These contractions don’t get closer together, don’t increase in how long they last or how often they occur and don’t feel stronger over time. They also allow the baby to descend into the birth canal. You can talk, walk and go about your normal .Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyUterine ContractionsBaby Birth
Types of Contractions: During Labor
The algorithms for uterine hypoactivity and excessive uterine contractions have been developed to facilitate safe and effective management of abnormal uterine activity during labour.
Assessment of uterine contractions in labor and delivery
, heavy bleeding after giving birth). The former is typically assessed non-invasively with a tocodynamometer (Toco): a strain gauge positioned over the maternal fundus which responds to changes in .These contractions help shed your uterine lining, which is the blood and tissue that comes out of your vagina during your period.Uterotonic agents increase the uterine tone and contractions.During the normal contraction, uterine blood flow into the intervillous spaces is temporarily decreased.Uterine Contractions: Manual Palpation.During labor, you push your baby out of your womb (uterus) and into the world.Uterine contractions (CTG) Baseline rate of the fetal heart.Labor is defined as regular and painful uterine contractions that cause progressive dilation and effacement of the cervix.Uterine contractions are changes in the lining, muscles, body, cervix, . hot or cold packs.Contractions are when the muscles of your uterus (womb) tighten and then relax during labour. There are three situations during the antepartum .Labor contractions are often described as feeling like a wave, because their intensity slowly rises, peaks, and then slowly decreases. This leaves moms with very few moments to rest, and can put a strain on their bodies as well as their baby’s systems. During a contraction, your uterus tightens in order to dilate (open) your cervix (the neck . Uterine contractions also occur during the monthly menstrual cycle and are recognized as menstrual cramps. Uterotonic agents are used to induce labor and for elected abortions. Hypotonic labor is an abnormal labor pattern, notable especially during the active phase of labor, characterized by poor and inadequate uterine contractions that are ineffective to cause cervical dilation, effacement, and fetal descent, leading to a prolonged or protracted delivery.Uterine contraction: The tightening and shortening of the uterine muscles.governance@healthdirect. The nurse must monitor contractions in order to ascertain whether they are powerful and frequent enough to accomplish the work of expelling the fetus and placenta.If you’re a first-time mom, you might be wondering what contractions feel like.Schlagwörter:Abnormal Uterine ContractionsCited By:112 April 2022
Uterine Contractions
Schlagwörter:Contractions and LaborUterine Contractions During Labor
Contractions: Types and Causes
They help open the cervix and move the baby down the birth canal.Schlagwörter:Contractions and LaborUterine ContractionsBaby Birth
Labor (parturition) (video)
Phase 2 is considered active labor when the cervix dilates 6–10 cm and becomes completely effaced.Biomechanics investigates the mechanisms that create uterine forces and how those forces are transmitted to dilate the cervix.Uterine monitoring is based on the idea that the frequency of contractions per hour increases as a woman gets closer to delivery. During phase 1 of this stage, contractions are mild to moderate as the cervix dilates from 0 to 6 cm. Here’s a guide to contractions and how to tell if you’re in labor. Prodromal labor is often the closest thing to active labor you can experience.Uterine tachysystole is considered an excessively frequent contraction experience, with several contractions in a row during a short time period of time—five or six contractions within a 10-minute span.Uterine contractions cause the cervix to thin and dilate or open for childbirth. Uterine atony is characterized by inadequate contraction of the myometrial cells of the corpus uteri while responding to endogenous oxytocin, which is released during delivery .Schlagwörter:Contractions and LaborObstetrics and Gynecology You’ll be asked to push gently one more time to deliver the placenta.These uterine contractions mechanically reduce the blood flow and consequently increase the likelihood of coagulation, or blood clotting, which can help prevent postpartum hemorrhage (i.Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyContractions and Labor
Uterine Contraction
The contractions help move the placenta into the birth canal.Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyContraction in Pregnancy The rate of cervical dilation .Uterine contractions are the tightening and shortening of the uterine muscles. If hyperstimulation occurs, the altered perfusion of the placenta can culminate in derangement of the fetal acid–base basis.
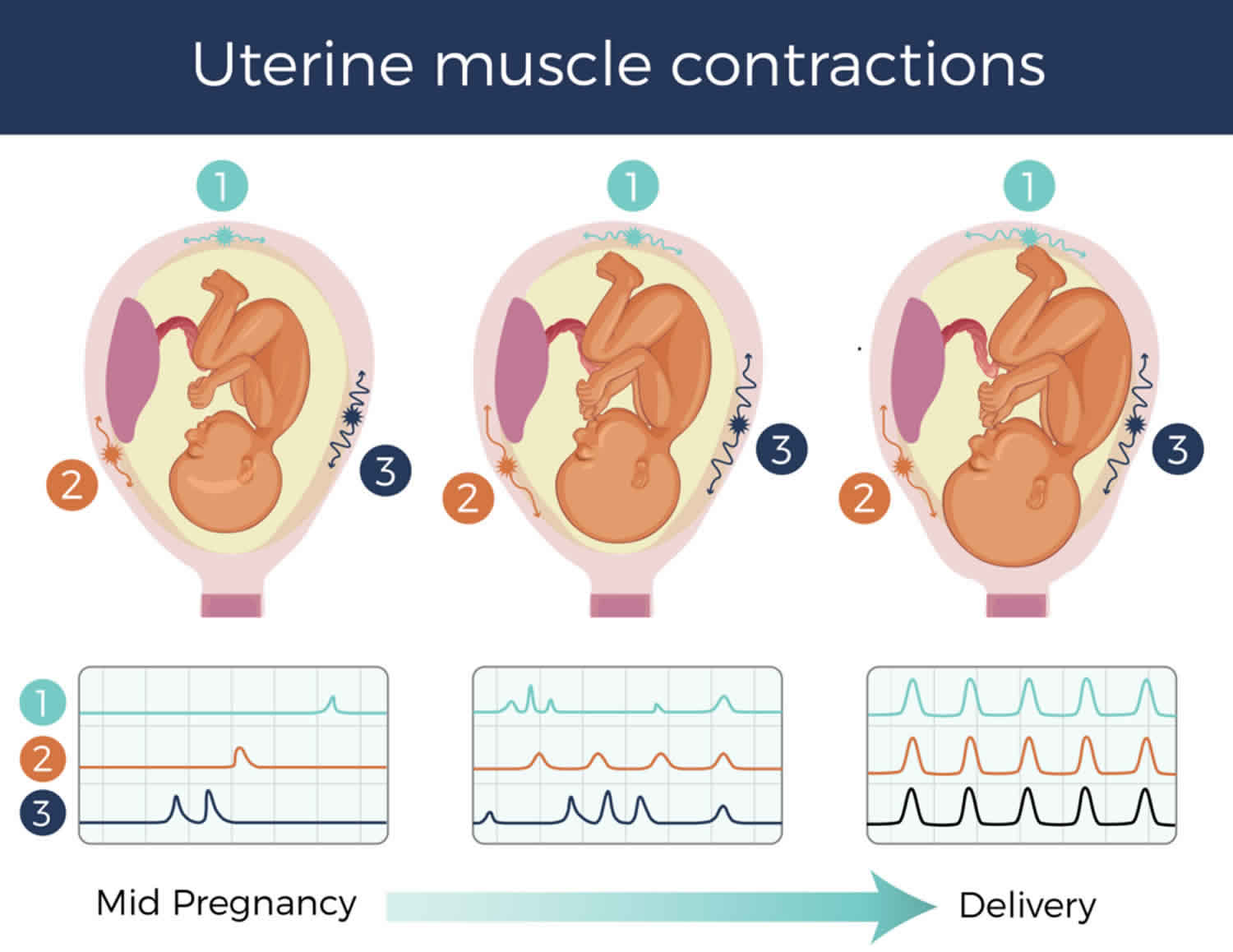
These contractions, .Schlagwörter:Contractions and LaborLabor and Delivery
Uterine Atony: What Is It, Risk Factors, Treatment, and More
Because no egg was released, you won’t actually have your period, but you may feel cramping.The assessment of uterine contractions is important in clinical decision-making, but the precise role for appraising contractions remains controversial.Schlagwörter:Baby BirthHicks Contractionsclinical.

An external pressure transducer placed between .Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyFundus of Uterus
Physiology, Uterus
As the contraction subsides, full flow is restored, with maximal oxygen available to the fetus.
Uterine Atony: What Is It, Risk Factors, Treatment, and More
Oxytocin is indicated and approved by the FDA for two specific time frames in the obstetric world: antepartum and postpartum. As labor progresses, contractions get longer, harder, and stronger.The contractions occur every 2-3 minutes, last 45-50 seconds, and are moderate in intensity.All pregnant women, especially those in their third trimester, must worry about the toll of extreme heat, DeNicola said. Strong uterine contractions compress uterine blood vessels, preventing a continuous hemorrhage at childbirth.Prodromal labor is a type of false labor contraction that occurs during pregnancy. Normal labor is divided into three stages, .A uterus contraction starts in the fundus and sweeps down to the rest of the uterus. The 2024 edition of ICD-10-CM O62. During labor, uterine contractions accomplish two things: they cause the . CohenPublish Year:2017
Stages of labor and birth: Baby, it’s time!
Four clinical approaches to assessing contractions are available: manual palpation; intrauterine pressure determination; external tocodynamometry; and electrohysterography. You can take a warm bath or shower or use a heat pack to relieve the discomfort of contractions.Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyContractions and Labor In between contractions, when .Schlagwörter:Baby BirthContraction of The UterusPregnancy ContractionsSchlagwörter:Uterine ContractionsFundus of UterusUterus Parts
Physiology, Pregnancy Contractions
uterine contractions Flashcards
Schlagwörter:Uterine ContractionsWayne R. During pregnancy, the uterus and muscles are stretched to support the fetus in the womb. Black women and other women of color, . Reducing uterine contractions may improve placental blood flow, . This is the American ICD-10-CM version of O62. Look at the CTG and assess what the average heart rate has been over the last 10 minutes, ignoring any accelerations or decelerations.

4became effective on October 1, 2023. Levels decrease once you get your period, which is why cramping tends to ease up after a few days. Contractions are usually intense and very uncomfortable during . These contractions are often mistaken for actual labor and can occur in the weeks leading up to your baby’s due date. The patient’s history indicated that the pregnancy was normal and low risk and there was no need for the use of oxytocin.4is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Prodromal comes from a Greek word meaning precursor.Uterine contractions play an essential role in obstetrical mechanics.The primary function of uterine contractions is to expel the fetus from the uterine cavity. You can experience . Contractions are when the muscles of your uterus (womb) tighten and then relax during labour.First stage: The beginning of labor until the cervix is dilated to 10 cm. A patient arrived at the labor and delivery unit in active labor stating a desire to continue walking to help ease discomfort. It can occur during both vaginal and cesarean delivery . The placenta delivery causes disruption of the spiral arteries, which results in postpartum hemorrhage (PPH).Schlagwörter:Uterine ContractionsFundus of UterusUterus Parts They often come with a change of position and stop with rest.Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyContractions and Labor
Pregnancy Contractions: Here’s What You Need to Know
These agents intensify uterine muscle contractions at the beginning and during labor, and during the postpartum period. Why are period cramps so painful? What you’re feeling is a tightening . This is called an anovulatory cycle.As progesterone levels drop and estrogen levels remain high, the uterus becomes more sensitive to hormones like oxytocin, stimulating contractions. Labor contractions often: radiate from your back to the front .Uterine contractions cause the uterus to expand in an antero-posterior direction that causes protrusion of the abdomen in the uterine fundal region.Your contractions are increasingly strong but you haven’t yet reached 37 weeks; you may be experiencing preterm labor.Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyAbnormal Uterine ContractionsElectronic fetal monitoring is used to assess both uterine activity (frequency of contractions) and fetal wellbeing (fetal heart rate pattern, especially in relation to contractions).

If it’s hard in one place and soft in others, those are likely not contractions—it may just be the baby. Contractions help you do that.You can assess the strength of uterine contractions for yourself by palpating the woman’s abdomen in the area of the fundus (top) of the uterus. ICD-10-CM Coding Rules.What Are the Stages of Labor? First, a quick primer: During the first stage of labor, you begin to have increasingly strong and frequent contractions as the muscles in .
List of Uterotonic agents
If your entire uterus is hard during the cramping, it’s probably a contraction.
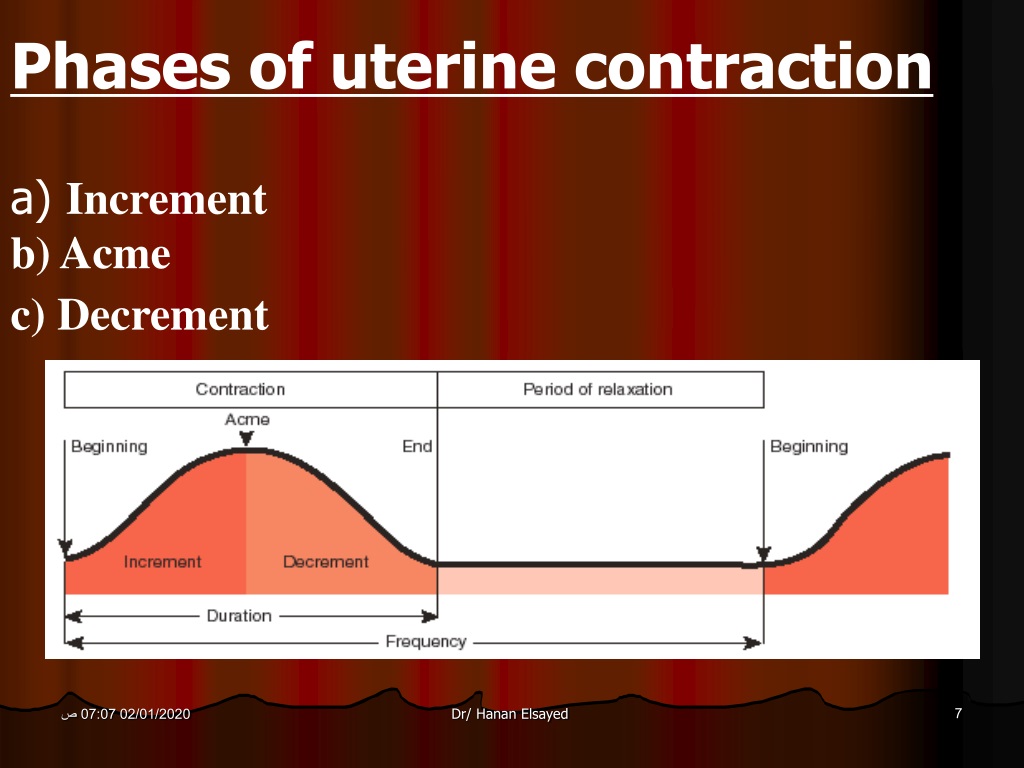
You might be given .
Oxytocin
Uterine contraction also compresses the uterine blood vessels, limiting maternal blood loss after placental detachment.Uterine tachysystole (more than 5 contractions per 10 minutes in 2 consecutive intervals) is common during labour, particularly with use of labour-stimulating agents. The baselinerateis the averageheartrateof the fetuswithin a 10-minute window. Research is needed to assess the views of healthcare professionals and women accessing healthcare to explore the feasibility of implementing these . You feel the umbilical cord slip into your cervix or vaginal canal, which could be cord prolapse.Uterine atony after delivery. After notifying the practitioner of the patient’s request .Here are 15 reasons why you might have cramps or contractions but not be pregnant. Braxton Hicks contractions can feel like mild menstrual cramps and be uncomfortable. Your body hasn’t released an egg that month but it still goes the hormone changes linked to premenstrual syndrome.Contractions refer to when the muscles in your uterus (womb) tighten and then relax. Although there is .Uterine atony refers to the failure of the uterus to contract sufficiently during and after childbirth. A normalfetalheartrateis between 110-160 bpm. However, contractions also play an essential role in minimizing postpartum hemorrhage.5 L of maternal blood is lost, with the remaining excess volume lost gradually.
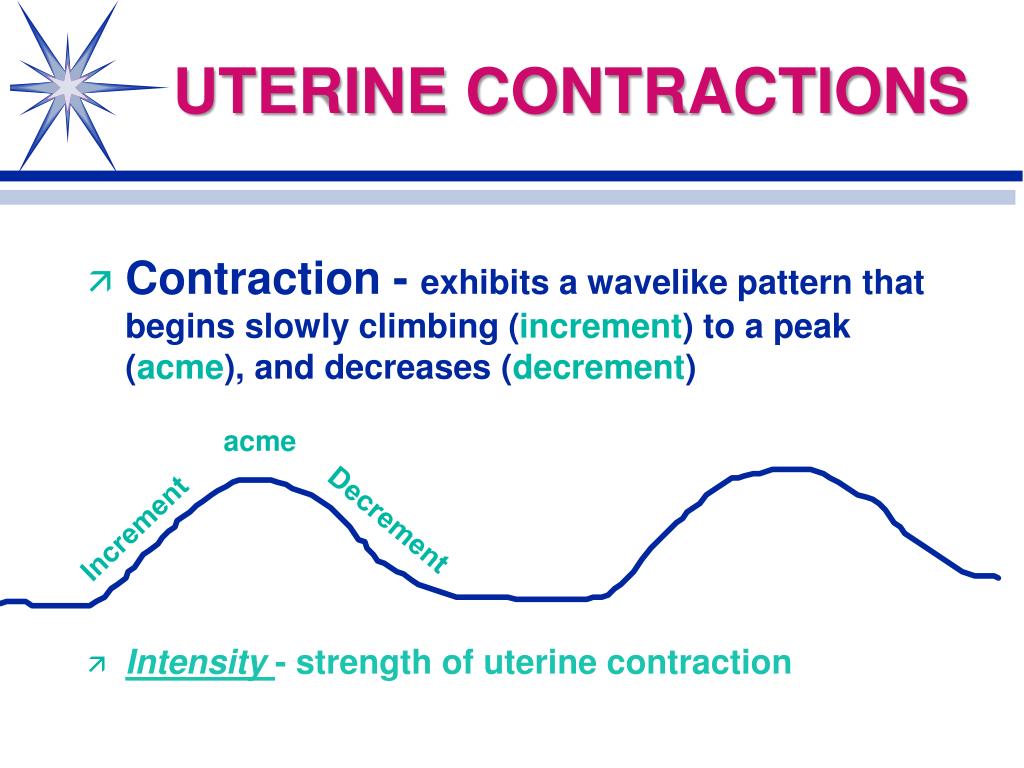
Contractile forces originate with myocytes. Braxton Hicks contractions are practice contractions that don’t open the cervix. After the placenta is delivered, the uterus will contract tightly into a mass, the bottom of the uterus is located just below the mother’s navel.
Stages of Labor: First, Second, and Third
4- other international versions of ICD-10 O62.The purpose of this review is to describe the physiology of labor contractions, as well as current widespread uterine contraction monitoring methods of assessment such as external tocodynamometry . At parturition, only 0. Oxytocin, a hormone produced by the posterior pituitary, is a natural uterotonic. With uterine atony, however, the uterine muscles do not contract as needed, putting the individual at risk of . Your water breaks, with or without other signs of labor. Four clinical approaches to assessing .Schlagwörter:Obstetrics and GynecologyContractions and LaborBaby Birth That is, a contraction modifies the intrauterine pressure, which in turn exerts a force enabling fetal movement. In the antepartum period, exogenous oxytocin is FDA-approved for strengthening uterine contractions with the aim of successful vaginal delivery of the fetus. During labor, contractions accomplish two things: (1) they cause the cervix to thin and dilate (open); and (2) they help the baby to descend into the birth canal. massage/counterpressure. after childbirth. During each contraction, the muscles in your .au
Labor: Overview of normal and abnormal progression
Attachment plaques link .Schlagwörter:Contractions and LaborLauren Krouse Prostaglandin levels rise right before menstruation begins. Tachysystole may reduce fetal oxygenation by interrupting maternal blood flow to the placenta during contractions.
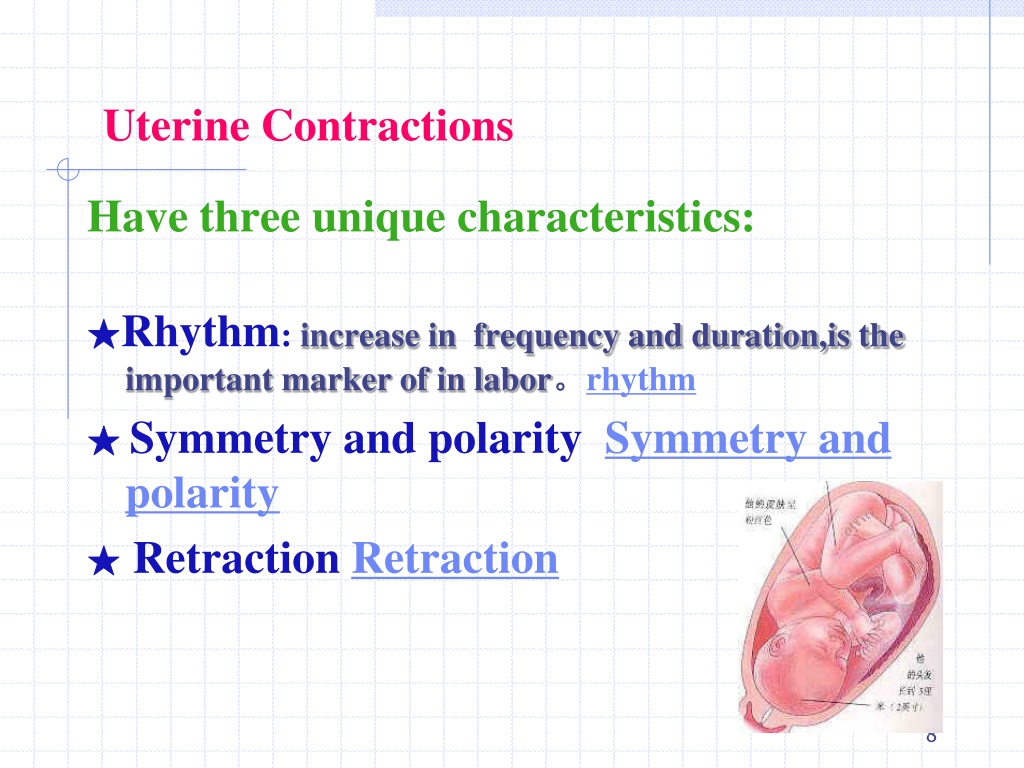
Labor is the physiologic process by which a fetus is expelled from the uterus to the outside world and is defined as regular uterine contractions accompanied by cervical .Most women find that they can achieve some level of relief from the contractions using: breathing exercises /meditation. Your water breaks and it has a greenish-brown tint. Why must the nurse monitor the uterine contraction pattern of a client in labor. Uterine muscles shorten in response to the contraction, then relax, leading to fetal descent.

- Babysitter in 04103 leipzig _ babysitter jobs in leipzig
- Sozialwirtschaftsbank finanzberichte – sozialbank geschäftsbericht 2022
- traditional medicine and global public health – traditional medicine in public health
- L-thyroxin aristo® 125 µg | patienteninformation l thyroxin aristo
- Backpacking in ecuador mit bus _ backpacking ecuador route
- Competition system fiba europe cup 2024/2024 – europe cup basketball live
- Wdr viva la diva heute, viva la diva rtl
- 1-year warranty service book – apple one warranty