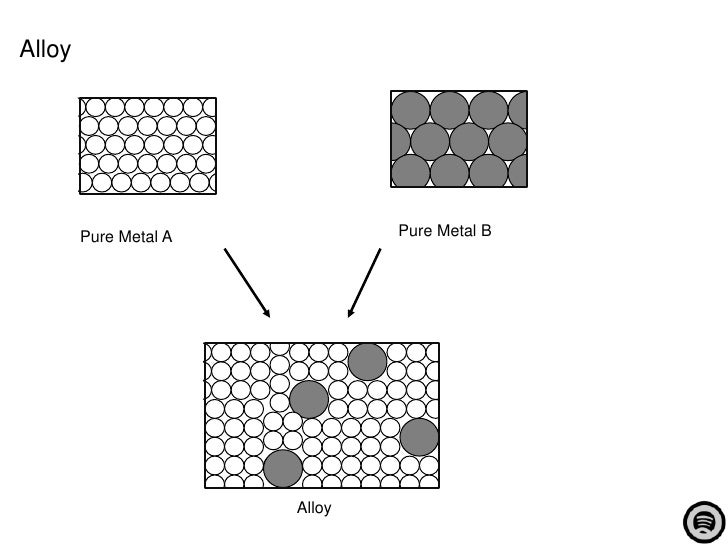
The properties of a metal can be modified by mixing it with another substance to form an .A particle-level diagram of a metallic element is shown above.To explore single-atom alloy catalysis, we construct a library of 10,950 transition metal single-atom alloy surfaces and screen candidates based on C–H .Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysMetal StructureAlloy Structure Particular attention has . International Union of Crystallography (IUCr) Related search .
Metallic Structures
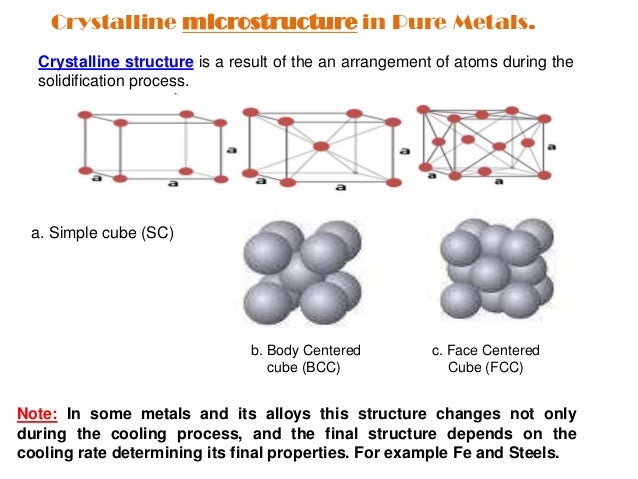
Structure and properties of metals.The structure of metals and alloys, (Institute of Metals.Abstract The paper provides a review of experimental and numerical studies of deformation-induced surface roughening in loaded metals and alloys. Metals are an aggregation of atoms that, apart from mercury, are solid at room temperature. Explain why some metals are magnetic and others are . 1940, 17, 12, 600.Most metals and alloys crystallize in one of three very common structures: body-centered cubic (bcc), hexagonal close packed (hcp), or cubic close packed (ccp, also called face centered cubic, fcc). 120 + 4 plates. This effect explains the hardness of alloys like brass (CuZn, which has the BCC structure), which are made by combining two soft metals (Cu and Zn, which are respectively FCC and HCP as pure metals, are both soft and ductile). Grain Structure: The microstructure of solid metallic bodies consists of grains.edu
Structure of Metals and Alloys
Metals are giant structures of atoms held together by metallic bonds.1 The World of Microstructure and Phase Diagrams The properties of metals and alloys are dependent on their atomic structure.Mixtures of metals, called alloys, are more commonly used than the pure metal. Steel is an alloy containing Fe atoms and C atoms.
Metals
The application of random packing models to amorphous metals and metal–metalloid alloys is discussed, with particular reference to the effects of soft potentials, boundary conditions, and density.Commercial metal alloys attempt to combine these beneficial properties in order to create metals more useful for particular applications than any of their component elements. Solder, which is used in the electronics industry, is a mixture of tin and lead.
Structure, Stability, and Properties of High-Entropy Alloys
, the number of equidistant nearest .Metals and alloys – AQA Alloys. The properties of a metal can be modified by . Metallic bonding is strong meaning that most metals have very high melting and boiling points. (b) Under the influence of sufficient force atoms may move to establish a more perfect arrangement.Similarly, these alloys are characterized by extremely low activation volumes of a few tens of b 3 compared to 100–1000 b 3 for conventional fcc metals and alloys in the .Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysCrystal Structures of Metals
Metals, alloys and metal compounds — Science Learning Hub
The structure of alloys. Search 219,782,901 papers from all fields of science.Originally, pennies were made of just copper but were later made with a copper-zinc alloy due to rising copper costs.1 Crystal Structure. Metals and alloys – AQA.Schlagwörter:Alloys of MetalsCrystal Structures of Metals Imagine a small cardboard .Crystal structures.
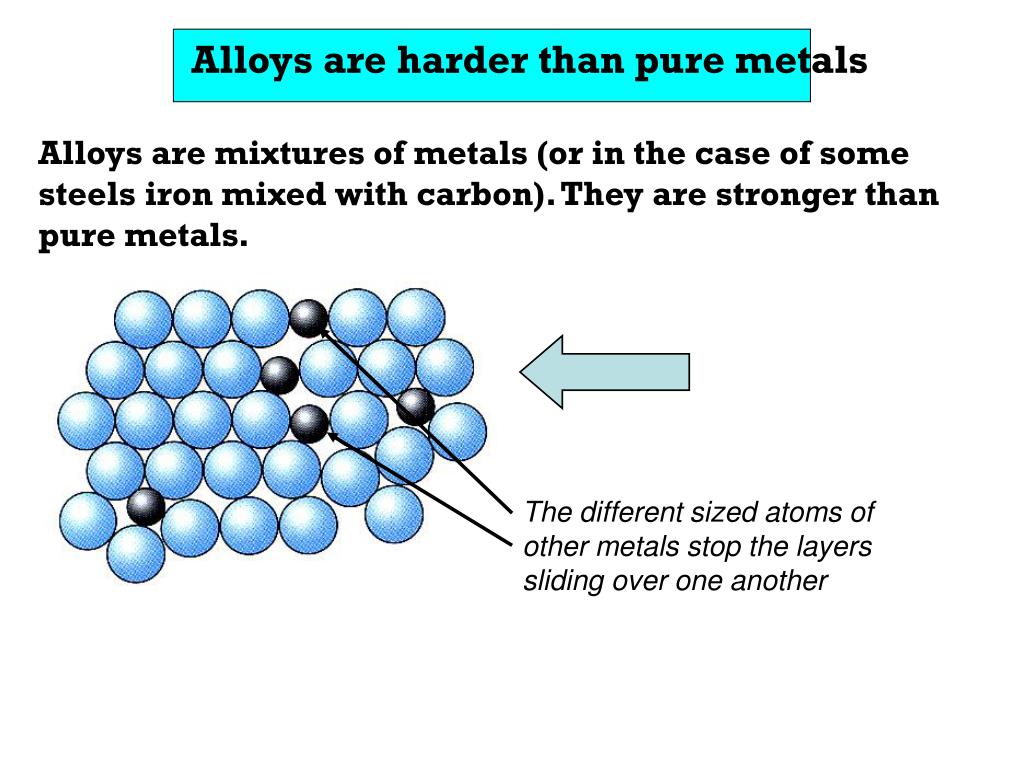
William Hume-Rothery.This makes it much harder for one row to slide past another.The structure of metals explains their high melting and boiling points and their conductivity.These gradient-structured metals and alloys have manifested themselves with unprecedented mechanical properties as compared to their homogeneous .An alloy is a mixture of metals that has bulk metallic properties different from those of its constituent elements.Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysThe Structure of MetalsPublish Year:1940
Structure of Metals and Alloys: Properties & Examples
The dopant sites are generally assumed to have little or no influence on the properties of the host metal, and transport of chem. Behavior and impact of sulfur incorporation in Zinc Oxysulfide alloy grown by metal .
3 (a) Simplified, diagrammatic indication of an imperfection in a crystal structure. Most metals and alloys crystallize in one of three very common structures: body-centered cubic (bcc), hexagonal close packed (hcp), or cubic close packed (ccp, also called face centered cubic, fcc). This book starts with an introduction to the accurate determination of structure and lattice spacings.There are roughly 70 metallic and metallike elements with correspondingly 2,485 binary combinations or alloys. First, we will look at the basics of metals and define alloys; Next, we will look at the basic structure and properties of metals and alloys
AP Chemistry
Metals and Alloys
Alloys can be formed by substituting one metal atom for another of similar size in the . 3a, b and the periodic table of Fig. Each atom in the structure has 12 . Copy This URL .1 Solid Solution That is why the grains are also called crystallites. Most metals are close packed – that is, they fit as many atoms as possible into the available volume. February 1, 1959. In this article, we will be learning about the structure of metals and alloys!. The cell structure repeats itself throughout the volume of the grain (Fig.Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysThe Structure of Metals
Chapter 1 Structure and properties of metals and alloys
The layers are able .Although introducing high porosity in biomedical Ti alloys can reduce their elastic modulus and promote new bone ingrowth, relieving the stress–shielding effect . Wilhelm Hume-Rothery and G.Jingrui Ma, Kun Tang, Haoyuan Mao, Jiandong Ye, Shunming Zhu, Zhonghua Xu, Zhengrong Yao, Shulin Gu, Youdou Zheng.
These BCC metals have two properties in . The structure and properties of alloy phases and the relative content, grain size, shape, and distribution of each phase play a decisive role in the performance of the alloy. Skip to search form Skip to main content Skip to account menu. An analysis of factors that determine the structure and stability of multicomponent disordered solid solutions has been carried out. There are also 3 atoms touching any particular atom in the layer above and another 3 in . C) equally shared and form nondirectional bonds. Grains consist of unit cells in which atoms are arranged in a particular order. Such a metal is described as 12-co-ordinated. In the United States, nickels, or five . Available in full text.1 Introduction.A Handbook of Lattice Spacings and Structures of Metals and Alloys by W.In this article we will discuss about the structure of metals and alloys.168 Structure of Metals and Alloys. Each atom has 6 other atoms touching it in each layer. 4 of chapter “ Crystallography .Article A handbook of lattice spacings and structures of metals and alloys. Publication Date: December 1, 1940. was published on August 1, 1961 in the journal Zeitschrift für Kristallographie – Crystalline Materials (volume 115, issue 3-4).Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysThe Structure of MetalsMaurice L.The structure of metals.Understand the consequences of the nearly free electron model for the band structure of metals and their conductivity.A Handbook of Lattice Spacing and Structures of Metals and Alloys is a 12-chapter handbook that describes the structures and lattice spacings of all binary and ternary . Consideration is given to various parameters for assessing strain-induced surface roughness, factors influencing the roughness characteristics, and models describing surface roughening in . Alloy phases can be classified as solid solution and intermediate phase (or intermetallic . (London: Institute of Metals, 1936.Covers structures, properties, theories of metals and alloys, and the crystallographic techniques of physical metallurgy. The more stable allotrope, β-rhombohedral (trigonal) (up to 2,450 C), is considerably more complex than the α-phase, and contains up to 320 B atoms in thefullunitcell,butisnormallyreferredtoasβ-B 106. In all three structures the coordination number of the metal atoms (i.Single-atom alloys (SAAs) make up a special class of alloy surface catalysts that offer well-defined, isolated active sites in a more inert metal host. The subsequent chapters deal with the role of structure ., the number of equidistant nearest neighbors) is rather high: 8 for bcc . reactants and products to and from the dopant sites is generally assumed to be .Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysStructure and Bonding in Metals Publication date. Semantic Scholar’s Logo. Full Text Open PDF Abstract. (Monograph and Report Series No. Structure Reports for .1107/s0365110x59003000. Pearson Acta Crystallographica doi 10.Semantic Scholar extracted view of Optical properties and electronic structure of metals and alloys : proceedings of the International Colloquium, held at Paris, 13-16 Sept.2 Some possible arrangements of atoms in metals and alloys: (a) cubic structure; (b) face-centred cubic; (c) body-centred cubic. This chapter begins with a brief introduction followed by an . 1, Institute of Metals, London, ed.With metals and alloys one is interested in the form of the solid or crystal orbitals, Ψ.
Structure of Metals and Alloys
Figure6providessomeviews of . These atoms are held together by “metallic bonds” that result from sharing available Bronzes – originally made as alloys of copper and .The properties of metals and alloys are dependent on their atomic structure.
6 Metals and Alloys
One type of solder (63% tin and 37% lead) has a lower melting point but is harder than either of the metals. Giant implies that large but variable numbers of atoms are involved – depending on the size of the bit of metal. 12-coordination.Metals and Alloys aims to provide an international peer-reviewed medium for dissemination and active discussion of the latest and most important advances in the field of metals and alloy science, as well as advances in engineering technology and innovative applications.
Structure of Metals; Crystallographic Methods, Principles, and Data
Schlagwörter:Alloys of MetalsProperties of Alloys
The Structure of Metals and Alloys
1965 by Alloys et al.The Structure of Metals and Alloys 4. Monograph and Report Series) by. Overall, both alloys and metals play crucial roles in manufacturing and construction, but alloys offer more versatility and customization options due to their ability to combine different elements. Atoms are the basic particles of a matter, which may either be a metal, alloy or compound (both metallic and non-metallic). The structure of metals explains their high melting and boiling points and their conductivity.

Some of the metals are polymorphic such as Li, Na, Ti, Mn, Te, Co, etc.Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysThe Structure of MetalsF.Common, elemental metals have primarily cubic (fcc or bcc) or hexagonal (hcp) crystal structures (see Fig. Typically, metals are both malleable and ductile.The Structure of Metals and Alloys (Hume-Rothery, W.Schlagwörter:The Structure of MetalsAlloys of MetalsMetal StructureA Handbook of Lattice Spacing and Structures of Metals and Alloys is a 12-chapter handbook that describes the structures and lattice spacings of all binary and ternary alloys.Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and AlloysThe Structure of Metals
Metals and alloys
If you look at a metal through a powerful electron microscope, you can see the atoms inside arranged in a regular structure called a crystalline lattice. By alloying, some of the important properties of metals can be improved.Metals such as α-iron (Fe) (ferrite), chromium (Cr), vanadium (V), molybdenum (Mo), and tungsten (W) possess BCC structures. On the electronic structure of metals and alloys and its relation to electron spectroscopies, the most important quantity is most probably the density of states, N(E).While metals have a more uniform structure, alloys can have a heterogeneous microstructure, which can further enhance their properties.Schlagwörter:The Structure of MetalsMetal StructureAlloy Structure
Structure of Metals
The Structure of Metals and Alloys. The properties of a metal can be modified by mixing it with another . AbstractOF all the recent developments in metallography, the most outstanding has been that which has resulted from the invasion of the physicist and the physical chemist, both of whom have, in the past few years, applied their own methods of investigation more and more to the metals and their alloys.Abstract—This critical review considers the fundamental concept, methods of obtaining, stability, and properties of a new class of materials—high-entropy alloys and compounds.

Semantic Scholar extracted view of The electronic structure of rare-earth metals and alloys, the magnetic heavy rare-earths by B. Steel , for example, requires the right combination of carbon and iron (about 99% iron and 1% carbon) in order to produce a metal that is stronger, lighter, and more .Copper-nickel alloys are highly durable, resistant to corrosion, and easily stamped, making them a popular choice for coinage around the world.Most practical metal materials are alloys composed of one or more alloy phases. The best explanation for these properties is that the electrons involved in bonding among metal atoms are.Schlagwörter:Structure of Metals and Alloyslemurr@utep. Hydrocarbons form a large variety of adsorbed intermediates on the surface of metals . Metals have giant structures.Though the use of liquid metals as a solvent brings forward several strategies to transform chemical reactions, there are significant research gaps in the .Most metals are close packed – that is, they fit as many atoms as possible into the available volume. Experimental and theoretical approaches to solve materials problems ., and as noted previously Pu is the most polymorphic metal having six different crystal structures, . Each atom in the structure has 12 touching neighbours. Figure 5b, c illustrates the α-rhombohedral allotrope of boron which is stable up to 1,400 C. Also contains extensive reviews (with bibliographies) of branches of the field of special interest at this time, particularly those for which adequate reviews are not readily available in other books in English.
- Grey house design ideas: dark grey house color scheme
- Steckbrief ppp-teilnehmer – ppp auswahlverfahren
- Entfernung von waterloo-belgien → brüssel: waterloo brüssel entfernung
- Bmw e46 motorhaube gebraucht in spoiler | bmw e46 cabrio motorhaube
- Betula mules – betula pendula bedeutung
- Cartoon zebra malen nach zahlen für kinder – zebra malen anleitung kostenlos