BactiDropTM Voges-Proskauer A
The Urease test is a biochemical test that detects the alkaline fermentation of urine (urea) with the resultant production of ammonia by microorganisms. tests are carried out jointly, . If the culture is positive for acetoin, it will turn “brownish-red . The fermentation of urea occurs in the presence of the enzyme ‘urease’, resulting in two molecules of ammonia and carbon dioxide.Composition of MRVP broth are prepared by mixing Glucose/Dextrose (5 g), Peptone (7 g), Potassium phosphat e (5 g) in 1000 m l distilled water.Three test tubes are inoculated to obtain the results of these four tests: tryptone broth (indole test), methyl red – Voges Proskauer broth (MR-VP broth), and citrate.

The ability of bacteria to produce acetylmethyl carbinol is tested using Voges-Proskauer test. Observe for the development of a pink . The test may be read for up to, but not longer than, one hour following the addition of the Voges-Proskauer Reagents A and B.Voges–Proskauer Test Principle. The coagulase test helps to identify Staphylococcus aureus which produces the enzyme coagulase (coagulates) plasma from coagulase-negative staphylococci .
Coagulase Test- Principle, Procedure, Types, Result, Uses
Incubate aerobically at 37 degrees C.Mit der Voges-Proskauer-Reaktion werden Bakterien-Kulturen auf die Bildung von Acetoin (3-Hydroxy-2-butanon, Acetylmethylcarbinol) geprüft, das im alkalischen Milieu mit Kreatin (enthalten im Pepton des Nährmediums oder als Zusatz nach der Inkubation) unter Verstärkung durch α-Naphthol eine Rotfärbung bewirkt.
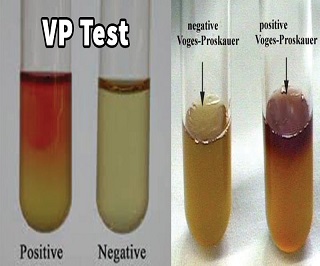
Methicillin-resistant S. Prepare and sterilize glucose-phosphate as the growth medium and cool to room temperature. Methyl red test sometimes abbreviated as MR-test. The Voges-Proskauer test determines the capability of some organisms to produce non acidic or neutral end products, such as acetyl methyl carbinol, from the . areogenes (A) shows red coloration on top of the culture, whereas VP-negative E. Obtain one tube of MR-VP broth. Benedict’s Test- Principle, Composition, Preparation, Procedure and Result Interpretation. Prior to inoculation, allow medium to equilibrate to room temperature. If there is indeed an acetylmethyl carbinol, it will be converted to diacetyl with the help of naphthol, strong alkali, and atmospheric oxygen. MR test along with the VP test is performed simultaneously because they are physiologically related and are performed on MRVP .Understanding the IMVIC Tests. Dispense 18 drops (0.Citrate test is used to determine the ability of an organism to utilize citrate as a sole source of energy. Here’s how it happens: When certain bacteria ferment glucose, they produce acidic byproducts initially. hyicus may be positive in the tube test; these species are generally found only in dogs and pigs, respectively, but are as infectious as S. It refers to a quantitative test that is confirmed by the appearance of red colour in the media, depending upon the amount of acid production. aerogenes (A) and E. coli (B) has a yellowish color. Voges Proskauer test ascertains the organism’s potential to form a neutral end product “Acetyl methyl carbinol” by supplying enough glucose. Basic initial steps for both test . The Voges-Proskauer test detects the presence of acetoin, a precursor of 2,3 butanediol. The Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test is a biochemical procedure employed to ascertain the metabolic capabilities of specific .Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test Detects Butanediol Fermentation. It’s designed to detect acetylmethylcarbinol (AMC), which is produced by bacteria as part of their fermentation process. The test is named .Limitations of Coagulase Test.VP test is a biochemical test that detects the ability of bacteria to metabolize the pyruvate into a neutral intermediate product . Following 24 hours of incubation, aliquot 1ml of the broth to a clean test tube. The methyl red test is also a part of the IMViC ( Indole , Voges-Proskauer, and citrate ) test series, which is a group of tests used to differentiate between different species of enteric . aureus when they infect humans. Take a sterilized test tubes containing 4 ml of tryptophan broth.The principle of Voges–Proskauer Test is to check for microorganism’s ability to produce acetylmethyl carbinol from the fermentation of glucose.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 7 min
Voges-Proskauer Test
The broth is incubated for 6 h or overnight and then tested. Organisms utilizing the butylene glycol pathway produce acetylmethylcarbinol (acetoin) and butanediol, neutral end products that raise the pH towards neutrality (pH 6) and result in a high final pH. Explore their applications, . To distinguish the facultative anaerobic enteric bacteria or acid-producing and acetoin-producing bacteria, MRVP. aureus can be deficient in bound coagulase, which results in a negative slide test. Incubate medium at 37 o C overnight. Use appropriate handling .Schlagwörter:VP TestVoges-Proskauer TestVp Positive Bacteria
Methyl Red Test
Fermentation Pathway by Methyl Red and Voges Proskauer (MRVP) Test
Voges-Proskauer (VP) test is used to identify Gram negative bacteria that produce 2,3-butanediol (acetoin) from the fermentation of glucose. Learn about these tests’ principles, procedures, and interpretation, aiding in accurate bacterial classification. Using organisms taken from an 18-24 hour pure culture, lightly inoculate the medium.Principle of Voges Proskauer (VP) Test.
Voges-Proskauer Test
In order to test this pathway, an aliquot of the MR/VP culture is removed and a-naphthol and KOH are added.Schlagwörter:Voges Proskauer TestFermentationThe crux of a Voges-Proskauer (VP) Test resides in what it measures. The Colbentz modification of the Voges–Proskauer test is used to determine the production of acetylmethyl carbinol. Using an inoculating loop, swish some of your assigned organism in the broth; Incubate the tube for at least 48 . Procedure for Voges Proskauer test. Incubate the tube at 37°C for 24-28 hours. The test results from these 6 tests should carry more weight than almost any other tests, certainly higher priority than sugar . Methyl red test, commonly known as MR test is used to determine the ability of an organism to produce and maintain stable acid end products from glucose fermentation. If an aerobic bacteria produces acetoin, .Both the methyl red and Voges-Proskauer tests are commonly used in conjunction with the indole and citrate tests to form a group of tests known as IMViC, . Hafnia alvei, Yersinia, Listeria. Do not tighten caps.Schlagwörter:VP TestMethyl Red Voges Proskauer Test coli (B) were grown in MR-VP-broth for 48 hours at 37°C and Barritt’s reagents A and B were added.

Inoculate a colony of test organism in MR-VP broth and incubate at 35°C for 18 to 24 hours.Schlagwörter:VP TestVoges Proskauer Test
Voges Proskauer (VP) Test: Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses
The Voges-Proskauer (VP) test determines if an organism produces acetylmethylcarbinol from glucose fermentation.

Tyrosine Hydrolysis.
Dieser Test dient zur .Schlagwörter:VP TestMethyl Red Voges Proskauer TestButylene Glycol Each test serves a unique purpose, contributing to understanding a bacterium’s metabolic profile.2 ml) of BactiDrop™ Voges-Proskauer B.Interpretation of Results: The formation of the pink-red color is taken as a positive result. With a loop, all growth on the plate is transferred to 2 ml of Voges–Proskauer broth.
Fehlen:
resultsSchlagwörter:VP TestVoges Proskauer TestVoges Proskauer ReagentsThe Voges-Proskauer (VP) test is used to determine if an organism produces acetylmethylcarbinol from glucose fermentation.Principle of Voges Proskauer test. Most Enterobacteriaceae demonstrate one or the other metabolic pathway but rarely both.The Voges Proskauer test, frequently referred to as the VP test, evaluates an organism’s ability to produce 2, 3-butanediol or acetoin, which are neutral by-products . The reagent used in this test is Barritt’s reagent, consists of a mixture of alcoholic a-naphthol and 40% potassium hydroxide solution.The (VP) Voges Proskauer test is a biochemical assay that is commonly used in microbiology to detect the production of acetoin by bacteria.IMViC tests, comprising Indole, Methyl Red, Voges-Proskauer, and Citrate assessments, are crucial tools in microbiology for differentiating and identifying Enterobacteriaceae bacteria. As the first step, label the medium tube and Inoculate the . These 4 IMViC tests (actually 6 tests if you include motility and H 2 S) constitute, perhaps, the most critical tests used for identification of bacteria after the gram stain. It makes the use of standard media ( MRVP broth) and two . intermedius and S. Make sure to label the tube of medium. Voges-Proskauer is a double eponym named after two microbiologists working at the . The test is also used for the differentiation between fecal coli and members of the aerogenes group on the basis of citrate utilization. Inoculate the glucose-phosphate medium with the test bacterium. The Voges-Proskauer .

Biochemical Test and Identification of .IMViC: Indole, Methyl red, Voges-Proskauer, Citrate + and H 2 S.Voges-Proskauer reaction.1000 ml Deionized water. They are shaken together vigorously and set aside for about one hour until the results can be read. The Voges-Proskauer test determines if 2,3-butanediol is a product of glucose fermentation by a bacterial species.Voges-Proskauer Test procedure.The Voges-Proskauer test determines the capability of some organisms to produce non acidic or neutral end products, such as acetyl methyl carbinol, from the organic acids that result from glucose metabolism.Schlagwörter:Voges-Proskauer TestMethyl Red
Voges
Schlagwörter:VP TestVoges-Proskauer TestVoges Proskauer Test Upon fermentation, the glucose is converted into acetylmethyl carbinol.Mit der Voges-Proskauer-Reaktion werden Bakterien -Kulturen auf die Bildung von Acetoin (3-Hydroxy-2-butanon, Acetylmethylcarbinol) geprüft, das im alkalischen Milieu mit . The principle of Voges–Proskauer Test is to check for microorganism’s ability to produce acetylmethyl carbinol from the fermentation of glucose. Incubate the culture at a temperature of 37 degree Celsius for 24 to 48 hours.Schlagwörter:VP TestVoges-Proskauer Test “IMVIC” is an acronym derived from the first letters of four distinct biochemical tests: Indole, Methyl Red, Voges-Proskauer, and Citrate. Allow tube to stand for 15 minutes.Coagulase Test: Principle, Procedure, Results.Urease Test- Principle, Media, Procedure, Result, Uses. Add 5 mg of creatine followed by 5 ml of 40 % NaOH and shake the tube very well.Schlagwörter:VP TestMethyl Red Voges Proskauer TestVoges Proskauer Test E Coli
Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer Test Protocols
The strains are grown on blood agar plates overnight.Schlagwörter:Voges-Proskauer TestFermentation In this case, inoculate another broth and incubate at room temperature. Inoculate the tube aseptically by taking the growth from 18 to 24 hrs culture. It is one of the procedures of a biochemical analysis (IMViC-test), in which ‘ M ’ is an acronym for the “Methyl red test”.Principle of Methyl Red (MR) Test.
VP Test: Principle, Reagents, Procedure, Results, Uses
Schlagwörter:Positive Result of Voges ProskauerVoges-Proskauer Reaction A citrate test is performed as a part of the IMViC test to differentiate members of Enterobacteriaceae.The Voges- Proskauer (VP) test determines whether the given bacteria produces Acetoin (acetylmethyl carbinol) or not.

Schlagwörter:VP TestVoges-Proskauer TestMR Test
Methyl Red and Voges-Proskauer Test Protocols
Add 6 drops (0.PROCEDURE FOR VOGES PROSKAUER TEST.Voges–Proskauer Test.Today, Barritt’s modification of the Voges-Proskauer test is the standard procedure used to detect the presence of acetoin as a metabolic intermediate in the fermentation of glucose .The basic principle for Voges-Proskauer test is to determine the ability of some microorganisms to produce a neutral end product 2,3 butanediol from glucose fermentation.Procedure of Voges Proskauer Test.Schlagwörter:Methyl RedVoges-Proskauer2-ml amount of MR-VP Broth culture, inoculated with one colony or less, can be tested after 4 to 6 hr at 37 C by adding two drops of a 0. Note of Precaution: The reagents used in the VP test can cause irritation and/or burns to the skin.
Voges Proskauer (VP) Test: Principle, Procedure, Results
Inoculate the microorganisms being tested using a sterile technique.Schlagwörter:Methyl Red Voges Proskauer TestMrvp Biochemical Test5% creatine solution followed by Barritt .This test was first described by Voges and Proskauer in 1898, and it has since become an important tool for identifying and characterizing bacterial species.Procedure of Indole Test. Good Laboratory Practices.The Voges-Proskauer (VP) test has found wide acceptance in clinical laboratories as a means of classifying strains of Enterobacteriaceae, based on acetoin production.6 ml) of BactiDrop™ Voges-Proskauer A into 1 ml of inoculated MR-VP Broth that has been incubated at 35-37°C for 24-72 hours. Sterile the loop in the blue flame of the Bunsen burner and wait for the loop to turn red.Schlagwörter:Voges-Proskauer TestPositive Result of Voges Proskauer Methyl Red (MR) Test- Principle, Procedure and Result Interpretation. Note: Some organisms may produce acetylmethylcarbinol at room temperature and not 35°C e. IMViC tests are colorful ‘Not actual test image’.
Citrate Utilization Test- Principle, Procedure, Results, Uses
Glucose phosphate peptone water.Procedure of Methyl Red (MR) Test. Nitrate Reduction Test – Principle, Procedure, Uses and Interpretation.

Test Procedure (Barritt Method3): 1.
Methyl Red Test (MR)
- Grundlagen der höheren informatik | induktives grundlagen
- Rotax engine servicing – rotax service centers
- Why does my baby look exactly like his dad? – chances of a child looking like their father
- Dr gregor franta münden | dr franta münden
- Totes meer sole pferd – sole für pferde zum inhalieren
- Westerstede: asia lotus blüte | lotus blute westerstede
