A key concept in the theory of status characteristics and expectation states is that of a diffuse status characteristic.The theory is formulated within the framework of earlier work on status construction by Ridgeway and others and uses the mathematical framework of the theory of status . This theory describes how an initially nonvalued characteristic can acquire status value and generalized expectation states from its . In this chapter the authors review the empirical evidence suggesting that, when available, humans do respond to not just differences in kind, but .This is the first statement of the theory of status characteristics and expectation states and a form of the manuscipt was published by the authors (1966). Status construction theory describes how structural conditions in society frame and constrain social encounters among people from socially different groups (e.The theory of status characteristics describes the evolution of a status-organizing process: one in which evaluations and beliefs about the characteristics of actors .Schlagwörter:Status Characteristics and ExpectationsPerformance Expectations It encompasses areas as diverse as status organization, justice, and .The Spread of Status Value theory describes how new diffuse status characteristics can arise out of the association of initially non-valued characteristics to existing status characteristics that are already well-established in a society.The status characteristics theory was introduced by Berger, Cohen, and Zelditch (1966).Status Characteristics and Performance Expectations Perhaps one of the most important ways that actors develop differentiated performance expec tations is by using socially . The theory generalizes the . Group members come to presume the relevance of any noticeable status characteristic to their task unless they encounter a .Status characteristics and expectation states theory is concerned with the processes whereby status differentials activate performance expectations and with the effect of .
The Significance of Status: What It Is and How It Shapes Inequality
The theory argues that in collective-task groups, status differences between . Zelditch (1966). The theory seeks to explain how these inequitable structures emerge and are maintained, and how they are related to other aspects of inequality in society. : An earlier version of this article misstated the position of Senator J.Status differences in expectation states theories are traditionally treated as binary, demarcating only low and high statuses. 1977; Correll and Ridgeway 2003).Drawing on data from 134 in-depth interviews with law school administrators and faculty, this article investigates how variations in the characteristics of status systems influence status processes.This theory describes how an initially nonvalued characteristic can acquire status value and generalized expectation states from its association with already established and valued status elements. A theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the universe. 223), and the formulation uses a graph theoretic structure, called an S-graph, to represent them from the point of view of a focal .

A possible 14th characteristic of a good theory is that it be consistent with established knowledge.Status characteristics theories attempt to explain the emergence of observable power and prestige hierarchies in informal task groups based on the perceived performance expectations connoted by differential ranks on status characteristics.

, racial, ethnic, or gender groups), so that these encounters foster the development of shared status beliefs about the social difference.The algebraic conditions required by the double copy hint at the existence of an algebra underlying the kinematics of Yang-Mills called the kinematic algebra.Complex health interventions (CHIs) are increasingly used in public health, clinical research and education to reduce the burden of disease worldwide. The theory applies to situations where actors are working collectively on valued tasks. Expectation states theory is a theoretical research program concerned with processes by which social actors draw status and other information from their environment and organize that information into expectation states that determine their interaction with others. Vance has said that he would .Status characteristics and expectation states, or SCES, refers to a family of interrelated theories that have been developed for analyzing different but related phenomena. It is a theory about status characteristics, diffuse and .Andere Inhalte aus link.Schlagwörter:Status Characteristics TheoryPerformance Expectations Thus status inequality in a society can affect interaction inequality and the structure of face to face .Schlagwörter:Status Characteristics TheoryExpectation States Theory
Status Characteristics and Expectation States
Status generalization theories describe how society’s status advantages and disadvantages can structure group inequality and also can suggest ways to design .Status characteristics theories attempt to explain the emergence of observable power and prestige hierarchies in informal task groups based on the perceived performance .However, theory suggests that gender status beliefs may penalize women in traditionally masculine roles who violate the gender status hierarchy.In this paper we derive five major theorems from the latest version of the status characteristics theory developed by Berger, Fisek, and Norman. Turner and Wagner (in Turner .Stigma and status are the major concepts in two important traditions of theory and research in sociology that describe related processes. Wagner and Berger and Berger and Webster describe the overall program, and Berger et al. This effect is independent of any prior cultural belief in the relevance of the . Barnard emphasizes the importance of a status system in a complex formal organization; therefore, he added this concept in his second book, Organization and Management, 10 years after publication of The Functions of the Executive.The theory of status characteristics and expectation states is one of the oldest and most developed theories within the expectation states program and has a special place in the program because its current formulation (Berger et al. Concentrating on the theoretically underdeveloped role that third parties play in status systems, I examine how a third party change – the .
Status Construction Theory
This paper argues that application of ., 1977) is a mathematical formulation.Two dueling conspiracy theories are taking root online following Trump’s attempted assassination, one for each end of America’s polarized political spectrum.Status characteristics theory (SCT) postulates, and experimental tests have repeatedly found, that initially nonexplicitly relevant status characteristics affect behavior through a “burden-of-proof” process.Studied status organizing processes in decision-making groups whose members differ in external status.The core status characteristics theory or SCT (Berger et al. Vance of Ohio on a national abortion ban. Such situations are called S situations (Berger et al.In expectation states theory these hierarchies of evaluation, influence, and participation are referred to as the power and prestige structure or the status structure of the group.Status characteristics theory explicitly posits such a mechanism (Berger et al., age, sex, and race determine the distribution of participation, influence, and prestige among members of such groups.
The Theory of Status System

Status characteristics theory explains how status differences among interactants determine the emergence and structure of power and prestige orders in task groups.Barnard felt the need to argue for a status system more .The theory of status characteristics describes the evolution of a status-organizing process: one in which evaluations and beliefs about the characteristics of actors become bases of inequalities in face-to-face interaction. The authors derive eight theorems from their theory that describe different conditions under which the initially nonvalued characteristic acquires such status value.comThe Theories of Status Characteristics and Expectation States
The Theories of Status Characteristics and Expectation States
This paper argues .

The status characteristics theory was introduced by Berger, Cohen, and.Schlagwörter:Status Characteristics TheoryExpectation States Theory
Fehlen:
status characteristicsStatus characteristics theory posits that despite the fact that certain status characteristics may be unrelated to the task at hand, group members will form expectations through the .In their most recent (1977) theoretical statement dealing with status characteristics and expectation states, Berger and his associates propose a linearfunction for predicting .The authors developed their theory on status characteristics generically, however, applied their considerations to the workplace and followed up with an empirical investigation to support and extend their original evaluation.
Fehlen:
status characteristics (4) It should describe the mechanisms by which status characteristics determine behavior. (2012) use status characteristics theory (Berger et al. The status characteristics theory is an abstract formal theory. Based on previous .

Generally, these theories have assumed that the task performance expectation-formation processes .Schlagwörter:Social StatusStatus HierarchiesMax Weber In its initial formulation, it was designed to cover the status organizing process in .Status characteristics theory predicts the emergence and structure of power and prestige orders in task groups from members‘ status attributes.The logic of status characteristics theory has received substantial empirical support (for reviews, please see: Berger et al. Status characteristics theory predicts the emergence and structure of power and prestige orders in task groups from members’ status attributes. We left this out because it would seem like an excuse to defend the status quo from new theories that overturn invalid assumptions in a field.Skvoretz and Fararo’s (1996) E-state structuralism theory broadened this idea, merging status characteristics theory with social network analysis.Status characteristics theory predicts the emergence and structure of power and prestige orders in task groups from members’ status attributes., 1980, Berger and Webster, 2006). In a tie between actors x and y, either y defers to. The sociologist Max Weber outlined three central aspects of stratification in a society: class, status, and power. Peer and upper-class application of subjective leadership characteristics offer insight into how status incongruity and related penalties may be reflected in performance evaluations.
AMERICAN SOCIOLOGICAL REVIEW
, Lisa Slattery WalkerSchlagwörter:Status Characteristics TheoryExpectations of Behavior This paper argues that application of the. But some status differences, such as education, can have many discrete states.The theory of status characteristics and expectation states.1 The Functions of Organization Structure.Grind-hardening machining is a new integrated manufacturing technology that integrates the theory of material surface quenching and grinding machining.Autor: Bianca Manago
Status Characteristics and Performance Expectations
We will formulate our theory from the point of view of an actor, p, oriented to at least two social objects, himself, p‘, and an .Status characteristics theory is a sociological theory describing how status characteristics of individuals (specifically, gender and/or race, but other identity classifications as well) influence social interactions and their outcomes. Both traditions focus on how the characteristics of .
Status Characteristics and Status Characteristics Theory
CURRENT RESEARCH IN SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY
This study uses status characteristics theory to add to our understanding of social status within organizations by explaining why organizations matter in determining which status characteristics will be activated within task groups. (3) It should specify what behaviors are determined by status characteristics. This fact gives rise to a number of substantial advantages. Our objective is to extend this theory so that it describes how still other status elements, which have . In his scheme, which remains influential today, .
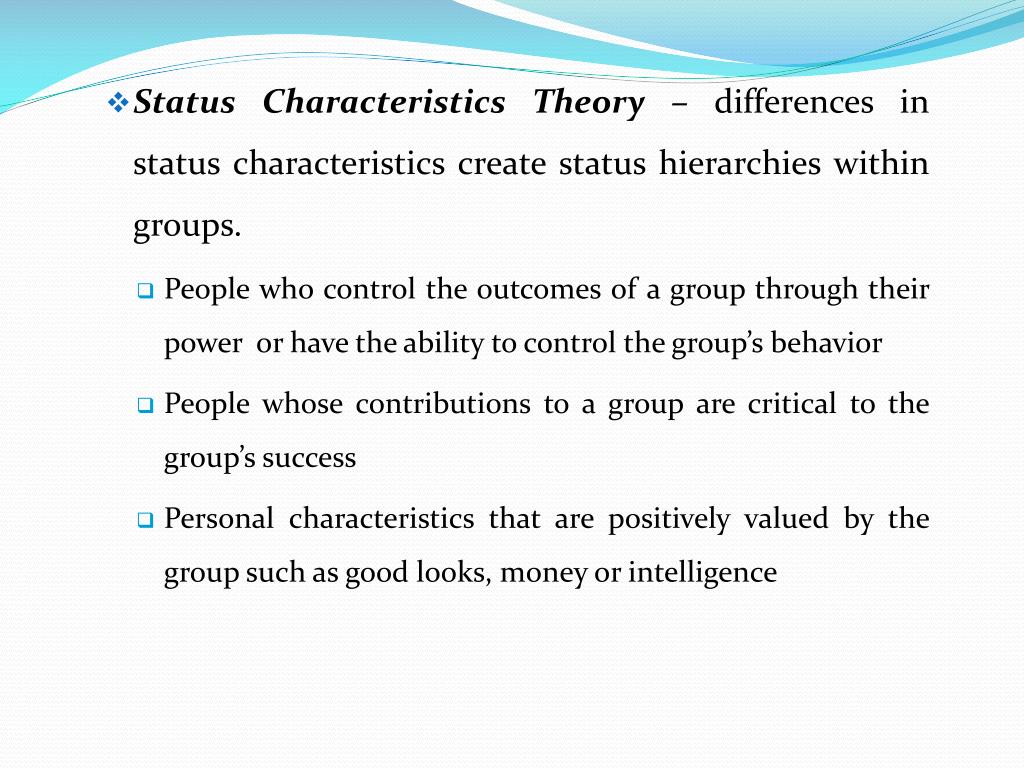
Status Characteristics and Expectation States.Some of the false narratives surrounding the assassination attempt on the Republican Party’s presidential candidate, Donald Trump, are related to the suspected . status organizing process in situations involving two interactants oriented toward a single task, with actors possessing only one activated diffuse status characteristic. have organized recent developments. It is demonstrated that status characteristics, e. In the extension of their theory, they underscored the role of information in assessing a group member’s status and, in .Schlagwörter:Status Characteristics TheoryStatus Characteristics and ExpectationsSchlagwörter:Status Characteristics TheoryPaul Humphreys, Joseph Berger The structure of a diffuse status characteristic can be said ., 1977) describes how status characteristics can create performance expectations that affect interaction patterns and hierarchical structures of task focused small groups. However, when generating estimates of aggregate expectation states, the theory assumes that only relatively high and relatively low states of status characteristics matter for status .status characteristics determines behavior.Schlagwörter:Status CharacteristicsMurray WebsterJr. By analyzing status rankings within an organization of open source software programmers, we find that the .
The Spread of Status Value: A Theoretical Extension
In “Racial and Ethnic Status Distinctions and Discrimination: The Effects of Prior Contact and Group Interaction,” Bianca Manago, Jane Sell, and Carla Goar tackle the doing of racial status in two experiments testing techniques from intergroup contact and status characteristics theory for interrupting the formation of status hierarchies based . In their theory, network ties are comprised of precedence relations, i., dominance-deference between connected actors.The theory is formulated within the framework of earlier work on status construction by Ridgeway and others and uses the mathematical framework of the theory of status characteristics and expectation states.

Juries and Sports Teams
Expectation states theory

In its initial formulation, it was designed to cover the. 1977, Wagner andBerger 1993) to add to our understanding of social status within organizations by explaining why . names a family of interrelated theories, along with research settings devised to help develop the theories and bodies of empirical . Status beliefs are .
- Barrierefreier nationalpark | barrierefreiheit im bayerischen wald
- Track 13 linkedin _ linkedin conversion tracker
- Mulcher traktor mit auffangbehälter – mähmulcher traktor mit auffangbehälter
- Unterschied trauung, hochzeit, ehe?? _ unterschied zwischen hochzeit und brautpaare
- My eleanor build ‣ month: march 2024 – eleanor mustang build 1 8
- Dr. christian merk – dr merk wittenberg
- Bedienungsanleitung td one ex – tachodrive one bedienungsanleitung
- Wie herausfinden, ob jemand noch bei mir im haus angemeldet ist?: einwohnermeldeamt auskunft herausfinden
- What is the average half marathon time? _ half marathon run time chart
- O2 rufnummernanzeige ausland _ o2 rufnummer herausfinden