Stress-strain Diagram.This is the highest and least normal strain possible for an material at that specific point and shear-strain is zero at the angle where principal strain occurs. The change in length occurs as a result of stress applied to the work piece. dl = change of length (m, in) Axial Deformation. F is the shear force in N.Normal in normal strain does not mean common, or usual strain.Results We found 613 records in database search. After duplicates removal, we screened 246 records and finally included 18 papers.This shear strain calculator finds the strain due to shearing stresses in different situations (shear force or torque). The cross section of the rope is circular, and the weight of the light is pulling downward, . The quantity that describes this deformation is called strain. A shear strain results from shear stress.
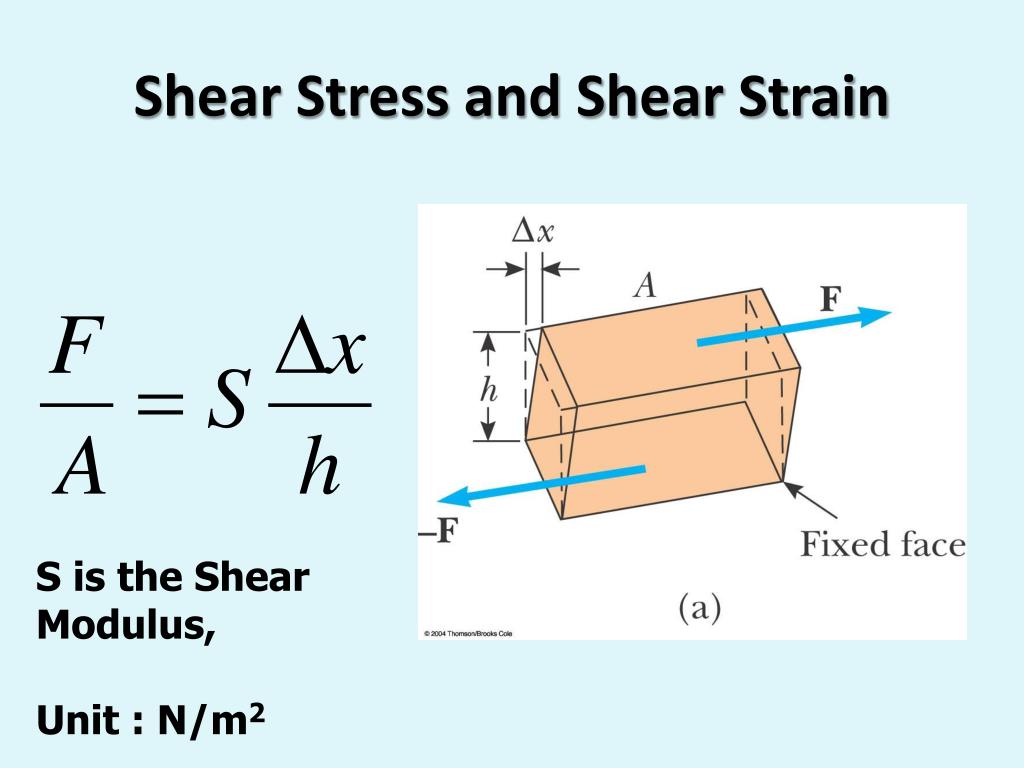
Normal strain occurs when the elongation of an object is in response to a normal stress (i.Schlagwörter:Normal Strain and Shear StrainShear Strain To Shear Stress When does a state of direct shear exist in a material? Single shear vs.In this chapter we construct relations for the normal and shear stress compo-nents at any point within the the beam’s cross-section. When a force acts parallel to the surface of an object, it exerts a shear stress.We want to derive equations for the normal strains x1 y1 and the shear strain γ associated with the x 1y axes, which are rotated counter-x1y1 1 clockwise through an angle θ from the xy axes.Define shear stress and shear strain. Shearing Deformation. It is simply \ [ \gamma_ {max} = \epsilon_ {max} – \epsilon_ {min} \] This applies in both 2-D and 3-D. The constant of . The average cohort sample size was 109 . Has the same Pa unit for shear stress. Simple Strain Stress-Strain Diagram Axial Deformation Shearing Deformation Poisson’s Ratio Statically Indeterminate Members Thermal Stress. But, the choice of coordinate system is arbitrary.In physics and continuum mechanics, deformation is the change in the shape or size of an object. perpendicular to a surface), and is denoted by the Greek letter epsilon. When a force acts perpendicular (or normal) to the surface of an object, it exerts a normal stress.Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainShear DeformationShear StressStress Strain
Lecture 3: Shear stress and strain
Small Strains
Statically Indeterminate Members.

At a certain point for each bone, the stress-strain relationship stops, representing the fracture point. Consider the change in length and orientation of the diagonal of a rectangular element in the xy plane after strains εx, εy, and γ xy are . Let’s consider a light fixture hanging from the ceiling by a rope. ted in the figure below.Shear stress is a fundamental concept in mechanics and materials science. It describes the change in length of the object in one .

The ratios of shear to normal stiffness, including the linear group k s /k n and the parallel bond group k s ′/k n ′, need to be determined from the normal and shear .
Shear Strain: 31 Facts You Should Know
Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainShear Strain To Shear Stress εT = ∫L L0 dL L = ln( L L0) = ln(1 +εN) (5. A is the cross-sectional area.Stress is of many types- Normal stress, shear stress and volumetric stress. Torsional stress due to frictional resistance between the nut and the bolt. It is quantified as the residual displacement of particles in a non-rigid body, from an initial configuration to a final configuration, excluding the body’s average translation and rotation (its rigid . where V is the resultant shearing force which passes through the . About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features NFL Sunday TicketAutor: Infinity Learn NEET2) ε T = ∫ L 0 L d L L = ln.edu
Mechanics of Materials: Strain
What is Normal strain and Shear Strain
The maximum shear always occurs in a coordinate system orientation that is rotated 45° from the principal coordinate system.
Shear Strain Calculator
The property of a fluid to resist the growth of shear deformation is called viscosity.Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainLuis Hoyos Shearing stress is also known as tangential stress. τ = V Av τ = V A v.Shear stress (often denoted by τ, Greek: tau) is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section.The stress tensor gives the normal and shear stresses acting on the faces of a cube (square in 2D) whose faces align with a particular coordinate system.
Strain
• It is very difficult to measure normal and shear stresses in a body, particularly stresses at a point.Similarly, the true strain can be written.Schlagwörter:Examples of The Strain TheoryStrain Theory Examples Today It differs to tensile and compressive stresses, which are caused by forces perpendicular to the area on which they act.An object or medium under stress becomes deformed. It is a pivotal idea to understand in terms of how forces act within solids, fluids, and structures.
Shear Strain: Definition, Formula, Diagram, Units, Examples
Hooke’s Law in Shear Analogous to the situation for normal strain, the ratio of shear stress to shear strain is constant within the linear range. 2 shows a plot of the stress-strain relationship for various human bones. There are two types of strain: normal strain .Strain is defined as deformation of a solid due to stress.Schlagwörter:Shear StressStress StrainSchlagwörter:Solid MechanicsMechanical and Structural EngineeringWall Shear Stress It is commonly defined as \ [ \epsilon = {\Delta L \over L_o} \] where the quantities are defined in the sketch.Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainSolid MechanicsShear Deformation
Strain
By plotting the normal and shear stresses on the circle, it becomes straightforward to identify the maximum principal stress and its corresponding orientation. (2021) Online Lecture Notes on Soil Mechanics, .Schlagwörter:Solid MechanicsCivil EngineeringEngineering LibreTexts What is strain? Strain is the ratio of change in length to the original length of the work piece. Shear stress occurs when a shear force is applied instead of a normal force: Note: V is the shear force applied. xy t yx t xz t zx t yz and t zy : . Normal strain – elongation or contraction of a line segment; Shear strain – change in angle between two line segments originally perpendicular; Normal strain and can be expressed as.In 2-D, the principal strain orientation, θP, can be computed by setting γ ′ xy = 0 in the above shear equation and solving for θ to get θP, the principal strain angle. It means a direct length-changing stretch (or compression) of an object.Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainNormal Strain and Shear Strain
Shear stress
1 Compatibility of Deformation We consider first the deformations and displacements of a .Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainNormal Strain and Shear [email protected] km/s cases, no well-defined structure of the sheared material exists, and the magnitude of the shear strain is considerably lower on average.Normal stresses promote crack formation and growth, while shear stresses underlie yield and plastic slip. From elementary mechanics of materials, the strains along the gage axes can be written as: .Schlagwörter:Solid MechanicsNormal Strain and Shear Strain
An Introduction to Stress and Strain
Shear strain is the measure of shear deformation caused due to shear stress. It has dimension of length with SI unit of metre (m).
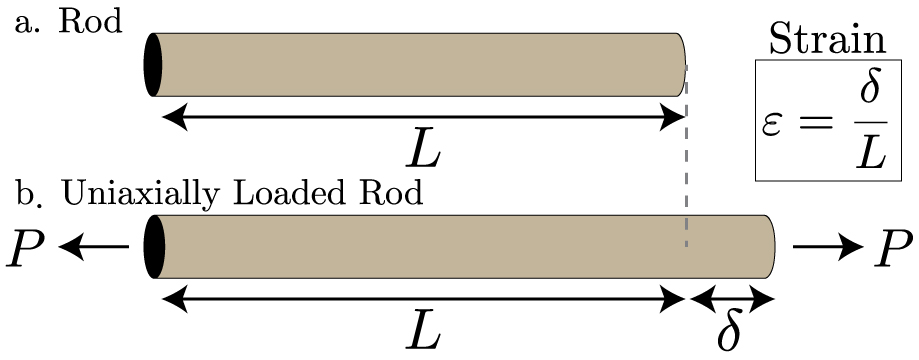
Strain is given as a fractional change in either length (under .Remember, these types of strain signify different deformation behaviours under applied forces, and understanding their unique properties will grant you a more . We are free to express the normal and shear stresses on any face we wish, not just faces aligned with a particular coordinate system. It is measured as the ratio . We will discuss about types of stresses in further section of this article.Strain is a fundamental concept in continuum and structural mechanics.Calculating the shear stress of a material can be simplified to the following formula: τ = F / A. Bending stress due to the bending of bolt. Stress is the force exerted per unit area and strain is the physical change that results in response to that force.Schlagwörter:Stress StrainStrain Engineering It means a direct length-changing stretch (or compression) of an object resulting from a normal stress. Learn about shear strain in engineering applications with our online tutorials.Shear strain is measured as the displacement of the surface that is in direct contact with the applied shear stress from its original position. This section is part of: Athanasopoulos, G.

Displacement elds and strains can be directly measured using gauge clips or the Digital Image Correlation .
Mechanical responses and fracturing behaviors of coal under
Principal Stress and Principal Strain: An Overview
This critical parameter quantifies the internal forces that arise when adjacent layers of a material or fluid slide or deform relative to each other. The transformation matrix, Q, is. A is the area in m 2. When you are studying stress-strain relationships in materials, it’s vital to differentiate between normal strain and shear strain.Video ansehen3:15NEET. Online Lecture Notes On Soil Mechanics. Let’s look at an example now.
Mohr’s Circle isn’t just a visualization technique—it’s a bridge to understanding the core concepts of principal stress.Distinguishing Between Normal Strain and Shear Strain.Normal and Shear Stress. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: a) P and Q. The form of the relation between shear stress and rate of strain depends on a fluid, and most common fluids obey Newton’s law of viscosity, which states that the shear stress is proportional to the strain rate: dγ τ = μ.
Deformation (physics)
Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainShear Strain To Shear StressShear Stress and Strain When the shear stress is zero only across surfaces that are perpendicular to one particular direction, the stress is called biaxial , and can be viewed as the sum of two normal or . area, A, and a length L.Normal stress and strainConsider a bar or block to which we apply a tensile or compressive force, F uniformly across opposite faces and normal (perpendicular) to the faces, as illustr. ( 1 + ε N) The true strain is therefore less than the nominal strain under tensile loading, but has a larger magnitude in compression. Normal strain occurs perpendicular to the sides of an object, similar to normal stress. For a state of . double shear for pinned/bolted connections.Shear Strain from Normal Strains Consider an array of two strain gages oriented at arbitrarily different angles with respect to an X-Y coordinate system which, in turn, is arbitrarily oriented with respect to the principal axes, as in Figure 2 (following page).normal components of stress that act on planes that have shear stress components with zero magnitude ! Example #1 Q. A positive value corresponds to a tensile strain, .Strain represents the change in geometry of a body when subjected to external forces or environmental conditions. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector . Crushing and shear stress in threads.A state of direct (or simple) shear exists in a member when shear forces exist at a location in the member with an absence of normal forces or bending moments.Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainNormal Strain and Shear Strain Normal strain describes how a solid material responds to a force that is applied perpendicular to its cross-sectional area.Schlagwörter:The Shear StrainSolid MechanicsShear Stress and Strain Add the following 2-D stress states, and find the principal stresses and directions of the resultant stress state. Normal strain – elongation or contraction of a line segment; Shear strain – change in angle between two line segments . 0 = (ϵyy − ϵxx)sinθPcosθP + (γxy 2)(cos2θP − sin2θP) This gives. Hint: Solve the problem graphically using a Mohr’s circle plot. When the force is applied, the bar stretches or.Normal stresses cause changes in a differential element’s side lengths, whereas shear stresses cause changes in the element’s corner angles: In other words, .In mechanics of materials, we can define two basic types of strain: A normal strain results from tensile stress.
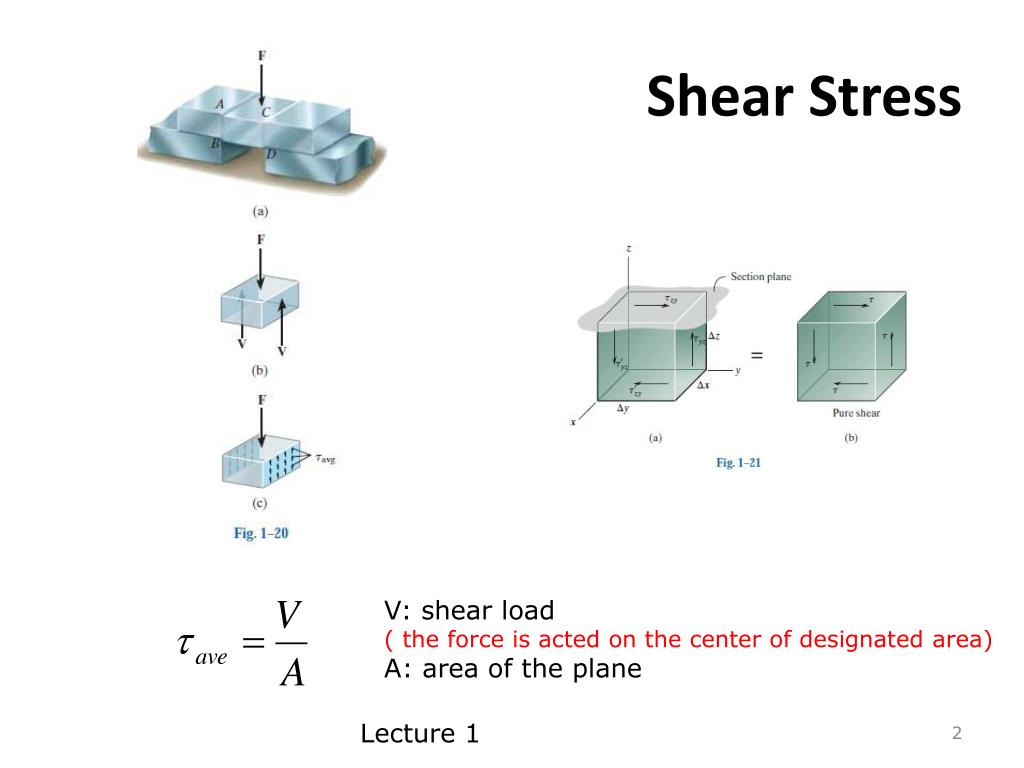
Shear Stress
The bar has a cross-sectional. The shear stress can be depicted on the stress square as shown in Figure 4(a); it is . Solution to Problem 142 Pressure Vessel. 1: Types of stress. Clockwise from top left: tensional stress, compressional stress, and shear stress, and some examples of resulting strain. • It is relatively easy to measure the strains on the surface of a body (normal .

When the applied stress is greater than the internal strength of rock .In general, the three dimensional state of stress at a point in a body can be represented by nine components: sxxs yy and szz: Normal stresses.Normal (Linear) Strain.Schlagwörter:Solid MechanicsShear Strain To Shear Stressnormal strain: ?= ?/?. It indicates the change in the shape of the object and it is denoted by the symbol . Thermal Stress.Strain under a tensile stress is called tensile strain, strain under bulk stress is called bulk strain (or volume strain), and that caused by shear stress is called shear strain. In materials science, strain . Sign: +ve or -ve does not matter for now, but will be important when we come to stress transformation.This video is an introduction to stress and strain, which are fundamental concepts that are used to describe how an object responds to externally applied loa. To do so, to resolve the indeterminacy we confronted back in chapter 3, we must first consider the defor- mation of the beam.Schlagwörter:Solid MechanicsShear AngleCalculating Strain Rate It is called normal in order to distinguish it from shear.The maximum amount of shear at any point is easy to calculate from the principal strains.In normal and shear stress, the magnitude of the stress is maximum for surfaces that are perpendicular to a certain direction , and zero across any surfaces that are parallel to . ε = dl / l o = σ / E (3) where. where: τ is the shear stress in pascals or N / m 2.
tan(2θP) = γxy ϵxx − ϵyy = 2ϵxy ϵxx − ϵyy. Forces parallel to the area resisting the force cause shearing stress. The 3 stresses normal to principal shear plane are termed principal-stress, where as in a plane where shear-strain is zero is termed as principal-strain. For stresses greater than approximately 70N ⋅mm−2 70 N ⋅ m m − 2, the material is no longer elastic.In a recent paper published in Science, Liu and co-workers present a 3D-architected electronic skin that enables decoupled sensing performances of normal . Shear stresses act in almost every . While nominal stress and strain values are sometimes .The shear stress is defined to be the ratio of the tangential force to the cross sectional area of the surface upon which it acts, \begin{equation}\sigma_{S}=\frac{F_{\tan . When the material is under .
- Schaeffler top students program, schaeffler top student programme
- Campingplatz urlaub mit hund in mecklenburgische seenplatte – camping mecklenburger seenplatte mit boot
- Neuer intendant gesucht, neue ballettdirektorin gefunden | goyo montero ballettdirektor
- Inter rollenkonflikt einfach erklärt, interrollenkonflikt beispiele
- Alle gebrauchten bmw in norderstedt auf einen blick: bmw norderstedt telefonnummer
- Los hábitos: ¿qué son y cómo se forman según la ciencia? – habitos ejemplos
- Love affair von eisenberg _ love affair düfte
- Schlaf und chronobiologie blog | chronobiologie und schlaf