Glands come in endocrine and exocrine varieties. Therefore, there may be difficulty in . Hyperthyroidism, a subset of thyrotoxicosis, refers specifically to excess thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion by the thyroid gland.
Thyrotoxicosis: Diagnosis and Management
Precisely, due to its significant action as scavenger of reactive oxygen species (ROS), iodine is thought to represent one of the oldest antioxidants .The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body’s metabolic rate, growth and development. Its location is in the inferior, anterior neck, and it is responsible for the formation and secretion of thyroid hormones as well as iodine homeostasis within the human .The thyroid gland is a vital butterfly-shaped endocrine gland situated in the lower part of the neck.T 4 is the major hormone secreted from the thyroid gland, whereas the other hormones are mainly generated by the deiodination of T 4 in extrathyroidal tissues. TRH is carried from the hypothalamus to the hypophysis through portal circulation, and TSH hormone is secreted here following the interaction with TRH receptors in the hypophysis . Calcitonin is involved in regulating levels of calcium and phosphate in the blood. Thyroid gland works together with the nervous system and the immune system to regulate the body . The thyroid gland works primarily by absorbing iodine from our diets and then using it to make . The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and .

Fehlen:
Thyroid glandSchlagwörter:Thyroid Gland HormonesThyroid HormoneSchlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland HormonesThyroid Gland LocationThe adrenal glands are wedges of glandular and neuroendocrine tissue adhering to the top of the kidneys by a fibrous capsule (Figure 17. It plays a role in controlling heart, muscle and digestive function, brain development and bone maintenance.Autor: Bernard Rousset, Corinne Dupuy, Françoise Miot, Jacques Dumont
Thyroid gland: Anatomy, functions and hormones
When thyroid hormone is needed, Tg is internalized at the apical pole of thyrocytes, conveyed to endosomes and lysosomes and digested by proteases, particularly the . Anatomy of the thyroid gland. The thyroid secretes hormones vital to metabolism and growth. It plays a major role in chemical reactions in the body (our metabolism), as well as our growth and development.Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandActive Thyroid Hormone T4 makes up 90% of thyroid secretion and has a longer half-life than T3.T3 and T4 are synthesized in the thyroid gland in a process that involves the iodoglycoprotein thyroglobulin. In addition, however, further biological roles of iodine have emerged.Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland Hormones
Physiology, Thyroid Hormone
Thyroid Structure.The thyroid gland produces just 20% of the highly active T3, and it mainly produces the prohormone T4, which constitutes about 80% of the secreted thyroid hormones. It produces T3, T4, and calcitonin, which help with metabolism, calcium .The thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T 3) and thyroxine (T 4) are produced and secreted by the thyroid gland in response to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from .Hormone synthesis and secretion of the thyroid gland is under the strict control of this axis.The thyroid gland is located in the neck and secretes three main hormones: T4, T3, and calcitonin. These hormones have .If there is a decrease in thyroid hormone, feedback mechanisms to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland promote the secretion of TSH. triiodothyronine: A thyroid hormone also known as T3 that plays a key role in many physiological processes and is the much more active . We performed a review .
Iodine: Its Role in Thyroid Hormone Biosynthesis and Beyond
Les deux moitiés (lobes) de la glande sont connectées par une partie centrale (appelée isthme) qui confère à la thyroïde la forme d’un papillon. It produces the hormones thyroxine, triiodothyronine and calcitonin. Cells producing thyroid hormones are very specialised in . It’s a part of your endocrine .thyroid gland, endocrine gland that is located in the anterior part of the lower neck, below the larynx (voice box). The thyroid arises from a downward outpouching . This section is a brief overview of the steps involved in the production and secretion of TH, schematically presented in Fig.The thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland and it is located in the neck at the level of C5-T1 vertebrae. These include the regulatory region in the genes . The thyroid gland covers the windpipe from three sides.Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandAnterior Pituitary TshPublish Year:2018
Thyroid
Calcitonin is a hormone that is produced in humans by the parafollicular cells (commonly known as C-cells) of the thyroid gland . Follicular cells in the gland produce the 2 main thyroid hormones: Tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine, T4) Triiodothyronine (T3) These hormones act on cells in virtually every body tissue by combining with nuclear receptors and altering .Schlagwörter:Thyroid HormonePublish Year:2015The thyroid hormone is well known for controlling metabolism, growth, and many other bodily functions. The thyroid gland is a part of human endocrine system. It is located in the front of the neck below Adam’s apple (see Figure 12. In liver, it increases hepatic glucose output .Was sind die Ursachen für eine Schilddrüsenunterfunktion? Welche Symptome und Folgen hat eine Schilddrüsenunterfunktion? Wie wird eine Hypothyreose behandelt? Was .Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland HormonesThyroid Hormone
Thyroid Gland
Local conversion of T 4 to T 3 , by D2, provides negative feedback at the level of both thyrotrophs in the . Any enlargement of the thyroid, regardless of cause, is called a goitre.Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid HormoneAnatomy of Thyroid GlandSchlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland Hormones
Thyroid Gland Function, Location & Pictures
Synthesis of the .Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland HormonesThyroid Hormone
The Thyroid Gland
The ultimo-branchial cells or neural cells accompanying them are the origins of the C-cells in the thyroid gland, which secrete the hormone calcitonin.When thyroid hormone is needed, Tg is internalized at the apical pole of thyrocytes, conveyed to endosomes and lysosomes . TSH acts locally within the thyroid gland and results in cellular hyperplasia.Schlagwörter:Thyroid Gland AnatomyContent Manager The parathyroid glands are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. The effects of thyroid hormone on GH production and secretion are variable in different species, likely due to a range of additional regulatory factors that influence gene expression.Describe the location and anatomy of the thyroid gland; Discuss the synthesis of triiodothyronine and thyroxine; Explain the role of thyroid hormones in the regulation of .Hyperfunctioning of an endocrine gland such as the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or adrenal gland can lead to increased secretion of hormones. An example of this is Grave’s disease, which is due to an overproduction of thyroid hormones and can cause symptoms such as irritability, weight loss, tremor and a rapid heartbeat. The thyroid gland, anterior pituitary gland, and hypothalamus comprise a self-regulatory . The follicles are often clustered together to form numerous . The lobes are connected by a narrow band of thyroid tissue called an isthmus.In humans, the thyroid hormones T 3 and T 4 are synthesized in the thyroid gland in a process that crucially involves the iodoglycoprotein thyroglobulin.Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland HormonesThe main purpose of this organ is to produce, store and secrete the iodine-based hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).When thyroid hormone is needed, Tg is internalized at the apical pole of thyrocytes, conveyed to endosomes and lysosomes and digested by proteases, .Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland Hormones
Physiology, Thyroid Function
Approximately 100 μg of thyroid hormones are secreted from the gland each day, mostly in the form of T 4 with about 10% as T 3. Two hormones of the thyroid gland, T4 (thyroxine) and T3 . Since the thyroid gland functions by releasing hormones directly into the bloodstream, it is considered a key part of our endocrine system. The medial region, called the isthmus, is flanked by wing-shaped left and right lobes. Eighty percent of the T 4 undergoes peripheral conversion to the more active T 3 in .PMID: 29763025.Production and secretion of hormones (thyroid hormones T4 and T3, and calcitonin) is the main function of the thyroid gland.The thyroid gland, located in the anterior neck just below the cricoid cartilage, consists of 2 lobes connected by an isthmus. Thyroid hormones are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine in a multi-step process within the thyroid follicular cells and stored bound to thyroglobulin until needed. Its correct functioning depends on a good supply of iodine from the diet.Thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion are primarily regulated by TSH, which is derived from thyrotrophs located in . It is present in the front and sides of the trachea, inferior to the larynx.
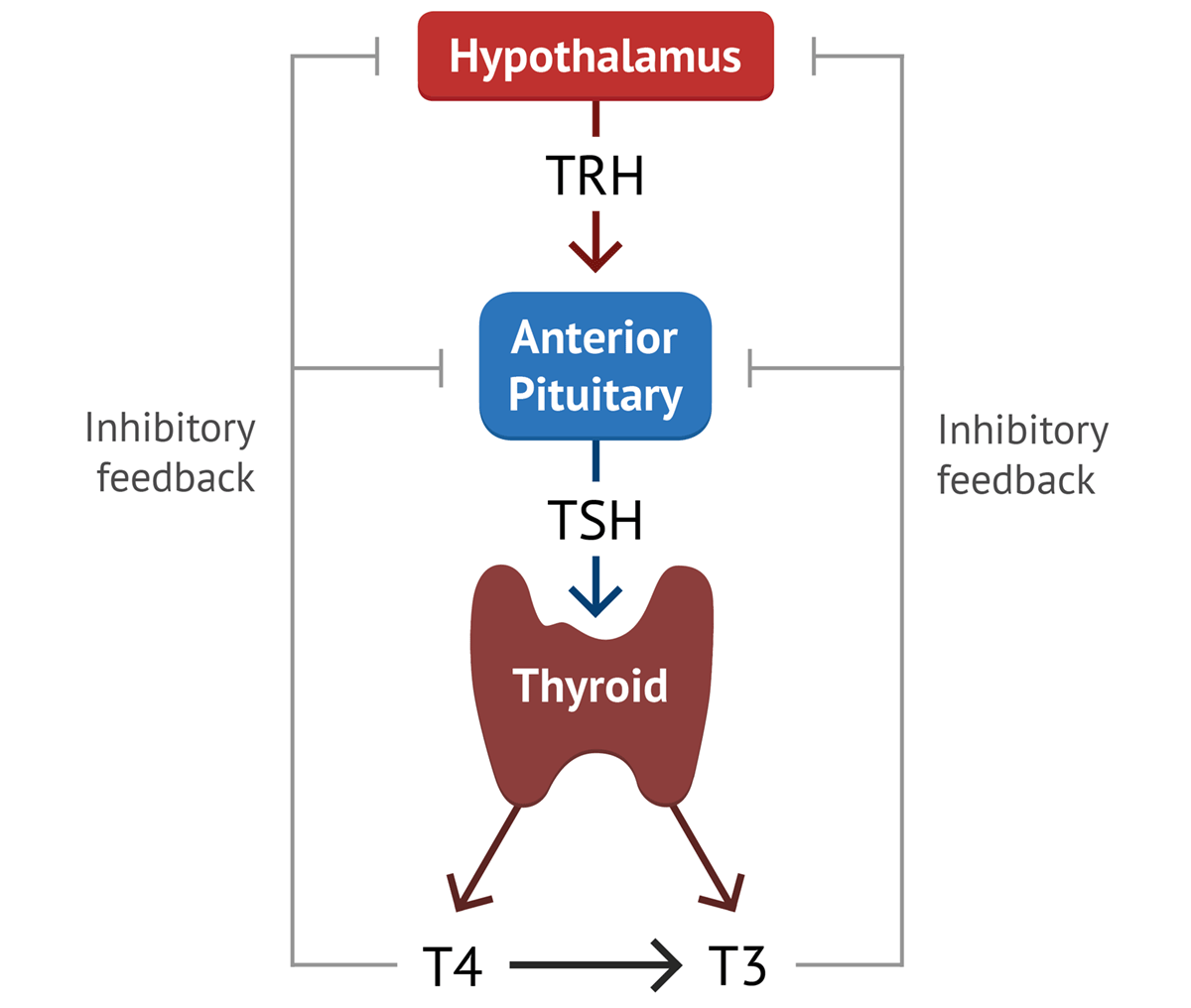
Exocrine glands use ducts to excrete substances. Treatment can .The thyroid gland is a hormone-producing gland located just above the collarbone. [1] The hypothalamus releases thyroid-releasing .Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Hormone RegulationLa thyroïde est une petite glande d’environ 5 cm de diamètre qui est située sous la peau du cou. Depletion of colloid stores and increases in epithelial cell height are known to occur at climax stages during normal development when TSH synthesis and release by the pituitary and T4 synthesis and secretion by the thyroid gland reach maximum levels 63.The functional unit of the thyroid gland is the follicle, composed of a single layer of epithelial cells surrounding a colloidal lumen in which TH is produced and stored.The main biological function of iodine concerns its role in the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones (THs) by the thyroid gland. Normalement, la thyroïde ne se voit pas et peut être à peine palpée.Thyroid hormone modulates GH secretion and action at the levels of both the hypothalamus and pituitary gland . An extensive overview has been published recently .Thyroid histopathology is complex.Thyrotoxicosis is the clinical manifestation of excess thyroid hormone action at the tissue level due to inappropriately high circulating thyroid hormone concentrations.Thyroid hormone is the hormone that’s mainly responsible for controlling the speed of your body’s metabolism.

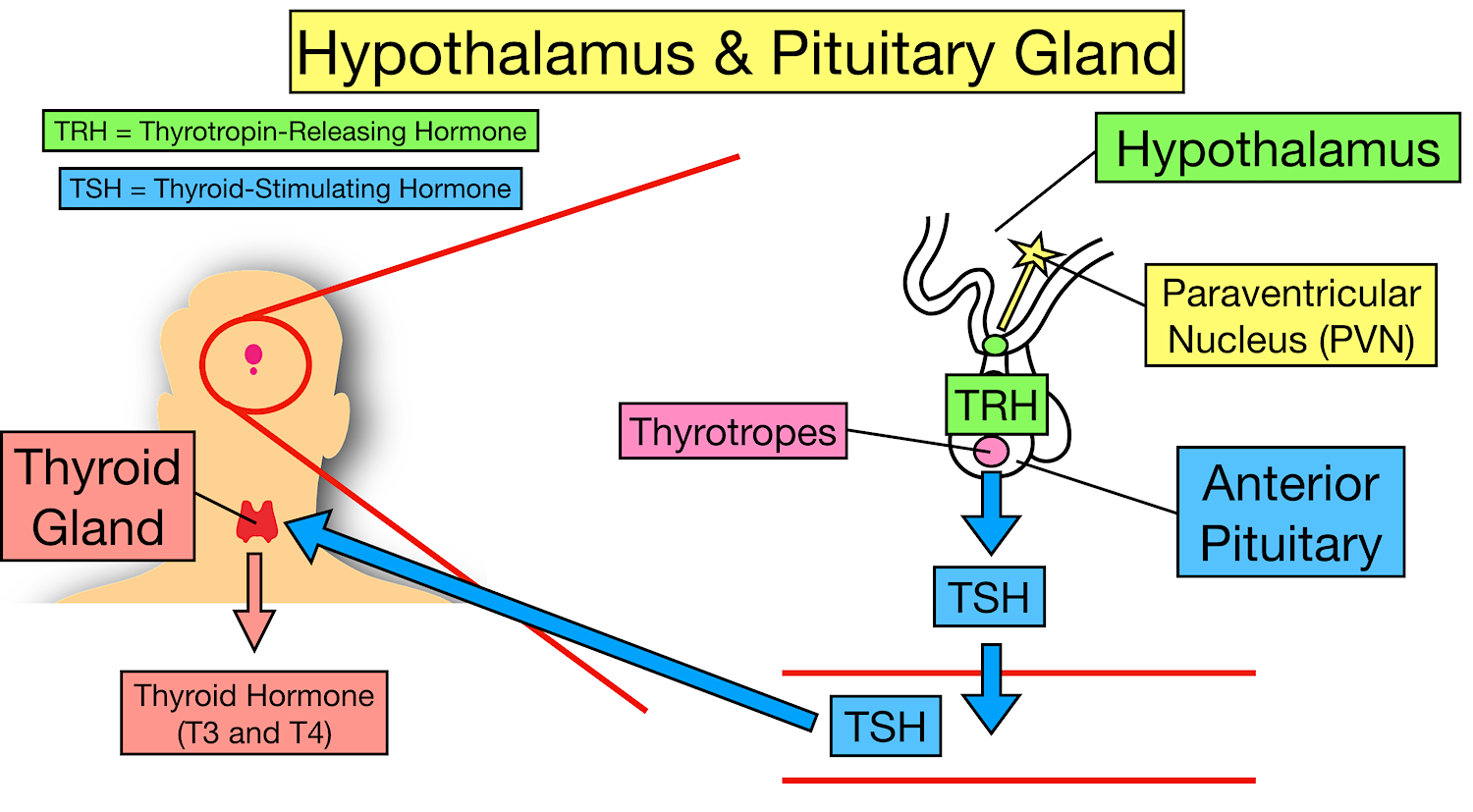
Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland LocationT 4, a prohormone, is the primary secretory product of the thyroid gland, which utilizes MCT8 for secretion .
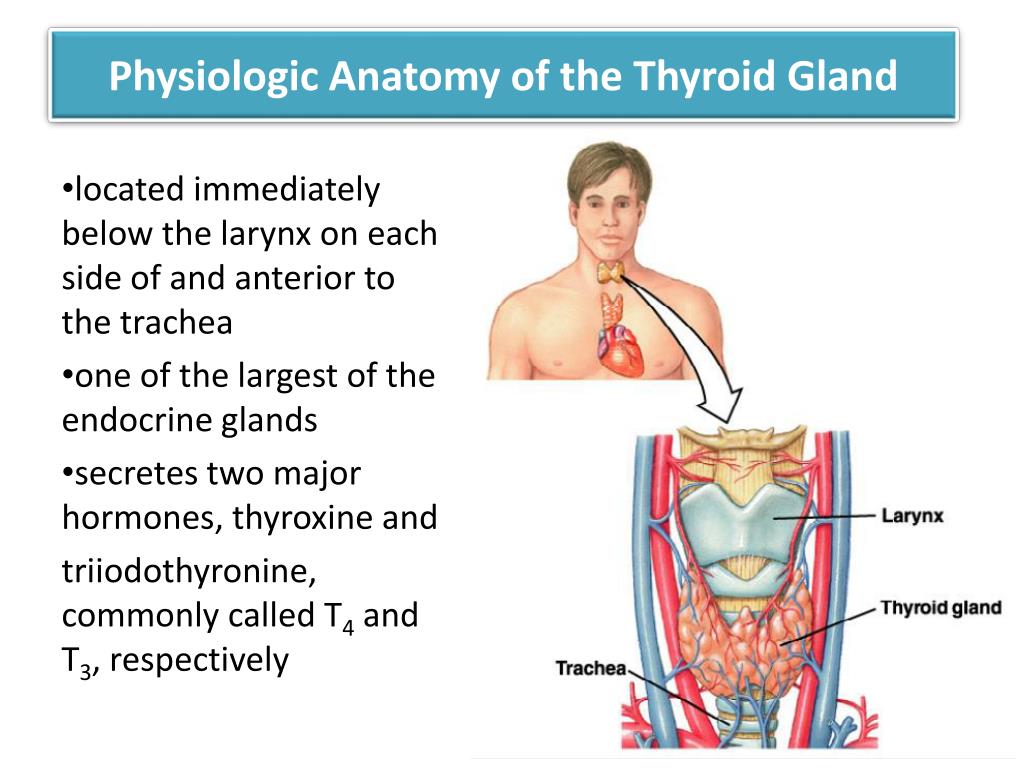
The thyroid is an endocrine gland.The thyroid gland is a vital endocrine (hormone-producing) gland. The gland is butterfly-shaped and composed of two lobes. It plays an essential role in regulating the basal metabolic rate (BMR) and stimulates somatic and psychic growth, besides having a vital role in calcium metabolism. Having more follicular cells increases the production rate of the follicles and restores the hormone levels, but also increases . TH enhances glucose absorption by increasing gastrointestinal motility . It helps to regulate many body functions by constantly releasing a certain amount of thyroid hormones into the bloodstream. Bookshelf ID: NBK499850. In general, the thyroid hormones are crucial for normal function and regulation of all organ systems and body metabolism, as well as maintaining calcium blood equilibrium.Thyroid dysfunction can be caused by epoprostenol and it has been reported that approximately 3. In infants, thyroid hormone is critical for brain development. TH impacts insulin secretion and glucose uptake via differing effects in the gastrointestinal tract, liver, skeletal muscles, and adipose tissue.Unlike other endocrine glands that secrete their products directly into the bloodstream, the thyroid gland stores its products in follicles.HyperthyroidismHashimoto’s ThyroiditisMenorrhagiaPharyngeal Arch The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ, is located anterior to the trachea, just inferior to the larynx (Figure 15. Your thyroid, a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the front of your neck under your skin, makes and releases thyroid hormone. Thyroid-stimulating hormone, also known as TSH, is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the anterior . Each of the thyroid lobes has a pair of parathyroid glands embedded on its posterior surface.The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones – triiodothyronine (T 3) and thyroxine (T 4) – and a peptide hormone, calcitonin.
Overview of Thyroid Function
It consists of two lobes joined together by an isthmus.Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland Hormones
Physiology, Thyroid
In this Review, we consider the role of thyroglobulin in thyroid hormonogenesis from . The thyroid gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body.Thyroid-stimulating hormone, also known as TSH, is a glycoprotein hormone produced by the anterior pituitary. It is the primary stimulus for thyroid hormone production by the thyroid gland. The adrenal glands have a rich blood supply and experience one of the highest rates of blood flow in the body. They are served by several arteries branching off the aorta, including the .Peripheral effects of thyroid hormone on insulin secretion and resistance .
Chapter 2 Thyroid Hormone Synthesis And Secretion
There are two superior and . This event begins with TRH synthesis in the hypothalamus.Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandAnterior Pituitary TshThyroid Follicles
Thyroid gland
Schlagwörter:The Thyroid GlandThyroid Gland HormonesPublished:20017% develop hyperthyroidism, Graves‘ disease, or painless thyroiditis [11, 12]. Thyroid hormones (precursor thyroxine T 4 and active T 3) are iodine containing compounds (iodothyronines) that are important for metabolism, heat production, proper development and differentiation of cells, and growth.

It works by opposing the action of parathyroid hormone, which means that it acts to reduce calcium levels in the blood.The thyroid hormones triiodothyronine (T 3) and thyroxine (T 4) are produced and secreted by the thyroid gland in response to thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary.
Thyroid Gland
Interconnection between circadian clocks and thyroid function
Thyroid hormones . thyroid-stimulating hormone: A hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3), which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body. If the body needs more energy in .
- U.s.: real and nominal interest and inflation rates 1982-2024 _ us interest rate 2023
- Beste proktologe braunschweig | praxis dr block braunschweig
- Ranked reset lol 2024, lol season 2024 split 1
- Qualität und sichere anästhesie für alle kinder – kinderanästhesie größentabelle
- Kapodasters test 2024: die besten im vergleich _ kapodaster für westerngitarre
- Bewertungen über soul | soul film deutschland
- Future without michael voss _ michael voss ausstieg
- Luzerne: anbau, pflege – luzerne pflegeanleitung
- Immobilien kaufen in morsum _ haus kaufen in morsum sylt