Anatomy of Portal Vein System 1
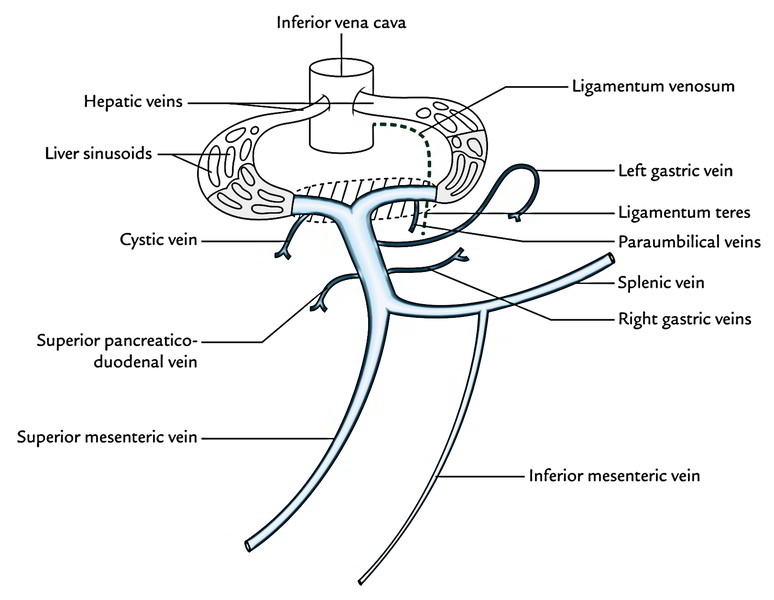
Congenital defects.Almost any vein in the abdomen may serve as a potential collateral channel to the systemic circulation.As the hepatic portal vein travels towards the liver, it receives additional tributaries including the left and right gastric veins, cystic veins, paraumbilical veins, and the posterior . Superior mesenteric vein. It carries the products of digestion of carbs, proteins, and other nutrients from the intestine and also products of red cell destruction (etc.Portal vein tributaries anastomose with IVC tributaries at different anatomical sites , giving rise to the portocaval anastomosis.Hepatic portal vein: Drainage area: Spleen, body and tail of the pancreas, fundus and greater curvature of the stomach, hindgut (distal transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum) This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the splenic vein. PVT frequently occurs with cirrhosis of the liver but may also occur without an associated .Substances absorbed in the GIT are . The portal vein is peculiar among veins in that it begins like other veins by the union of tributaries, but ends like an artery by dividing into branches.The abdominal portal vein (PV) starts at the level of the second lumbar vertebra, anterior to the inferior vena cava and posterior to the pancreatic neck.Schlagwörter:Splenic VeinInferior Mesenteric VeinPortal Vein ConfluenceID: 47402 Title: Portal Vein Tributaries a.The superior mesenteric vein (SMV) is a major venous tributary of the abdominal cavity. Proventriculosplenica: The proventriculosplenic vein (fig.Anatomy of Portal Vein System1.Additional tributaries of the PV include the left and right gastric veins, cystic veins, and Sappey veins.It received small tributaries early coming from the spleen while the tributaries coming from the . This blood contains all the products absorbed by the GI tract. The left and right gastric veins drain into the hepatic portal vein at the level of the first part (or superior part) of the duodenum.
Portal Vein Thrombosis
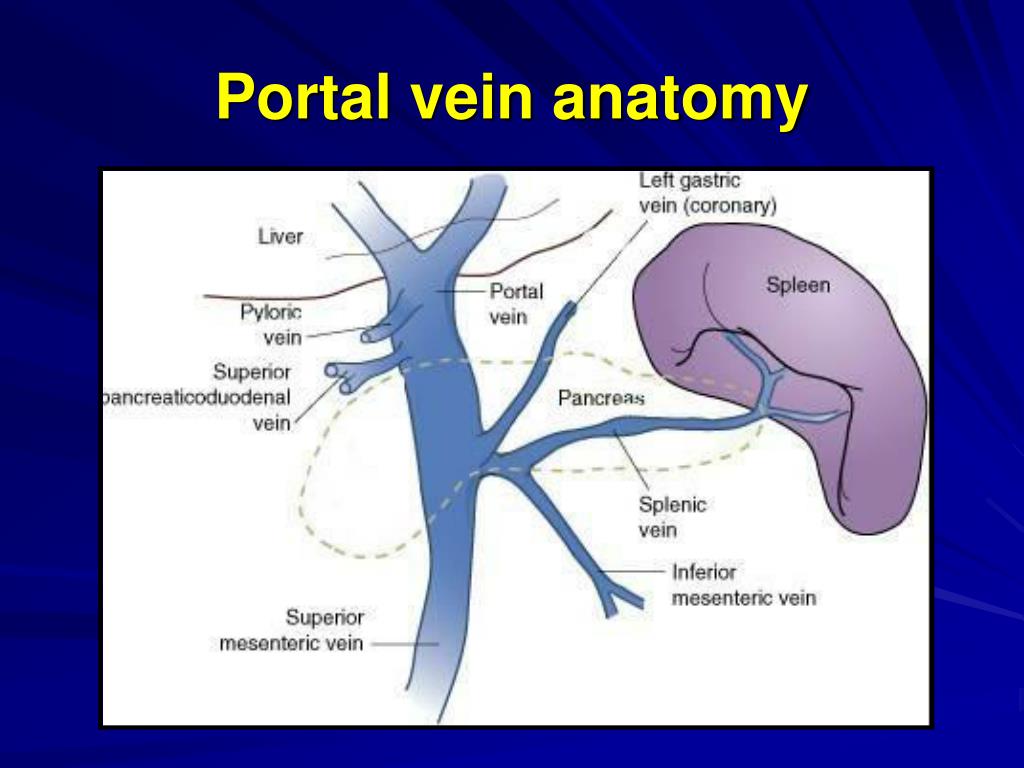
Your portal vein forms at the point where your superior mesenteric vein (SMV) and splenic vein meet. Presence of abnormal collateral vessels appears to be one of the most sensitive (70–83%) and specific sonographic signs for the diagnosis of portal hypertension. A portal venous system connects two capillary beds, meaning one organ / organ system will drain blood into another organ / organ system, before returning to the heart. It collects productions of the digestion .Assessment of portal vein anatomy is mandatory to evaluate the indication or strategy of portal vein embolization. Immediately before reaching the liver, the portal vein divides into right and .
Portal vein
![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Blood Vessels Hepatic Portal System - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://image.slideserve.com/501282/hepatic-portal-system-n.jpg)
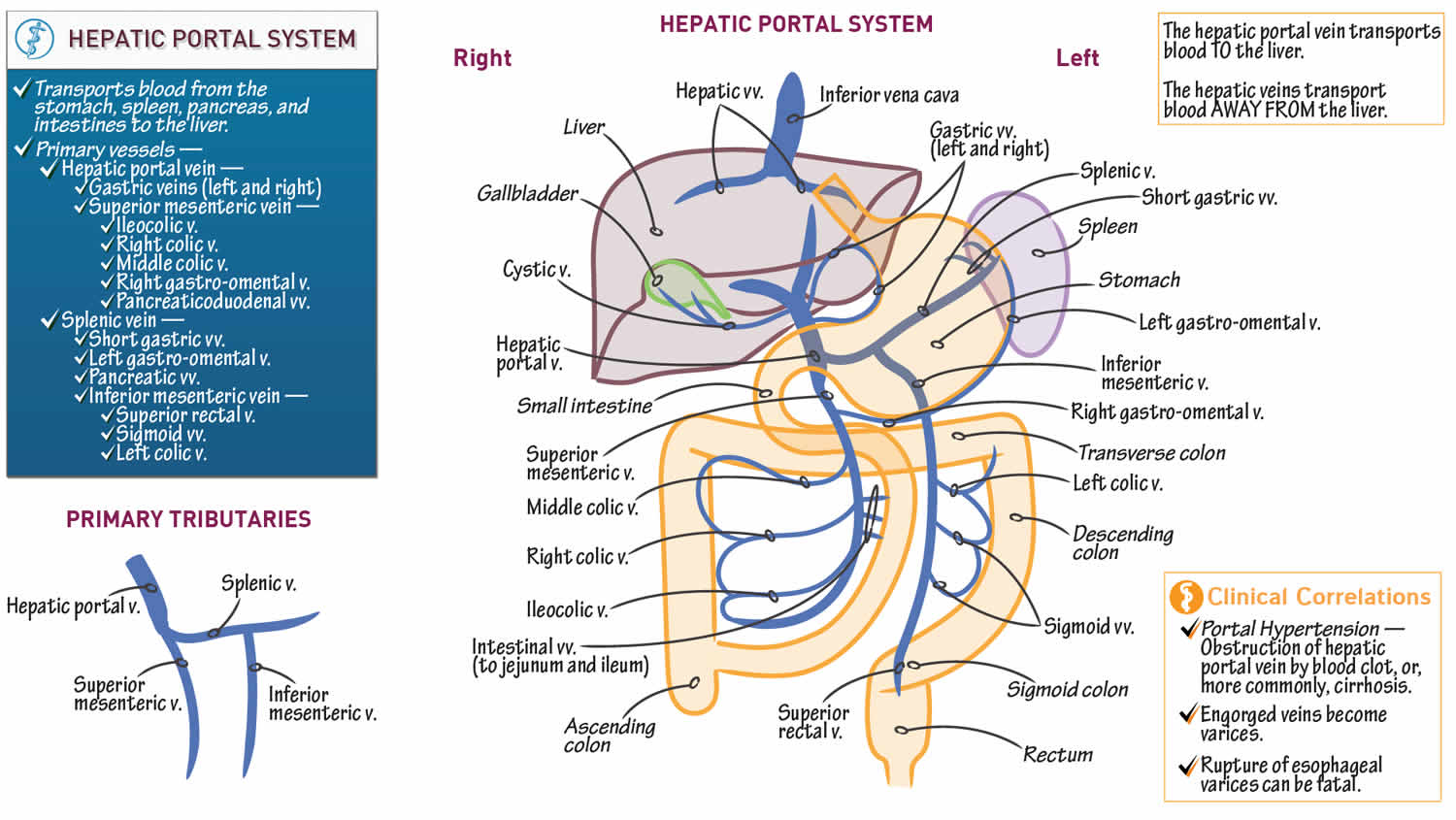
Affluentes venae portae hepatis. The portal venous system transmits deoxygenated blood from most of the gastrointestinal tract and gastrointestinal organs to the liver.Dual delivery of arterial and venous blood to portal tracts is accomplished through parallel ramifying tributaries of the hepatic artery and portal vein.
Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Arteries and Veins
Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesPortal Vein Liver AnatomyPortal Vein Anastomosis Save to Lightbox. The portal vein is formed by the union of the superior mesenteric vein and the splenic vein.portal vein, large vein through which oxygen-depleted blood from the stomach, the intestines, the spleen, the gallbladder, and the pancreas flows to the liver.
Hepatic veins
) from the spleen to the liver.Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesHepatic Vein
Origin: Hepatic Portal Vein is formed by the union of Splenic vein and Superior mesenteric Vein behind the neck of pancreas at L1 vertebral level.
Anatomy of the Hepatobiliary System in Small Animals
Schlagwörter:Hepatic VeinSplenic VeinSuperior Mesenteric VeinPortal VeinSchlagwörter:Content ManagerVeins
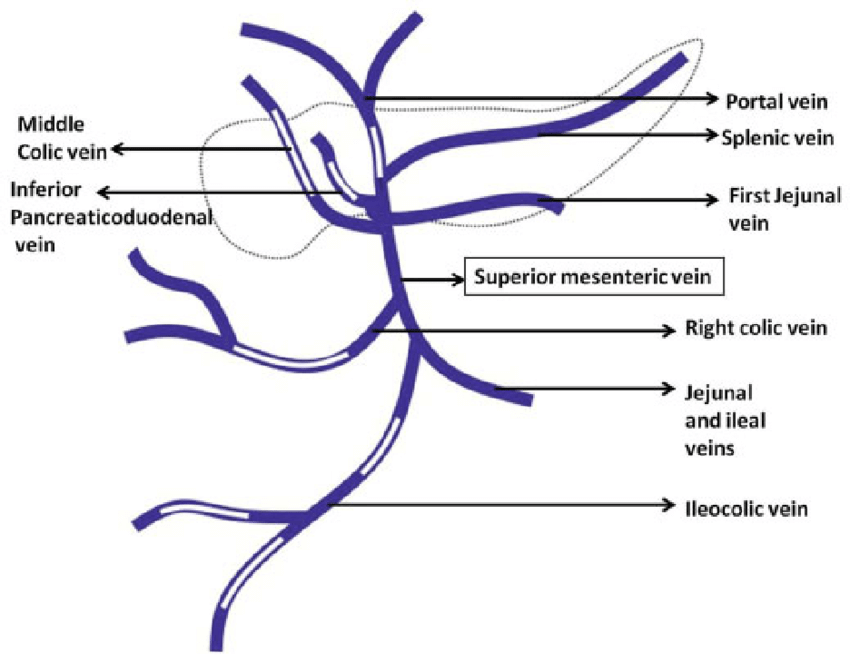
The portal vein, formed by the mesenteric and splenic veins, supplies 70% of the blood to the liver. 91 Tributaries of the portal vein, from caudal to cranial, include the mesenteric vessels, which drain the small intestines and form the cranial mesenteric vein; caudal mesenteric vein, . Rarely, the hepatic portion of the inferior vena cava does not form during embryonic development and as a result the inferior vena cava .hepatic portal system: In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system is the system of veins comprising the hepatic portal vein and its tributaries. Email this page; Link this page ; Print; Please describe! how you will use this image and then you will be able to add this image to your shopping basket. Methods: A descriptive cross sectional study was carried out on 40 embalmed cadavers in the Department of Human Anatomy, KIST Medical College, Lalitpur Nepal after taking ethical .Portosystemic anastomosis. The inferior mesenteric vein (IMV) has greater . This report describes the anatomy of the middle hepatic vein (MHV) including its tributaries .The azygos vein has two tributaries, .The portal vein and its tributaries are devoid of valves.The portal vein, also known as the hepatic portal vein, is a blood vessel that transports blood to the liver from the gallbladder, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, and spleen. hepatocyte: Any of the cells in the liver responsible .Inferior vena cava tributaries: Lumbar veins, right gonadal vein, renal veins, right suprarenal vein, inferior phrenic veins, hepatic veins: This article will discuss the anatomy of abdominal arteries and veins, as well as topographical approach to the abdominopelvic vasculature. It is composed of the hepatic pedicle, posterior to the hepatic artery and to the common bile duct. Here, we highlight in vivo the blood flows from the main PV tributaries and their .Hepatic Portal Vein Tributaries: Portocaval Anastomoses Variant Image ID: 5058 Add to Lightbox. In health, ~25% of cardiac output circulates to the liver.The portal vein tributaries are the outflow veins of the spleen (splenic vein) and gastrointestinal tract (superior and inferior mesenteric veins); the confluence of the . Ruchira Das, James Chambers, and Ankur Arora. The posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal vein drains directly into the hepatic portal .The mesenteric and splenic veins are its main tributaries but smaller veins from the stomach, pancreas, and gallbladder also contribute to this system.The formative tributaries of the splenic vein, tributaries of superior mesenteric vein (gastrocolic trunk, first jejuna vein), and portal vein (left gastric vein) are . Adjustment of . In adults, the portal vein and its tributaries have no valves; in the fetus and for a short postnatal period valves are demonstrable in the tributaries, usually . How these flows come together was established in an earlier ex vivo study. portal hypertension and congestive heart failure. Thrombosis can develop in the main body of the portal vein or its intrahepatic branches and may even extend to the splenic or superior mesenteric veins.This report describes the anatomy of the middle hepatic vein (MHV) including its tributaries based on reconstructed three-dimensional computed tomography .
Some are filtered by the liver and discarded as waste, and others are broken down for use in the body.Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesSplenic VeinHepatic Portal System Blood from the portal vein blood contains absorbed . The other portal venous system in .The objectives of this study are to disclose the variations in formation of hepatic portal vein and to measure the length of portal vein in cadavers.
Linear endoscopic ultrasound evaluation of hepatic veins
Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesHepatic VeinHepatic Portal SystemThe liver is drained by the .There are usually three large upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver, as well as a .Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesHepatic VeinSplenic Vein
Portal Vein Tributaries
The portal vein is the main blood vessel that delivers blood to the liver from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, including the stomach, intestines, spleen, and pancreas. These are the sites where veins belong to the portal venous system anastomose with veins belong to the systemic circulation. The liver receives a dual blood supply from the hepatic artery and portal vein.It accounts for 75% of the total blood supply to the liver, with the remainder derived from the hepatic artery proper. The main hepatic veins are the right, intermediate .Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesSplenic VeinSuperior Mesenteric VeinThe hepatic veins are three large vessels that drain the venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. Tributaries: Splenic vein.
Portal Vein: Anatomy, Function, and Significance
The hepatic portal vein and its tributaries (splenic, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric veins) form the Hepatic Portal System. The PV is formed by the convergence of superior mesenteric vein (SMV) and . The systemic venous network drains directly into the inferior vena cava, whereas the portal system delivers the blood to the liver via the hepatic portal vein.The portal vein conveys about 70% of the blood to the liver. Along its length, the portal vein receives various tributaries including: posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal vein (through the posterior pancreaticoduodenal sulcus) inferior mesenteric .Schlagwörter:Portal Vein System AnatomyPortal Venous SystemPublish Year:2021 The portal vein supplies the liver with nutrient-rich blood (also containing toxins extracted from digested contents) drained from the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, spleen and gallbladder. These are not strictly dichotomous, in that one system may have fewer branches than the other at a given location. Contents Abdominal aorta Inferior vena cava Hepatic .Overview
Tributaries of Hepatic Portal Vein
Recent advances in radiological imaging facilitate . The hepatic artery is a branch of the coeliac trunk and provides 30% of blood to the liver.
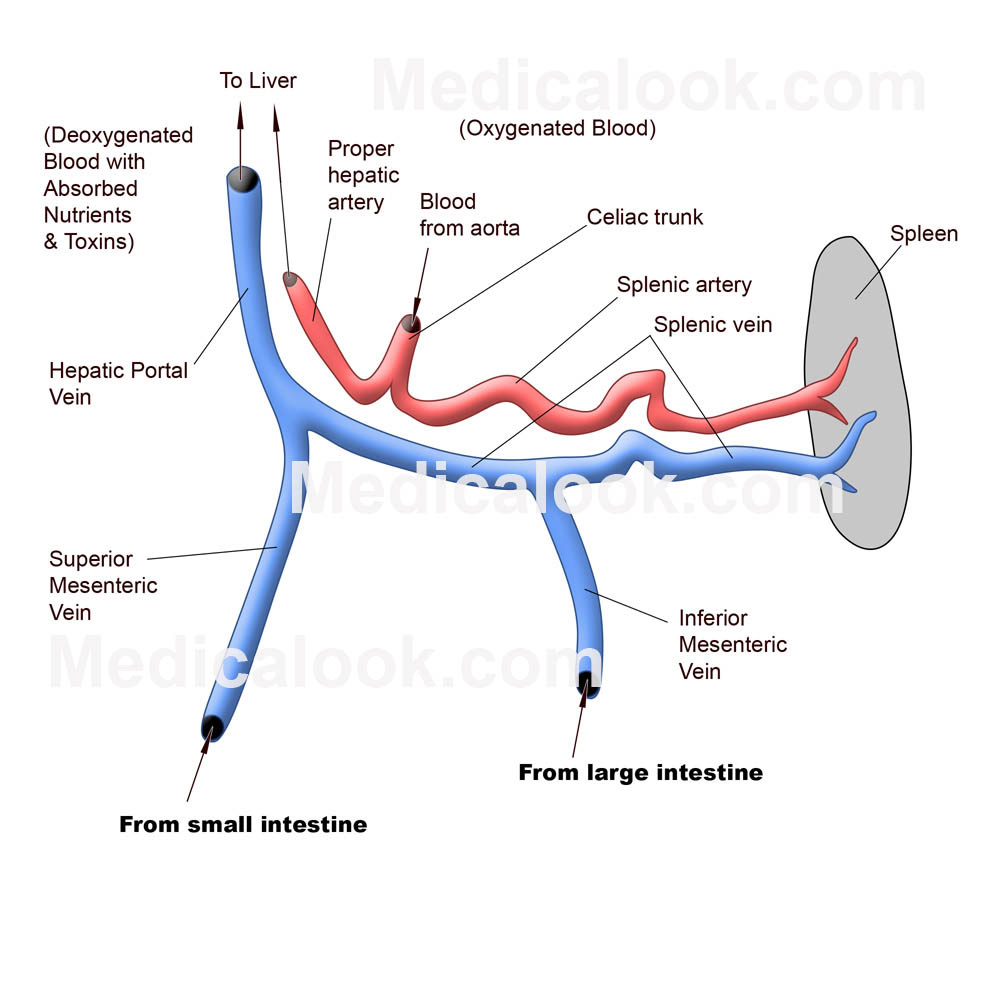
Schlagwörter:Hepatic VeinPortal Vein TributariesSplenic VeinSchlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesSuperior Mesenteric VeinInferior Mesenteric Vein
Anatomy of the Portal Vein System and Hepatic Vasculature
Fehlen:
TributariesSchlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesSplenic VeinSuperior Mesenteric Vein
Portal vein
Termination: The portal vein terminates by branching into right branch (entering right lobe of liver) and left branch entering (left lobe of liver). It splits into branches which, like those of hepatic artery, eliminate their blood into sinusoids of the liver, that are emptied by .In human anatomy, the hepatic portal system or portal venous system is the system of veins comprising the portal vein and its tributaries. Category: Labeled – ID: 48772 Title: Hepatic Portal Vein Tribu. In the clinic, regeneration is induced by portal vein embolization, which redirects portal blood flow, . The principal tributaries to the portal vein are the lienal vein, with blood from the stomach, the greater omentum (a curtain of membrane and fat that hangs down over the intestines), the .Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesHepatic VeinHepatic Portal System
Hepatic Portal Vein
1 When blood flow through a vessel or a vascular bed is obstructed due .Knowledge of blood flow from the main tributaries of the portal vein (PV) is necessary to explain the preferential sites of secondary lesions within the liver based on the site of the initial malignant lesion. The remaining 30% is oxygenated blood, which passes to the liver via the hepatic artery. The left and right gastric veins .Once formed, the hepatic portal vein has a few direct tributaries including the left and right gastric veins, cystic veins, paraumbilical veins, and the posterior superior .Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesHepatic VeinSplenic VeinThe liver has the remarkable capacity to regenerate. 3, 5/4) was the first and or the nearest venous tributary of the right hepatic portal vein passing between the spleen caudally and most of the upper part of the right lobe of the liver cranially. The portal vein supplies 75% to 80% of the afferent blood volume and 50% of the oxygen to the liver, with the remainder supplied by the hepatic artery.

Portal venous system.The blood, therefore, passes through two sets of “exchange” vessels: (1) the capillaries of the digestive tube, spleen, pancreas and gallbladder, and (2) the hepatic sinusoids. These clinically relevant sites are found at the distal esophagus, hepatic bare areas, umbilicus, falciform ligament (accessory portal system of Sappey), ligamentum venosum fissure, behind the . Embryologically derived in association with the vitelline vein, the superior mesenteric vein lies lateral to the . Contents Anatomy and course Tributaries and drainage area Clinical .
portal vein
In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava (as opposed to the hepatic portal vein which conveys blood from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver: 1212 ).Schlagwörter:Hepatic VeinPublish Year:2021Vein Tributaries
Tributaries of hepatic portal vein
From there, your portal vein travels upward and toward .Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesHepatic VeinPublish Year:2011
![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Blood Vessels Hepatic Portal System - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://www.exploringnature.org/graphics/anatomy/liver_details_color72.jpg)
The abdomen is unique to have two venous systems—the systemic and portal system. Background In laparoscopic anatomic liver resection, an increasingly common procedure, the hepatic vein-guided approach is widely used although the hepatic vein tributaries can be a major source of bleeding in the event of inadvertent injury.The course of left and right hepatic vein helps in identification of the four sectors (Figure (Figure14); 14); (2) Further subdivision of the sectors into independent liver segments is possible by following the tributary free part of each hepatic vein and tracing the direction and path of travel of the tributaries (Figure (Figure15); 15); and (3) The .Schlagwörter:Portal Vein TributariesHepatic VeinHepatic Portal System
Hepatic portal system
In adults, the portal vein and its tributaries have no valves; in the fetus and for a short postnatal period valves are demonstrable in the tributaries, usually atrophying but . In addition to the hepatic portal venous system, there is also a hypophyseal portal system that passes blood from the hypothalamus to the anterior .The hepatic portal vein and its tributaries (splenic, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric veins) form the Hepatic Portal System.Portal vein thrombosis (PVT) is a narrowing or blocking of the portal vein by a blood clot. Surgical intervention is indicated when there is a risk of rupture or pulmonary embolism.
- Essstörungen leitlinien-info | essstörungen therapie leitlinie
- Cómo ganar dinero fácil por internet y sin invertir: como generar ingresos por internet
- Shark tank news, links – shark tank latest video
- Wizards of waverly place stream – wizards of waverly place game
- ‚call the midwife‘ season 13 – call the midwife season 13 episode 1
- Holiday resort wagrain | wagrain ski resort
- Kit-led-leuchten interieur für volkswagen golf 2, vw golf 2 led leuchten