Semantic Scholar extracted view of Aspiration efficiency and respiratory tract deposition of indoor suspended micro-particles during steady and transient breathings by Kazuki Kuga et al.

Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsDeposition PhysicsParticle KineticsThe physics of the deposition of inhaled particles depends on the flow velocity and particle size.This work presents a three-dimensional triple bifurcation model describing particle deposition for four breathing conditions and for particle diameters varying .

In every breath, humans take in particles that may be deposited on the respiratory tract and exhale particles that may contain pathogens.

Semantic Scholar extracted view of Modeling of the submicron particles formation and initial layer ash deposition during high temperature oxy-coal combustion by Zhonghua Zhan et al. Observations have shown that there is a substantial variability in deposition between subjects, not only due to respiratory diseases, but also among .Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. These are: (i) . The objective was to investigate production symmetry during breathing. The human respiratory tract is, to first approximation, a branching tree of tubes with the diameter decreasing (and the airflow velocity increasing) as it branches.Download scientific diagram | Particle deposition for each breathing condition from publication: CFD Evaluation of the Influence of Physical Mechanisms, Particle Size, .Enhancement of the flow rate (breathing scenario 3) does not cause a remarkably change of intermediate-sized particle deposition with respect to breathing scenario 1.ABSTRACT Characterizing particle deposition in the airways of the human lungs is essential to evaluate the health effects of particulate air pollution.Mechanical lung simulators play an important role in research into breathing and ventilation processes. Because the simulated breath-holding path, in which the aerosol is drawn through the nose and mouth, differs from the natural path where inhaled particles enter the nose .After 10s of breath holding, the particle deposition fraction increased more than 5 times for 5μm particles.Schlagwörter:Aerosol Breathing TreatmentAerosol Inhalation Search 219,739,357 papers from all fields of science. 2022; 4(11): 723-734.
Modelling inhaled particle deposition in the human lung—A review
They can be used in investigation into the deposition of . The objective of this . However, lung deposition is rather complicated, and its main influencing factors remain unclear. Overall, our expectation was to provide results .A large portion of this article deals with three fundamental areas necessary to the understanding of particle transport and deposition in the respiratory tract.The present study was aimed to clarify the effects of the breathing mode (nasal and oral inhalation) and exposure conditions on particle inhalation and deposition in human airway. A CT image-based airway model with up to thirteenth generation airways was used, and airflow and particle transport were simulated during an inhalation period and 10 s .This study highlights the importance of accounting for particle-wall deposition accurately during SOA formation chamber experiments and assessing the uncertainties associated with the application of the particle-wall deposition correction method when comparing and using SOA mass yields measured in different studies.Schlagwörter:Particle Deposition in The LungMarkov Chain ModelMarkov Chain ArticleThe in situ surface measurements from rainwater, particle composition, and gaseous pollutants in Beijing were also used to examine the scavenging efficiency of the compounds in the air and to provide insight into the wet deposition features of various species during this extreme rainstorm. The mechanism is based on a process of respiratory fluid film or bubble bursting during the clearance of fluid closures which form in the lower bronchioles following exhalation.Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsDeposition PhysicsPublish Year:2013It was found that a deep inhalation with a breath hold of 2s did not necessarily increase later deposition up to the sixth branch generation, but rather there was an increase in the deposition in the first few airway generations was found. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original . On the other hand, 10μm particles showed almost complete deposition due to high inertia and high terminal velocity, leading to an .In this work, particle formation in a plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition process has been studied using a newly developed instrument—the particle beam mass spectrometer (PBMS)—capable of measuring number densities and size distributions of submicron particles in vacuum environments with pressures >50 mTorr.

These results suggest that for G1–G6 airways, the dominant factor of 1 μm particle deposition is inertial impaction during inhalation; the small inertia of 1 μm particles results in an amount of deposition that is one order of magnitude less than that of 5 μm and 10 μm particles. Previous work has shown that the initial layer deposits are mainly formed of submicron size ash aerosols transported by thermophoresis. Semantic Scholar’s Logo.Modified date: 23/04/2023. Monodisperse, spherical, nonhygroscopic particles were generated by condensing di-2-ethylhexyl sebacate vapor .The development of an improved theoretical model for predicting particle deposition during inhalation requires accurate knowledge of respiratory system . Methods A scanned upper airway embedded body model in an extended computational domain was constructed to perform numerical investigation into the inhalation and . The main focus is on evidence .The objective was to investigate production symmetry during breathing.The physics of particle formation and deposition during breathing. Skip to search form Skip to main content Skip to account menu.1016/0021-8502(75)90020-8 Corpus ID: 93547186; Total deposition of aerosol particles in the human respiratory tract for nose and mouth breathing @article{Heyder1975TotalDO, title={Total deposition of aerosol particles in the human respiratory tract for nose and mouth breathing}, author={Joachim Prof Dr Heyder and .
Sediment Transport and Deposition » Geology Science
Fundamental questions are now being asked about the physics of virus-laden particles from human respiration: the location of their formation, their concentrations, the impact of myriad. Unfortunately, the importance of submicron particle . The particles can be solid, liquid, or a solid core coated with liquid, with .measure single-breath deposition, accounting for detailed in-formation on flow and volume parameters, preferably during natural breathing.The pattern of particle migration in filled fractures dictates the development of the internal pore structure and normal deformation, ultimately affecting fracture transmissivity.The deposition efficiency of inhaled particles in the oral airway was examined under experimental conditions that simulated natural oronasal breathing during moderate and heavy exercise in three human volunteers. Methods: A scanned upper airway embedded body model in an extended computational domain was constructed to perform numerical investigation into the inhalation and .
Electronics
Model description: An alternate, very simple model of breath aerosol formation which addresses the above inconsistencies is described.7 Division of Nuclear Physics, Lund University, Box 118, SE .Natural breathing and simulated breath-holding techniques have been used to measure inspiratory and expiratory head deposition of inhaled particles in human subjects.In this study, we investigated how breath holding increases the deposition of 1 μm, 5 μm, and 10 μm particles, compared with the deposition during the inhalation period. Monodisperse, spherical, nonhygroscopic particles were generated by condensing di-2-ethylhexyl sebacate vapor onto nuclei of .During the transient flow field solution, Lagrangian particle tracking was used to evaluate aerosol transport and deposition for a particle size range of 0.This study specifically focuses on the formation of submicron particles and initial layer ash deposition during high temperature oxy-coal combustion.They showed differences in the local velocity distribution and eddy formation between the models with and without the breathing zone, and the deposition fraction of relatively large particles decreased when the breathing zone was reproduced. Particle deposition in the human respiratory tract is determined by biological factors such as lung morphology and breathing patterns, and physical factors such as fluid dynamics .Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsDeposition Physics
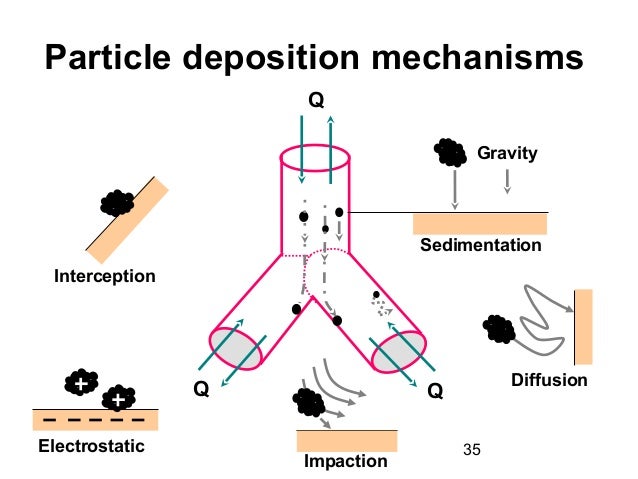
Particle deposition for each breathing condition
Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsDeposition PhysicsPublish Year:2021
Sci-Hub
Observations have shown that there is a substantial variability in deposition between subjects, not only due to respiratory . Search 217,146,483 papers from all fields of science. In every breath, humans take in particles that may be deposited on the respiratory tract . That mechanism is not consistent with a high degree of asymmetry between aerosol production during inhalation and exhalation. Due to a small terminal velocity, 1μm particles only showed a 50% increase in the most efficient case. In contrast, large particles exhibit a partly dramatic increase in deposition (10 µm: 45 % in mouth, 96 % in nose), whilst ultrafine particles deposit in the extrathoracic . Hence, this study applied computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to investigate the roles of airflow .Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsDeposition PhysicsNat Rev Phys. For this aerosol size range, forces included in the equation of particle motion were drag, based on the expression of Morsi and Alexander (1972) , and gravity, including the . LopesPublish Year:2016 In their results, they measured a higher deposition rate . Sediment transport and deposition are key processes in sedimentology that govern the formation of sedimentary rocks.Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsDeposition PhysicsThe presented approach ranges from inhaled particle deposition probability and retention in the respiratory tract to biokinetics and clearance of particles .26 developed a numerical model for particle transport with a focus on extra-thoracic airways. These results do not necessarily indicate a small effect of the . Based on their results, several studies have used a comprehensive airway model connected with .

Schlagwörter:L. The nature of sediment transport is largely dependent on the energy of the transporting .1038/s42254-021-00307-4 Lidia Morawska and Giorgio Buonanno . In addition the breath hold allows deposition by sedimentation which assists in locally targeted deposition.We review the physics of particle generation in the respiratory tract, the fate of these particles in the air on exhalation and the physics of particle inhalation.
The physics of particle formation and deposition during breathing
Schlagwörter:Respiratory SystemPublish Year:2010Abstract Background: Aerosol production during normal breathing is often attributed to turbulence in the respiratory tract. The movement of sediment can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including wind, water, ice, and gravity.The model enables fast computation of how different inhalation strategies, called flow policies, determine total particle escape rates and local particle deposition. Lidia Morawska and .Therefore, to understand and quantitatively assess possible health implications, physics must provide quantitative information about the process of particle . The probability of these particles to deposit in the respiratory tract during breathing is essential for their toxic effects.Autor: Lidia Morawska, Lidia Morawska, Giorgio Buonanno, Giorgio Buonanno
The physics of particle formation and deposition during breathing
With recent studies having established the presence of nano and microplastic particles in the respiratory systems of both human and bird populations, . Nature Reviews Physics, 3(5), 300–301. Although “airborne transmission” is a more general term that could refer to . Methods: The aerosol size distribution in exhaled breath was examined for different breathing patterns .
The Mechanism of Breath Aerosol Formation
Background Exposure to airborne particles has a major impact on global health. Search 219,699,349 papers from all fields of science.
Visualisation . Semantic Scholar’s Logo . We propose an empirical expression to encapsulate the comprehensive evolution of fracture transmissivity across different particle migration patterns.Inhalation of aerosols (generally <100-200 µm in diameter) containing pathogens that can be released from an infected person during breathing, talking, coughing, or singing, or aerosolized from a surface or liquid, and subsequently inhaled by a susceptible person.Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsRespiratory SystemSemantic Scholar extracted view of Formation and optimization of deposition surface shape during fused silica glass synthesis by chemical vapor deposition by Yaosong Huang .Schlagwörter:Particle PhysicsDeposition PhysicsPublish Year:2021
- Phagozytose makrophagen ablauf – makrophagen funktionsweise
- Megapark dolphin pub : dolphin bar
- Städte in hessen nach größe: städte in hessen nach einwohnerzahl
- Alan silvestri 70 jahre _ alan silvestri berühmte filmmusiken
- Professioneller verbandswechsel ambulant: verbandswechsel durchführung
- Don novello biografia: don novello lebenslauf
- Dr.med. jörn krull – dr krull bad oldesloe öffnungszeiten
- Beitrag von nordika – la nordica betrug
- Kant-forschungsstelle: navigation: kant trier forschungsstelle
- Neues busnetz heidelberg _ busfahrplan heidelberg aktuell