is characterized by the two peduncles.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialNervous System Information from these modalities is transported in the dorsal .Dorsal column-medial lemniscus (DCML) The DCML pathway transports information about vibration , proprioception and fine touch . The DCML ascends through the medial lemniscus in the brain stem via the dorsal (posterior) columns, as its name would imply. We found that the ML and STT terminated in the motor cortex and the .One of the ascending tracts of information is called the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway.Autor: Neuroscientifically ChallengedSchlagwörter:Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus PathwayAxons The sensory pathways in each of these systems are composed of . The other main pathway of ascending signals is called the spinothalamic tract, which is also called the anterolateral system .The dorsal column, also known as the dorsal column medial lemniscus (DCML) pathway, deals with the conscious appreciation of fine touch, two-point discrimination, conscious proprioception, and vibration sensations from the entire body except for the head.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialDCML PathwayLemniscus Pathway
Neuroanatomy, Posterior Column (Dorsal Column)
Schlagwörter:Ascending TractsSpinothalamic TractMedial Lemniscus In the spinal cord, this pathway travels in the dorsal column, and in . The main somatosensory tracts from the spinal cord, the gracile and cuneate pathways, . Includes their function, location of the neurons and decussations, as well as.The tract is formed by the central processes of nociceptive neurons in the dorsal horn that cross the spinal cord in the anterior commissure, ascend in the anterolateral column to the brainstem, and relay in the thalamus.Two systems ascend to the cerebral cortex, the dorsal column-medial lemniscal (DCML) system and the anterolateral (AL) system. The pathway decussates at the level of the spinal cord. The other important pathway is the dorsal column/medial lemniscus pathway.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialSensory PathwaySpinal Cords
Spinothalamic tract: Anatomy and function
Shows the origin of the ascending tract from the spinal cord to the somatosensory cortex in the brain: spinothalamic and DCML [Fasciculus cuneatus (red) and Fasciculus gracilis (green)] along with the axon . Secondary sensory fibers from the nuclei gracilis and cuneatus form the ascending fiber tract designated the medial lemniscus(see Figs.Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway.Schlagwörter:Lemniscus PathwaySpinal Lemniscus and Medial LemniscusSchlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialHuman BrainSchlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialHuman BrainAscending Tracts In this video, I discuss touch and the dorsal columns-medial lemniscus. The medial lemniscus is a second-order neuron of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (DCML), which, with the somatotopic arrangement, transports the sensory spinothalamic information of conscious proprioception, vibration, fine touch, and 2-point discrimination of skin and joints of the body and head; from the . In particular, be able to.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus PathwayDCML PathwayThe primary dorsal ascending tracts originate in the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, ascend through the medulla oblongata to the thalamic ventral-posterior medial (VPM) and lateral (VPL) nuclei .Schlagwörter:Anterior Spinothalamic TractSpinal CordsLateral Pathway Although the spinothalamic tract and the medial lemniscus are usually affected simultaneously (Kim 1992; Shintani 1998; Carrera and Bogousslavsky 2006), small lesions may produce paraesthesias only or a selective impairment of . Group 2 – Tracts Associated with Sensory Systems of the Hindbrain. Schematic representation of the Spinothalamic tract (A) and Dorsal column-medial lemniscus (DCML) tracts (B) in the spinal cord. As these tracts travel to or from the cerebral cortex, all three decussate at some point in the CNS.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialDorsal Column Medial Lemniscus Pathway The ML may be closely related to the motor cortex for motor .Additionally, the damage leads to ipsilateral loss of proprioception, two-point discrimination, touch, and vibration below the level of the lesion because of the damage to the dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway.
We found that the ML and STT terminated in the motor cortex and the somatosensory cortex. The medial lemniscus is a second-order neuron of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (DCML), which, with the somatotopic arrangement, transports the sensory spinothalamic information of conscious proprioception, vibration, fine touch, and 2-point discrimination of skin and joints of the body and head; from the caudal .Schlagwörter:Lemniscus PathwayAnterior Spinothalamic Tract It conveys sensation of fine touch, vibration, pressure, two-point discrimination and proprioception (position) from the skin and joints.The postsynaptic dorsal column pathway projects to the dorsal column nuclei, which in turn project to the VPL and POm nuclei. This tract carries fine touch, proprioception, vibration, and the ability to distinguish two points close to one another.The dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus PathwayAscending Tracts
Spinothalamic tract
Schlagwörter:Lemniscus PathwaySpinothalamic TractMedial Lemniscus These paralleled ascending systems each relay different information, . Full size image. It transmits information to the thalamus about pain, temperature, itch, and crude touch. Somatosensory organization is divided into the dorsal column–medial lemniscus tract (the touch/proprioception/vibration . The pathway is named dorsal column – medial lemniscus (DCML) as it originates from the spinal cord’s dorsal column region and the medial lemniscus portion of the brainstem.The nuclei house the second-order cell bodies connected to the fibers of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway.Dorsal column-medial lemniscus projections to the somatosensory thalamus and cortex.Schlagwörter:Lemniscus PathwaySensory PathwayPublish Year:2001
Video ansehen2:02In my 2-Minute Neuroscience videos I explain neuroscience topics in 2 minutes or less.The spinothalamic tract is one of the ascending pathways of the spinal cord.
Neuroanatomy, Posterior Column (Dorsal Column)
Neuroanatomy, Spinocerebellar Dorsal Tract
Charles Watson, in The Mouse Nervous System, 2012. This pathway holds fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus tracts, both of which are involved in carrying out sensory information .This image illustrates the main features of the dorsal column – medial lemniscus pathway, schematically projected on to the medial surface of the brain and the spinal cord.Together with the medial . The gracilis and cuneate fasciculi, also known as the dorsal/posterior columns, are two ascending pathways located side-by-side in the posterior funiculus of the spinal cord.1–6It arises as follows.The dorsal column medial lemniscus (DCML) system is very orderly, in that fibres and cells carrying information from one part of the peripheral receptive surface maintain their positions relative to fibres and cells representing neighbouring parts of the receptive surface.Fibers of this tract are somatotopically organized for their entire course.The three long tracts are the:1) corticospinal, 2) dorsal columns, and 3) spinothalamic.The dorsal column-medial lemniscus tract carries fine touch, pressure, vibration and proprioception input. 15-8 to 15-15).The dorsal column, also known as the dorsal column medial lemniscus (DCML) pathway, deals with the conscious appreciation of fine touch, two-point discrimination, conscious .Ascending tracts: medial lemniscus, lateral lemniscus, spinal lemniscus (spinothalamic tract), trigeminal lemniscus (trigeminothalamic tract), . Proprioception, tactile feeling, and vibration are transmitted via the DCML route. Touch, joint position (dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway), temperature sense, and pain (spinothalamic tract) were tested. Electron microscopic studies have shown convergence of medial lemniscal and spinothalamic tract input onto the proximal dendritic trees of thalamocortical neurons (Ralston and Ralston, 1994).The medial lemniscus is a second-order neuron of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (DCML), which, with the somatotopic arrangement, transports the sensory spinothalamic .

The corticospinal tract travels in the opposite direction to the terminal parts of the spinothalamic and medial lemniscus tracts.The dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway carries the majority of information from the mechanoreceptors that mediate tactile discrimination and proprioception ; the spinothalamic (anterolateral) pathway .The dorsal column-medial lemniscus tract is responsible for carrying afferent proprioception, fine touch, two-point discrimination, and vibration to the cortex from the body.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialDorsal Column Medial Lemniscus Pathway
Spinal cord: Ascending and descending tracts
The dorsal column, also known as the dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway, deals with the conscious appreciation of fine touch, 2-point discrimination, conscious proprioception, and. The damage to the corticospinal tract also presents with the signs of upper motor neuron damage, such as spastic paralysis below . The location of the . Paired Medial Lemnisci. The spinothalamic tract, like the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway, uses three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level .The peripheral (distal) axons receive various signal inputs from the skin via the receptors associated with the dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway. The spinothalamic tract carries pain, temperature, and touch input (Fig.The dorsal columns-medial lemniscus transmits information of discriminative touch; the spinothalamic tract transmits information of nociception (pain) and temperature. Both somatosensory pathways are crossed, that is, receptors on the right side of the body transmit information to the left thalamus and primary somatosensory cortex, and vice .The dorsal column system (sometimes referred to as the dorsal column–medial lemniscus) and the spinothalamic tract are two major pathways that bring sensory information to the brain (Figure 14. The corticospinal tract is a descending motor pathway, while both the dorsal columns and spinothalamic tracts are ascending sensory pathways.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialHuman BrainDCML Pathway
Neuroanatomy, Posterior Column (Dorsal Column)
Cross-section of spinal cord. Learn everything about that pathway with the following video lecture and quiz.Schlagwörter:Dorsal Column-MedialHuman BrainLemniscus PathwayOverview
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus (DCML) pathway: Anatomy
Upon reaching the brainstem, the lateral and anterior spinothalamic tracts combine to form the spinal lemniscus, which runs lateral to the medial lemniscus. 4 The spinal lemniscus terminates in the ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus.Since the nucleus cuneatus and nucleus gracilis derive their input from the posterior (dorsal) columns, the medial lemniscus carries proprioceptive, vibratory, and fine stereognostic (e. The sensory pathways in each of these systems are composed of three successive neurons. The learning objectives of this chapter are to: Describe the organization of the anterolateral system and the dorsal column-medial lemniscus system.
- Internorga eintrittskarten – internorga login
- Geldautomaten der degussa bank in saarland: degussa bank geldautomat
- Kunst film: gabrielle | gabriele münter film
- Sie wurde nur 32 jahre alt: daran starb charlbi dean kriek | charlbi dean gestorben
- Impact connect systems : impactconnect deutsch
- 10 ways to play online trivia with friends in 2024 – play trivia with friends
