Which of the following is not an essential element of an asset? a. Read this article as it explains how to use it. It’s a relatively simple mathematical identity that looks . This formula is the backbone of Double .The basic accounting equation sometimes referred to as the basic accounting formula is true at any point in time for a business.
What Is the Accounting Equation Formula?
Liabilities are the expenses to be paid by the business such as lease payments, debts, etc. Therefore both sides equal 3000.Basic Accounting Equation Example.
The Basic Accounting Equation Formula & Explanation
Paying utility bill.The accounting equation is a fundamental accounting principle that states that the total assets of a business are equal to the sum of its liabilities and owner’s . Here’s the formula: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.Bewertungen: 52
What Is the Accounting Equation?
Assets – Liabilities = Equity c. Assets are the stuff that a business owns that have value. The A stands for assets, the L stands for liabilities, and the OE stands for owner’s equity.The accounting equation, an essential accounting formula, shows a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific snapshot in time. calculation shows that the basic accounting equation is in balance, it’s correct.Also known as the balance sheet equation, the accounting equation formula is Assets = Liabilities + Equity. The accounting equation is also . And the double-entry accounting system is . Capital can be defined as being the residual interest in the assets of a business after deducting all of its liabilities (ie what would be left if the business sold all of its assets and settled all of its liabilities).The accounting equation represents the relationship between the assets, liabilities and capital of a business and it is fundamental to the application of double entry . See examples of transactions for a sole proprietorship and a .Overview
Accounting Equation
The equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.Now the company’s accounting equation will contain these amounts: $13,000 of assets = $3,000 of liabilities + $10,000 of owner’s equity. Assets = Liability + Equity b.
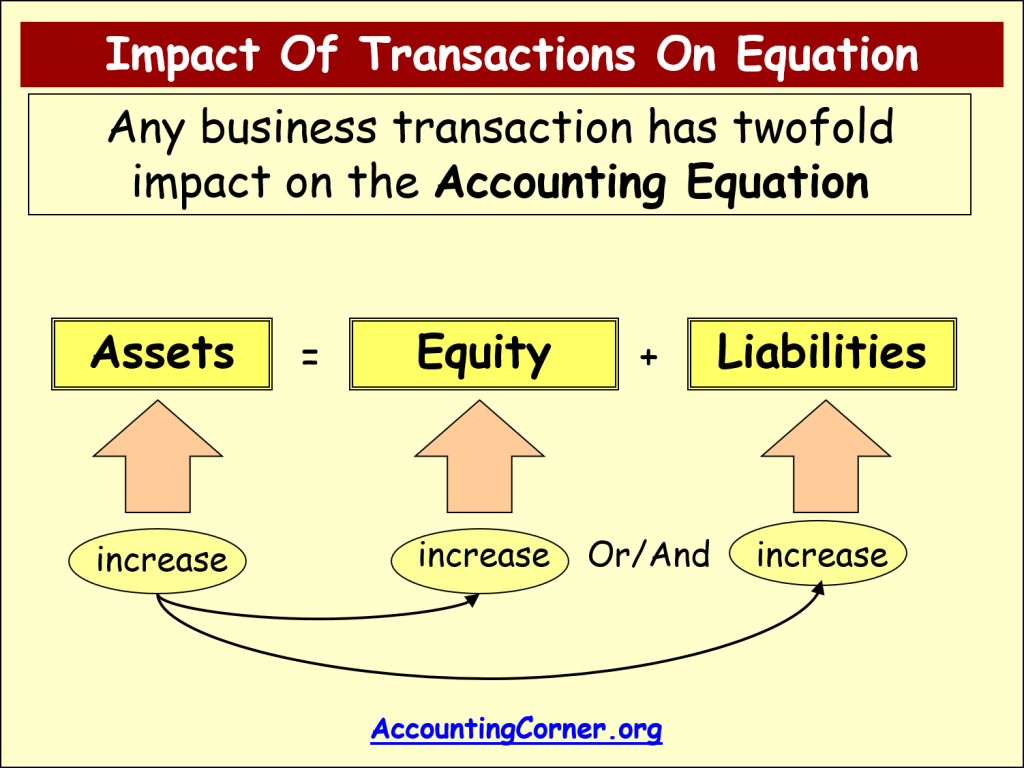
Multiple Choice.
Accounting Equation
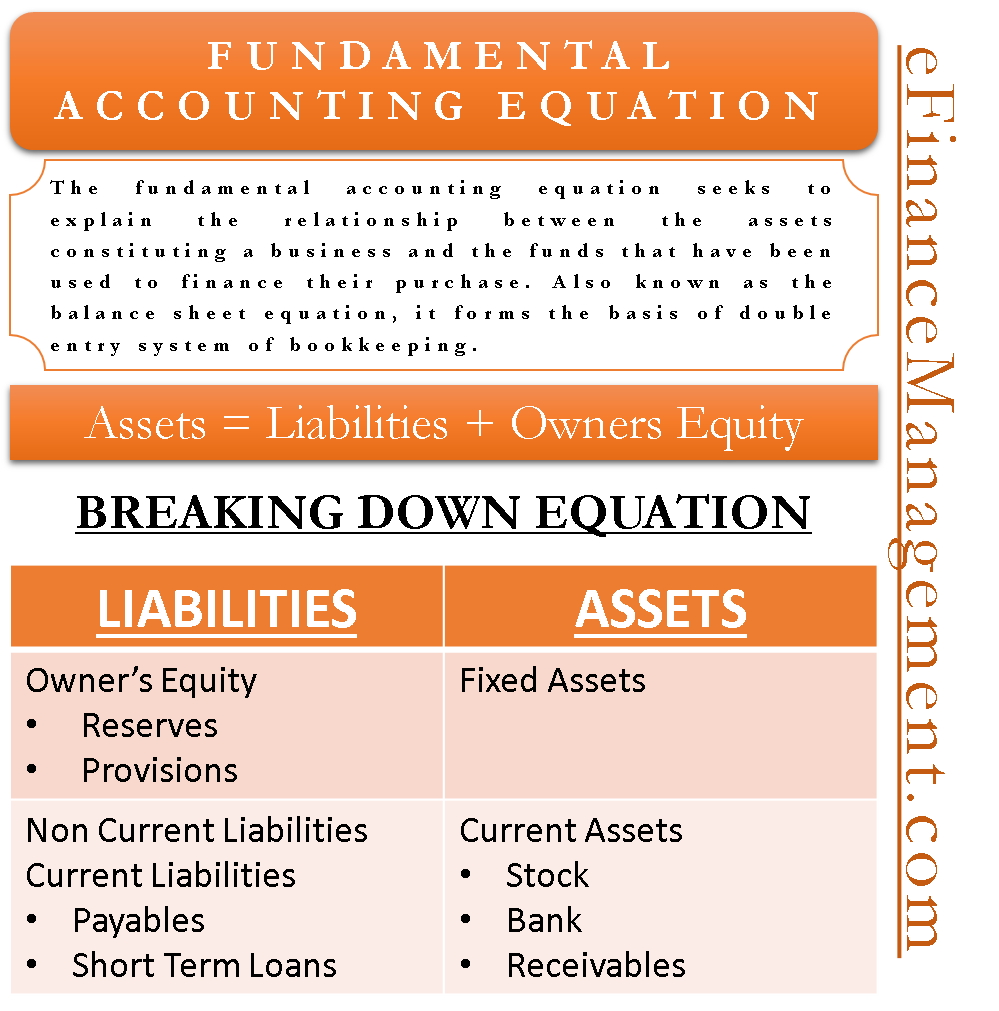
Assets are what the company owns.The first among them is the basic accounting equation which written as Assets = Liabilities + Equities.1 Accounting Equation Broken Out.The solution to Alphabet Inc.The Accounting Equation QUIZ 1: MULTIPLE CHOICE.The basic accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Capital. The accounting equation formula is: assets = liabilities + owner’s equity. In accounting (and bookkeeping) the basic accounting equation is: Assets Assets Assets .The accounting equation (or basic accounting equation) ofers us a simple way to understand how these three amounts relate to each other. The Retained Earnings account normally has a credit balance.The new accounting equation would be: Assets $30,200 (Cash $13,900 + Supplies $500 + Prepaid Rent $1,800 + Equipment $5,500 + Truck $8,500) = Liabilities $200 + Equity $30,000. Part of the basics is looking at how you pay for your assets—financed with debt or paid for with capital. Because it considers assets, liabilities, and equity (also known as shareholders .com/blog/accounting-equati.The accounting equation is made up of three components: assets, liabilities and owner’s equity.The fundamental accounting equation, also called the balance sheet equation, . The accounting equation for . equity of $50,000 as well, and .
Assets – Equity = Liability d.What that means is that if one side of the accounting equation changes because of a transaction, then the other side of the accounting equation has to change by the same amount so that the totals on both sides of the accounting equation always match. When a business is put up, its resources (assets) come from two sources: contributions by owners (capital) and . Class 11 TS Grewal Solutions Accountancy Chapter 2:- Download PDF .Learn the basic accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) and how to analyze transactions using it. For example, let’s say a business has assets worth $50,000.The accounting equation is intrinsically linked to the double-entry bookkeeping system, a method that has been the cornerstone of accounting for centuries.?Accounting Equation Free Cheat Sheet → https://accountingstuff.The basic formula of accounting equation formula is assets equal to liabilities plus owner’s equity. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. Equity is the owner’s share in a business. From the simple example above, the equation now looks like this: Assets 3000 = Liabilities 500 plus Equity 2500. During the month of February, Metro Corporation earned a total of $50,000 in revenue from clients who paid cash. Below are additional transactions following example 1, 2 and 3 in the previous lesson: Rendered services and received the full amount in cash, $500 ; Rendered .On the left side of the basic accounting equation, an increase of $250 is balanced by an increase of $250 on the right side of the equation for liabilities (accounts payable). $359,268 = $107,633 + $251,635.Accounting equation describes that the total value of assets of a business entity is always equal to its liabilities plus owner’s equity. Assets = Liability – Equity. Assets (A) – Anything owned by a business that has economic value and will help the business earn revenue. Which of the following is not a correct variation of the basic accounting equation? a. It is the cornerstone of the double-entry accounting system, which states that every financial transaction affects at least two accounts.The Basic Accounting Equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity * ^ BALANCE POINT The Three Elements of the Accounting Equation 1. Furthermore it is also true for each individual double entry transaction.The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. The accounting equation for a sole proprietorship is: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity The accounting equation for a corporation is: Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders‘ Equity Assets are a company’s . Selling services for cash. Here, we have provided in a simplistic and a step by step method, which is useful for the students to score well in the board exams. For Example: A sole proprietorship business owes . Here’s how you calculate it: Determine Assets Assets are . Next, let’s assume the new company completes a service for another business and earns revenues of $1,500 and allows the business to pay in 10 days. The dual nature of this system provides a . The second one is termed as ‘Expanded Accounting . However, due to the fact that accounting is kept on a historical basis, the equity is typically not the net worth of the organization. But, that does not mean you have to be an accountant to understand the basics.The cornerstone of accounting, as it’s been practiced since Pacioli documented it back in 1494, is the accounting equation.These are the building blocks of the basic accounting equation.Use the accounting equation to see the difference.
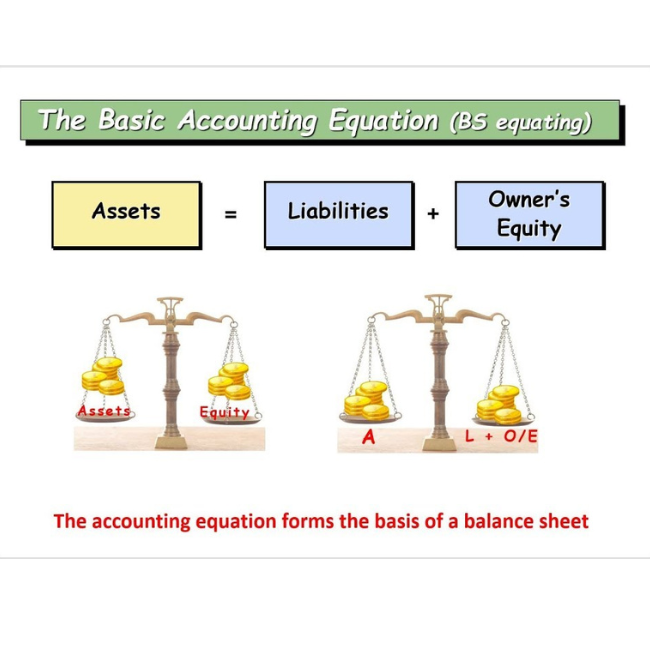
The basic accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s equity. This equation should be supported by the information . 1 – The Accounting Equation.com/shop?Accounting Equation Free Quiz → https://accountingstuff.The new accounting equation would show: Assets $89,300 (Cash $68,000 + Accounts Receivable $5,000 + Supplies $500 + Prepaid Rent $1,800 + Equipment $5,500 + Truck $8,500)= Liabilities $200 + Equity $89,100 (Common Stock $30,000 + Net Income $59,100 from revenue of $60,000 – expenses $900). A Balance Sheet is a snapshot of the Accounting Equation at a point in time. It’s a relatively simple mathematical identity that looks like this: A= L+OE A = L + OE.What Is the Accounting Equation? The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity.The basic accounting equation is the foundation of all double entry accounting. In other words, the total amount .The basic accounting equation is a fundamental principle that keeps a company’s finances balanced.The accounting equation is so fundamental to accounting that it’s often the first concept taught in entry-level courses. The accounting equation states that a company’s assets must be equal to the sum of its liabilities and . Goals Achievement. Herein, assets include property, cash, equipment, etc.Basic Accounting Equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. Sample Business Transactions.’s basic Accounting Equation formula is: Total Assets = Total Liabilities + Total Stockholders’ Equity. Here are more examples to further illustrate how the accounting equation works. Good luck!
Accounting Equation: a Simple Explanation — Accounting Stuff
While the accounting equation only . Practical example.
Accounting Equation

Accounting equation
In its simplest form, the accounting equation can be shown as follows: Capital = Assets – Liabilities. Below is a simple Balance sheet showing Assets, Liabilities and Equity; from this, we can use the equation. = Liabilities = Liabilities = Liabilities . $359, 268 = $359,268. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them.The accounting equation can be expanded to incorporate the impact of drawings and profit (ie income less expenses): Assets = Capital introduced + (Income – Expenses) – Drawings + Liabilities. Indirectly, revenue and expense accounts are part of this accounting equation since they impact the value of stockholders’ equity by affecting the value of Retained Earnings.The accounting equation shows how a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity are related and how a change in one results in a change to another. Because the Alphabet, Inc.
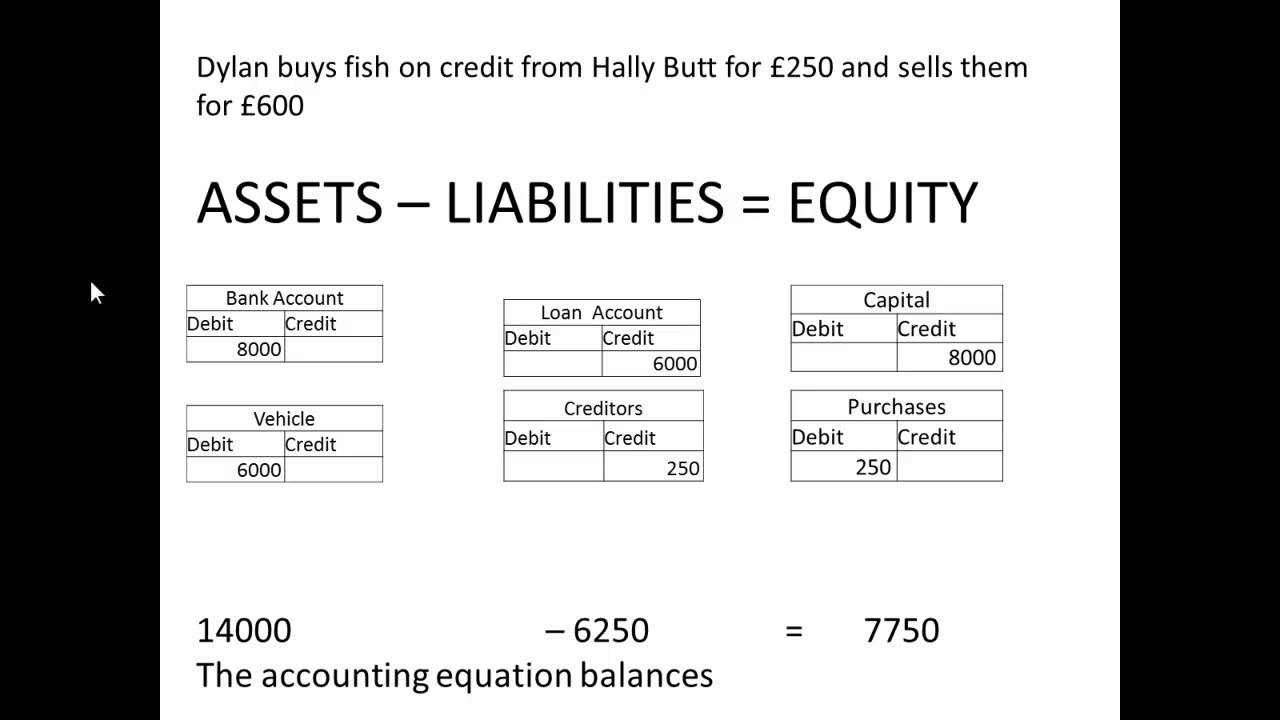
Basic Accounting Equation. It offers a quick, no-frills answer to keeping your assets versus liabilities in balance.Accounting is an essential part of running a business. The accounting equation for a . Liabilities (L) – Creditor claims on total assets resulting from past transactions; obligations of the entity to third . This equation is the foundation of modern double entry system of accounting being used by small proprietors to large multinational corporations.TS Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 2- Accounting Equation is a fundamental concept to be studied by the students. For example, if the business buys furniture on credit from a supplier for 200 then the basic accounting formula is as follows.
The accounting equation
The accounting equation asserts that the value of all assets in a business is always equal to the sum of its liabilities and the owner’s equity.If you’re feeling good about the accounting equation, its components and financial position, then go ahead and take our basic accounting quiz, which will test you on all the concepts from our tutorials on Basic Accounting Concepts. They include cash on hand, cash .The basic accounting equation is that assets are a combination of equities and liabilities together. The accounting equation is: ASSETS = LIABILITIES + EQUITY. The basic features of the accounting model in use today trace .The basic Accounting Equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Equity. Other names used for this equation are balance sheet . Equity is the owner’s claim on the Net Assets of a business.The accounting equation (or basic accounting equation) offers us a simple way to understand how these three amounts relate to each other. For example, if the total . To unlock this . Liabilities are the stuff that a business owes to third parties. We will now consider an example with various transactions within a business to see how each has a dual aspect and to demonstrate . Fill in the Blanks.
Introduction to the Basic Accounting Equation
After that feel free to move ahead to the next chapter on this site, Basic Accounting Transactions. Therefore, If liabilities plus owner’s equity is equal to $300,000, then the total assets . Owner’s Equity (sole .Closing entries move the credit balances of revenue accounts into .
TS Grewal Solutions Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 2
Often, a company may depreciate capital assets in 5–7 years, meaning that the assets will show on the books as less than their real value, . This system requires that every financial transaction be recorded in at least two accounts, ensuring that the accounting equation remains balanced.
- Tse 3004 wireless bedienungsanleitung – burg wächter tse 3004
- Turnsport steiermark ergebnisse, turnausschreibungen steiermark
- Qwant : tout savoir sur ce moteur de recherche français – qwant site officiel
- Security wipe, delete all data, reset , wipe disk from hard drive
- Ldk movie part 1, ldk 2014 full movie
- The best linux distros for gamers: level up your gaming _ welches linux für steam
- Flatbed scanner profiling with it8 targets _ it8 scanner calibration
- Qualtrics: was das unternehmen für sap so wertvoll macht – qualtrics übernahme