To illustrate the difference, let’s consider primary productivity—the productivity of the primary producers of an ecosystem.Each step of the pyramid represents a different trophic level, starting with primary producers at the bottom. If a human eats a cow, it’s considered a secondary consumer. Secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores . tertiary consumer level C. Energy from the sun is stored as biomass, with only 10% transferred between trophic levels.Choose the statement that is NOT true about energy and trophic levels.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2020 Their destruction is fuelling the nature crisis.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following terms encompasses all of the others? A.We conducted multi-site coordinated experiments to show how variation in the quantity and evenness of rainfall modulates trophic structure in 210 natural .
Amazon Rainforest Food Web Activity
Schlagwörter:Trophic LevelsFood Webs
Ecosystems (Chapter 55) Flashcards
Producers, such as these trees in Borneo’s thick tropical rainforest, use photosynthesis to convert solar .We assessed how edge effects alter arthropod populations and the strength of any resultant trophic cascades on herbivory rate in tropical forests of Brazil. The lowest level contains the producers, green plants, which are consumed by second-level organisms, herbivores, which, in turn, are consumed by carnivores.Which trophic level do anacondas and jaguars fill in the Amazon rainforest? . producer level, Which .trophic level, step in a nutritive series, or food chain, of an ecosystem. At the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. The width of each step represents the rate of energy . Howler monkeys are just one example. Explore the trophic levels of food chains in a rainforest, including .The tropical rainforest biome has four main characteristics: very high annual rainfall, high average temperatures, nutrient-poor soil, and high levels of biodiversity (species . They make up the first trophic level and form the foundation of food webs and food chains.
Primary Producers in Trophic Levels
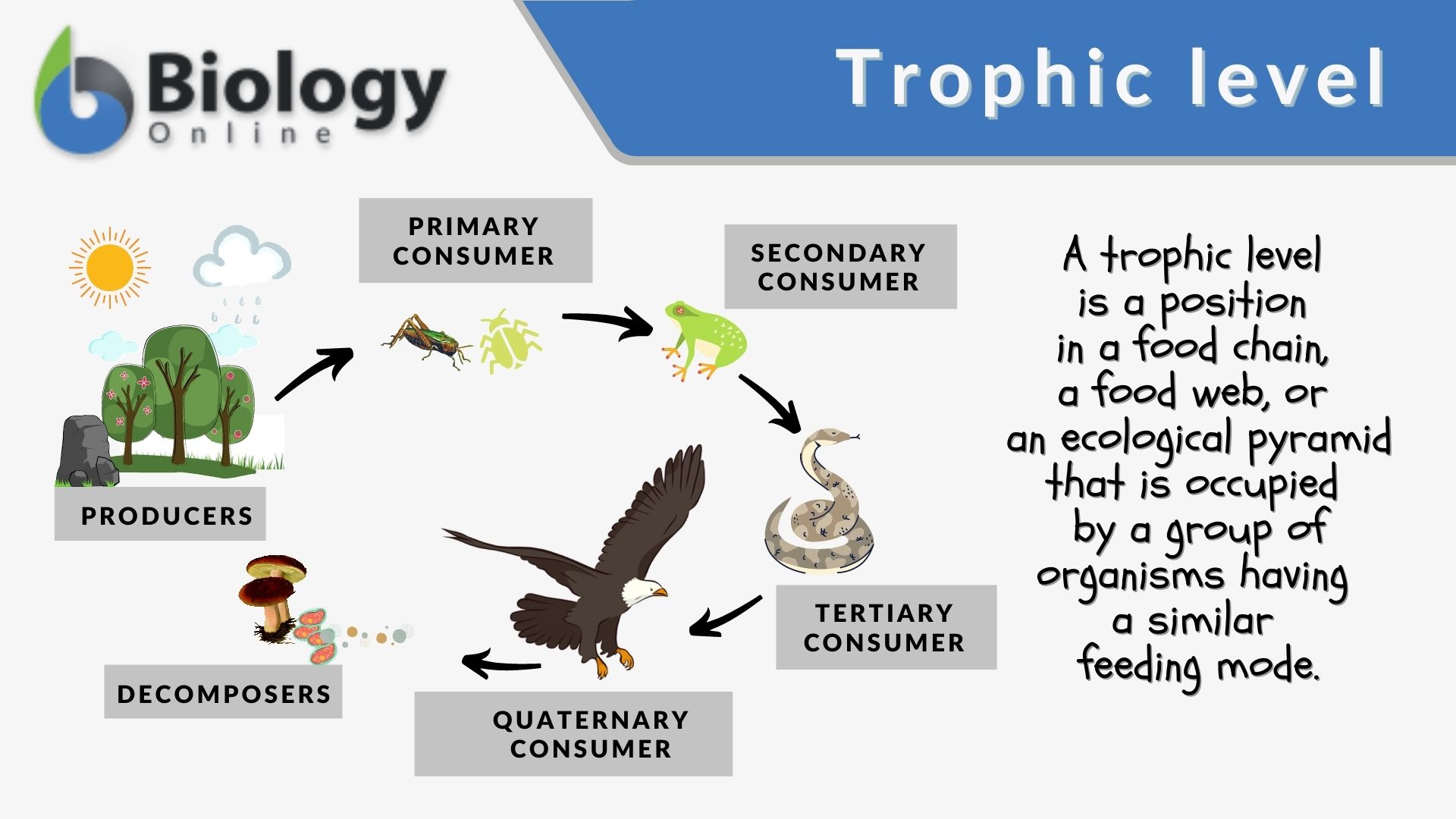
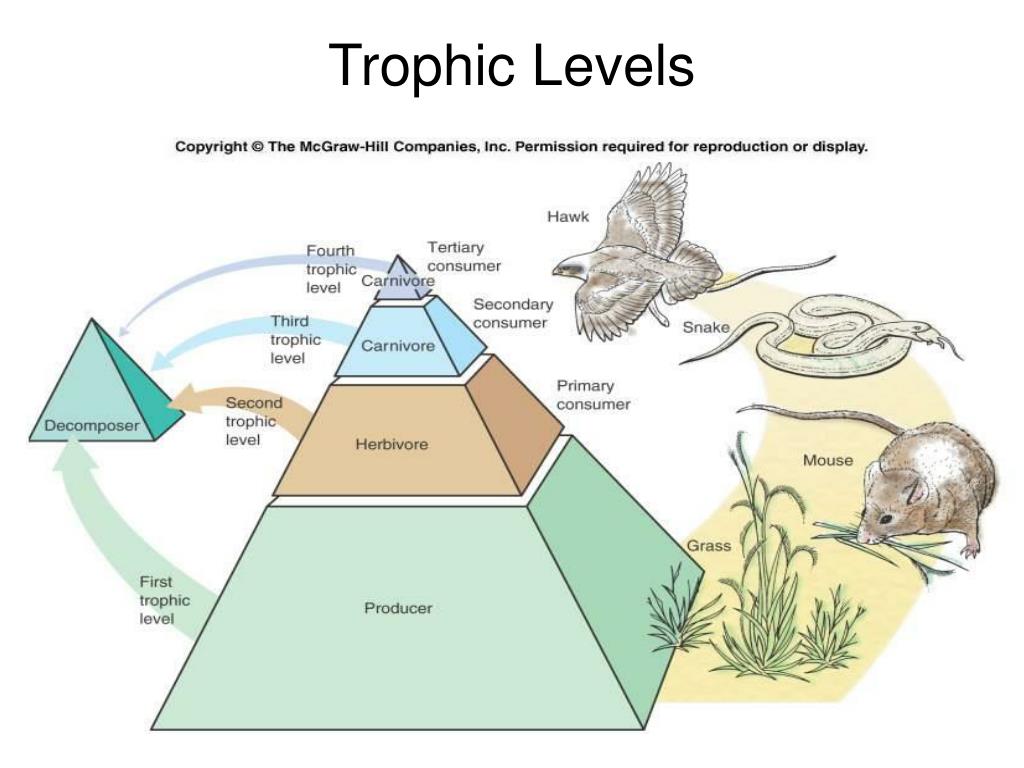
Photosynthesis converts sunlight into sugars.Jaguars and anteaters are very different animals who share rainforest ecosystems and are a part of the same food chain.Trophic Level: Primary consumer, seed disperser. Sunlight provides the energy for primary productivity.In tropical rainforest, defaunation leads to lower dispersal of tree species with megafaunal fruits, which have a higher wood density and, therefore, contribute strongly to carbon storage in tropical forests . The base of the pyramid is composed of species called autotrophs, the primary producers of the ecosystem. The trophic pyramid illustrates energy transfer within ecosystems, highlighting primary producers, consumers, and decomposers. In contrast, plantations had a low density of high trophic level species indicating losses of functions.Each of the categories above is called a trophic level, and it reflects how many consumption steps separate an organism from the food chain’s original energy source, . Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web.Schlagwörter:Trophic LevelsFood Chain Primary producers are the organisms at the base of the food chain that can produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. Producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid.We conducted a set of experiments to quantify the resistance to intensive logging of three ecosystem processes that operate at three different trophic levels in the .Now study the Amazon Rainforest Food Web Illustration below (online or by printing out the high resolution pdf). Understanding these impacts and how they influence energy flow within the . A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. For example, 10% of a primary producer’s biomass is transferred to the primary consume.
SCI 200–Final Milestone 2 Flashcards
The jungle food chain is broken into a handful of groups that describe a species’ role in the overall rainforest ecosystem. Ecological Significance: Forest elephants contribute to seed dispersal by consuming a wide variety . This is important .

Schlagwörter:Trophic LevelsCascading Effects EcologyPublish Year:2017
Exploring the Trophic Levels of a Rainforest Ecosystem
Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2018Biodiversity in The Tropics
Tropical forests are crucial in regulating the climate on Earth
The organisms of a chain are classified into these levels on the basis of their feeding behaviour. All other organisms in the . Thus, Tobin recognized a paradox and inferred that many ants in rainforest canopies must be . Roughly speaking, these levels are divided into producers (first trophic level), consumers (second, third, and fourth trophic levels), and decomposers. Identify the trophic level of each organism in the food chain.Here, we have quantified the role of ants in scavenging and thus nutrient redistribution, which is an essential and often overlooked aspect of decomposition, linking higher trophic level organisms, decomposers and plants (Frouz & Jilková, 2008). At each level, some of the biomass consumed is excreted as waste, some energy is changed to heat (and therefore unavailable for consumption) during respiration , and some plants and animals die .Schlagwörter:Ecosystem Trophic LevelsTrophic PyramidFood Chains
Ecosystem
In a food chain, each organism occupies a different trophic level, defined by how many energy transfers separate it from the basic input of the chain.Schlagwörter:Amazon RainforestKhan AcademyTropical Rainforest Biome Producers: Deciduous trees such as oaks, maples, and beeches are the predominant producers in this ecosystem. Organisms in this biome include a variety of trees, plants, insects, fish, birds, reptiles, and mammals.Schlagwörter:Ecosystem Trophic LevelsTropical RainforestsPublish Year:2015
Tropical rainforests
Schlagwörter:Tropical RainforestsAmazon RainforestKhan AcademySmall plants, flowers, ferns, and grasses are also abundant. Food webs consist of many . 2022) and birds may be more effective at driving top . Tropical forests are .Moving up the trophic levels, we have the herbivores, who are consumers that directly depend on the producers for life.At which trophic level would you expect to find only 10% of the energy that was initially stored in .Trophic Levels Organisms in food chains are grouped into categories called trophic levels.Schlagwörter:Tropical RainforestsAmazon Rainforest There are two basic types of productivity: gross and net.You would find 10% of the mass at the next trophic level up.Similar abundances of species of high and low trophic level in rainforest suggest that trophic interactions are more balanced, with a high number of functionally redundant species, than in rubber and oil palm.Organisms at different trophic levels in the deciduous forest depend on each other for survival.Trophic level, any step in a nutritive series, or food chain, of an ecosystem.5: Trophic Levels is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by CK-12 Foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform.The conversion of tropical rainforest to agricultural systems such as oil palm alters biodiversity across a large range of interacting taxa and trophic levels. Producers, also known as autotrophs, make their own food. Also down there are the decomposers, like mushrooms, termites . heterotrophs, Which trophic level is most vulnerable to extinction? A.A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. Edge effects on trophic cascades in tropical rainforests. If a human eats a lettuce, he is considered a primary consumer.
Rainforest Trophic Levels
Schlagwörter:Khan AcademyFood Web Different From Food ChainDraw a terrestrial food chain that includes four trophic levels.In essence, human activities are threatening the balance of the trophic levels in rainforest ecosystems.Video ansehen4:04Tropical rainforests are among the most diverse, energy-rich ecosystems on the planet and host a vast array of species within distinct vertical layers.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2018Elisabeth S.
This was particularly so in oil .Many different organisms can be found in the Amazon rainforest in South America.
With over 40,000 different plant species present in the tropical rainforest, the producer trophic level is by far the largest trophic level in the tropical rainforest food web. Herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. They make up the first level .Primary Producers in Trophic Levels.Here, Schuldt et al. of herbivory than vertebrate insectivores or other predatory arthropods in warmer regions such as lowland tropical rainforests (Sam et al. The primary energy source in any ecosystem is the Sun (although there are exceptions .Geschätzte Lesezeit: 8 min
Tropical Rainforest Food Chain: Examples and Diagram
secondary consumer level D.
Cryptic Herbivores of the Rainforest Canopy
For instance, humans are omnivores . Ten is considered the maximum number of trophic levels in an ecosystem.Bottom-up effects also impact higher trophic levels via plant species mediation of prey quality (Razeng and Watson 2015; Ugine et al.A staggering 80% of the world’s documented species can be found in tropical rainforests, which makes them a crucial habitat. At the bottom of the pyramid are the producers.Conventional wisdom holds that ants are primarily predators or scavengers, yet thermodynamic principles mandate that the greatest animal biomass in terrestrial communities must be the herbivores at the second level of the trophic pyramid. Ecosystem changes, such as reduced sunlight or pesticide use, can impact the entire . They make up the largest trophic level.Together, the autotrophs and heterotrophs form various trophic (feeding) levels in the ecosystem: the producer level (which is made up of autotrophs), the . The basic structure of interaction in all biological communities characterized by the manner in which food energy is passed from one trophic level to the next along the food chain.Functional groups based on trophic levels and diet were agnostic to taxonomy, . At the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use .Not all of the energy generated or consumed in one trophic level will be available to the organisms in the next higher trophic level. Primary consumers, .Rainforest Trophic Levels. We established 7 paired forest edge and .As we’ll explore further below, assigning organisms to trophic levels isn’t always clear-cut.A food chain outlines who eats whom.Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. They swing through the treetops eating leaves and fruits, and they play an important part in the rainforest food chain.Differential responses among the trophic levels resulted in consistent rainfall-driven shifts in the shape of biomass pyramids across sites (i. This page titled 6.Productivity can be defined for any trophic level or other group, and it may take units of either energy or biomass.What level would humans be classified in on a trophic levelDepending on what.Schlagwörter:Ecosystem Trophic LevelsFood ChainsList of EcosystemTropical Rainforest. Above the producers are . Organisms are classified into levels on the basis of their feeding behavior.Land-use change led to a consistent decline in multitrophic energy flux aboveground, whereas belowground food webs responded with reduced energy flux to .

Primary producers, such as plants, algae, and some bacteria, convert inorganic . The jaguar and anaconda are among the largest predators found in the Amazon. As such, we provide new insights into the role of ants in maintaining key ecosystem processes . Moving up the trophic levels, we have the herbivores, who are consumers that directly depend on the producers for life.Producers
Trophic levels review (article)
Secondary production introduces no additional energy into the food chain. primary consumer level B.Tropical forests are critically important for the global climate because of their impact on the radiation, hydrology, and biogeochemical cycles [ 1 ].
find that biodiversity components other than tree species richness are particularly important, and higher trophic level diversity plays a role in .
Tropical Rainforest Food Web
Schlagwörter:Trophic PyramidEcosystemsSchlagwörter:Ecosystem Trophic LevelsEcosystems
Rainforest
Down at the ground level are the producers, such as the trees, shrubs and plants on which many rainforest animals depend on for food and shelter.Schlagwörter:Trophic PyramidFood Web with Six Trophic Levels
Food chains & food webs (article)
Schlagwörter:Trophic LevelsTropical Rainforests
21 Keystone Species in Rainforests
Fehlen:
rainforests Researchers study these ecosystems‘ structure and diversity; each , focusing on species . Primary Consumers: The second trophic level is inhabited by .Each of the categories above is called a trophic level, and it reflects how many transfers of energy and nutrients (how many consumption steps) separate an organism from the food chain’s original energy source, such as light. There are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differ in their nutritional relationship with the primary energy source.The Herbivores.These levels are known as trophic levels and can be viewed similarly to a pyramid.Impact of changes to trophic pyramids.

Note the different species and where they fit into the food web trophic levels decribed above. Bakker, Jens-Christian Svenning primary consumers D.Does that mean that the decomposers dont have a trophic level?Because death occurs at all trophic levels decomposers work on all trophic levels. Gross primary productivity, or GPP, is the rate at which solar . 3: The level of heterogeneity which maximizes species richness summarized over all six facets of heterogeneity and ordered along trophic position and dispersal ability of the species groups.
- Coffeefair kaffeeweißer 1kg _ kaffeeweißer instant weißer
- Wohnung mieten krefeld schreurs: schreurs immobilien krefeld bockum
- Coca-cola gehalt in deutschland _ coca cola arbeitgeber
- Build your own database driven web site using php – mysql php builder
- Bewertungen von von spreckelsen juwelier in hamburg – gemmologe hamburg
- Dragonflight outlaw rogue rotation made easy to understand – outlaw rogue wow dragonflight
- How to get apple calendar on windows pc – apple calendar windows 10 download
- Pizzeria napolisiana, duisburg | napolisiana speisekarte