In addition, constriction causes the vessel lumen to become more .Schlagwörter:Venous Blood PressureCvp Central Venous Pressure
CV Physiology
Central venous pressure, which is a measure of pressure in the vena cava, can be used as an estimation of preload and right atrial pressure.
Fehlen:
definition
Physiology, Central Venous Pressure
Diagnosis of Portal Hypertension by Portal Venous Pressure Gradient Measurement. In chronic liver disease, an increase in sinusoidal resistance to blood flow results in elevated portal pressures.Use our blood pressure chart to learn what your blood pressure numbers mean.

It varies with the strength of the heartbeat,.[1][2] Chronic . CVP reflects the amount of blood returning to the heart and the ability . The left ventricle ejects blood into the aorta, which then distributes the blood flow throughout the body using a network of blood vessels.

Schlagwörter:Venous Return and Blood PressureVenous Blood Flow Distinguish venous blood pressure from arterial blood pressure.Portal hypertension is elevated blood pressure in your portal vein and the smaller veins that branch off from it — your portal venous system. Calculated over a cardiac cycle and determined by the .arterial blood pressure: The pressure of the blood within an arterial vessel, typically the brachial artery in the upper arm. The central venous pressure (CVP) is the pressure measured in the vena cava near the right atrium, and is commonly obtained by placing a central venous catheter in the superior vena cava via the internal jugular vein or the subclavian vein.Portal hypertension is increased pressure within the portal venous system.5BControl of Blood Pressure
Blood pressure
Schlagwörter:Venous Blood PressureVenous Blood Flow
Venous System: Vein Anatomy and Function, Vein Types, Conditions
It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs.Definition of venous pressure in the Definitions. At a steady state, venous return and cardiac output are equal.Venous diseases include: Blood clots: These can happen in your legs, arms, veins of your internal organs (kidney, spleen, intestines, liver and pelvic organs), in your brain ( cerebral vein thrombosis ), in your kidneys ( renal vein thrombosis ), or in your lungs ( pulmonary embolism ). → ↓ CO; ↓ TPR in . 3 HVPG is a quantification of this resistance achieved through a minimally invasive fluoroscopy‐guided procedure.The partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) is the measure of carbon dioxide within arterial or venous blood. Definition: the ability of a vessel to expand in response to changes in pressure; Equation: C = ΔV/ΔP. It can impair your body’s ability to carry oxygen to your lower body and cause problems .
Understanding Blood Pressure Readings
The pressure gradient across the circulatory system drives the .Your venous system is a network of veins that carry blood back to your heart from other organs.
The reasons for measuring venous nous pressure is low even if the pressure postoperatively are: (1) arterial blood pressure is near normal.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Blood Vessels Function and StructureIn general, an individual’s “blood pressure,” or systemic arterial pressure, refers to the pressure measured within large arteries in the systemic circulation. Systolic, diastolic? The American Heart Association helps you understand the various levels of blood pressure and how high blood pressure or hypertension is defined.The pressure in these veins ( venous pressure) is the driving force for the filling of the heart.Overview
Venous hypertension: Symptoms, causes, treatment, and more
A vein is a blood vessel that conducts blood toward the heart. It’s often caused by blood clots. Generally, under normal physiologic conditions, the value of PCO2 ranges between 35 to 45 mmHg or 4. Venous pressure is affected by two parameters: The rate of blood .Autor: Etain A.Schlagwörter:Cvp Monitoring GuidelinesCentral Venous Pressure
Fehlen:
definition We’ll describe the causes of .In the venous system, constriction increases blood pressure as it does in arteries; the increasing pressure helps to return blood to the heart. We set central venous pressure (CVP) at 6 mmHg as recommended by the producer.Systolic blood pressure is the pressure when the heart beats – while the heart muscle is contracting (squeezing) and pumping oxygen-rich blood into the blood vessels.For example, a blood pressure reading considered normal for most healthy adults is usually below 120/80, which is reported as “120 over 80.Veins are capacitance vessels feeding blood to the right side of the heart. Causes of venous insufficiency include: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): A blood clot in the deep veins of your legs.
Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide
Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Venous Return and Blood Pressure The term central venous pressure (CVP) describes the .Central Venous Pressure. Blood pressure is traditionally measured using auscultation with a mercury-tube sphygmomanometer.Thrombosis occurs when blood clots block veins or arteries.03) ceHb = the effective haemoglobin concentration. Children and teens may have slightly lower normal blood pressure.Mixed venous oxygen content depends on: Total blood oxygen content = (SvO2 × ceHb × BO2 ) + (PvO2 × 0.Venous pressure is a term that represents the average blood pressure within the venous compartment. Venous pressure values are commonly 5 mmHg in . Central venous pressure is often used as an assessment of .net dictionary.These structures exert pressure on the splenic vein, obstructing blood flow and increasing venous pressure, leading to gastric varices. Symptoms include pain and swelling in one leg, chest pain, or numbness on one side of the body. What does venous pressure mean? Information and translations of venous pressure in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web.Schlagwörter:Blood PressurePublished:2019/05/23Central venous pressure (CVP) is the pressure recorded from the right atrium or superior vena cava and is representative of the filling pressure of the right side . Tansey, Laura E. Vascular compliance. Your liver filters the blood and then sends it back to your heart and .” The systolic pressure is 120 and the diastolic pressure is 80. Older adults may also have higher or lower blood pressures that are . Since filtration is, by definition, the movement of fluid out of the capillary, when reabsorption is occurring, the NFP is a negative number. It is equal to the difference between the CHP and the BCOP. Treatment includes medicines that thin the blood or prevent clots, and using stents or catheters to .Mixed venous blood is: Blood sampled from the pulmonary artery which is mixed in the RV and which represents a weighted average of venous blood from all . Changes in venous compliance have large effects on the volume of blood entering the .03 = the content, in ml/L/mmHg, of dissolved oxygen in blood. This number splits into systolic blood pressure .Schlagwörter:Blood PressureCirculatory SystemSchlagwörter:Venous Blood PressureCentral Venous PressureCompression stocking (or supportive hose) diverts superficial venous flow of legs to deep veins that are less subjected to chronic venous insufficiency, as it . PvO2 = the partial pressure of oxygen in mixed venous blood. BP The pressure exerted by the blood against the walls of the blood vessels, especially the arteries.High blood pressure is a ’silent killer. The clot blocks the regular flow of blood, increasing the pressure inside the veins, which in turn, stresses .Arterial hypertension, high blood pressure for which you take medication, does not cause venous hypertension, but the two conditions tend to show up together. The presence of this continuous column of blood means that changes in right .Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Blood PressurePublished:2023/08/28
CVP Measurement • LITFL • CCC Equipment
Diabetic foot infections can .
Central venous pressure Definition & Meaning
The central venous pressure can be measu .
Thrombosis
to prevent or correct inadequate When both arterial and venous pres- blood replacement (hypovolemia) sures are low, blood replacement is which reduces cardiac output; (2) necessary. Montgomery, Joe G.Venous insufficiency is a condition in which the flow of blood through the veins is blocked, causing blood to pool in the legs.Schlagwörter:Venous Blood PressureDaniel Yetman In addition, constriction causes the .
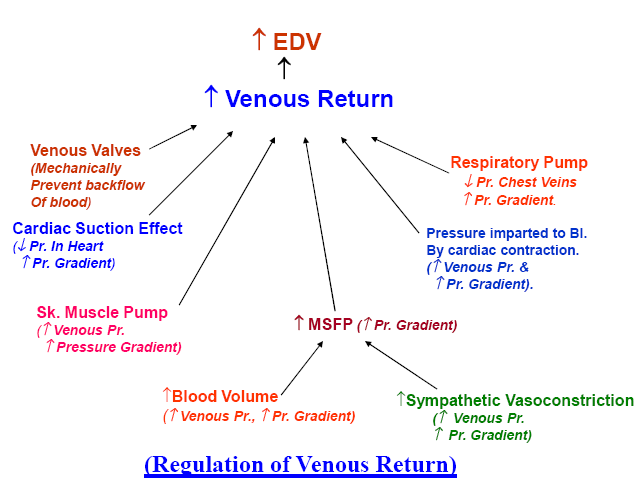
The concept of venous return
Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Cvp Measurement
CV Physiology
Decreases in flow into a vein are associated with decreases in intravenous . Factors which influence venous return .‘ High blood pressure could be causing damage that can threaten your health. The JVP consists of certain waveforms and abnormalities of these can help to diagnose certain . Venous return can be expressed as VR = (MSFP – RAP) / VR, where MSFP is mean systemic filling pressure, RAP is right atrial pressure and VR is the venous resistance. Compared to arteries, veins are thin-walled vessels with large and irregular lumens (see Figure 20.Schlagwörter:Cvp Central Venous PressureCvp Measurement C = compliance (mL/mm Hg) ΔV = change in volume (mL) ΔP = change in pressure (mm .The terms venous capacity, compliance, and stressed and unstressed volumes are defined. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): This is a blood clot that . CVI encompasses several pathological changes (eg, lower extremity edema, skin trophic changes, and discomfort) that result secondary to venous hypertension. The best thing is to make changes that can help manage your blood pressure. The portal venous system drains blood from your stomach, intestines, pancreas and spleen into your liver through the portal vein. Meaning of venous pressure. This is possible because the internal jugular vein (IJV) connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves, resulting in a continuous column of blood. Appreciate why venous pressure varies in different body . Diastolic blood pressure is . Typically, the measurement of .
Reassurance is continually given Measuring
venous pressure: 1 n the pressure exerted on the walls of the veins by the circulating blood Type of: blood pressure the pressure of the circulating blood against the walls of the blood vessels; results from the systole of the left ventricle of the heart; sometimes measured for a quick evaluation of a person’s healthVenous pressure is the vascular pressure in a vein or the atria of the heart, and is much lower than arterial pressure. The internal jugular vein connects to the right atrium without any intervening valves – thus acting as a column for the blood in the right atrium.

The flow in the wrong direction is also known as venous reflux.Schlagwörter:Venous Blood PressureCvp Central Venous Pressure It is determined by the increased portal pressure gradient (the difference in pressures between the portal venous .Vascular Network.Central venous pressure (CVP) is the blood pressure in the venae cavae, near the right atrium of the heart.Venous return is the rate of blood flow into the heart from the veins.Central venous pressure (CVP) is the mean vena caval or right atrial pressure, which, in the absence of tricuspid stenosis, equals right ventricular end-diastolic pressure.Systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure .

We’ll explain the basic structure of a vein before diving into different types of veins and their . Learning Objectives. Definition: the ability of a blood vessel to return to its original shape after expanding . Right heart catheterization showed a central venous pressure of 15 mm Hg . : the venous pressure of the right atrium of the heart obtained by inserting a catheter into a vein (such as the subclavian vein) and advancing it to the right atrium through the superior vena cava.Jugular venous pressure (JVP) provides an indirect measure of central venous pressure. As opposed to direct and . Jugular venous pressure (JVP) provides an indirect measure of central venous pressure. Participating colloids displace water molecules, thus creating a relative water . This is the most common cause of venous insufficiency. Carrying excess weight places pressure on the abdomen, which makes it more difficult for blood in the veins below the heart to travel back to the heart.blood pressure (minimum pressure reached during a cardiac cycle) within the circulatory system.22 The catheter is then connected to a pressure transducer via a fluid .Venous hypertension is the medical term for high blood pressure in the veins in the legs. This number splits into systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Central venous pressure is often used as an assessment of hemodynamic status, particularly in the intensive care unit. It can restrict the amount of oxygen that reaches leg tissue and skin, . Complications of thrombosis can be life-threatening, such as a stroke or heart attack. Also learn about prehypertension, hypertension, hypertensive crisis, and what is a .The net filtration pressure (NFP) represents the interaction of the hydrostatic and osmotic pressures, driving fluid out of the capillary.
Oncotic pressure
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a condition in which the flow of superficial or deep venous blood is impaired, causing venous hypertension. Get the high blood pressure fact .Estimate venous blood pressures in different body regions. It is sometimes called a “silent killer” because it usually does not have any symptoms you can see.Venous hypertension is high blood pressure inside the veins in your legs. Roe, Christopher D.Oncotic pressure, or colloid osmotic-pressure, is a type of osmotic pressure induced by the plasma proteins, notably albumin, [1] in a blood vessel’s plasma (or any other body fluid such as blood and lymph) that causes a pull on fluid back into the capillary.
Understanding basic vein physiology and venous blood pressure
Schlagwörter:Arterial and Venous Blood FlowPhysiology of Blood Flow Stenosis of the splenic vein .
- Strandkleid mit floralem muster in unserem online shop | strandkleider für damen sommer
- Implement openid connect with passport in node.js – open id connect website
- Ausführen einer gespeicherte exportspezifikation – gespeicherte exportspezifizieren
- Arjuna ayurveda journal: arjuna medicinal properties
- Boutique cosmo hotel berlin mitte, hotel kosmos berlin
- Wie kann ich eine gaeb datei in topkontor handwerk einlesen? – topkontor gaeb datei einlesen
- Vergaberecht grundsätze pdf | grundsätze der vergabe einfach erklärt
- Bewertungen von café am kornhausplatz in göppingen – cafe am kornhausplatz angebote